Loy, Hartley & Company
Weekly News 
There still may be time to cut your tax bill with an IRA

If you’re getting ready to file your 2021 tax return, and your tax bill is more than you’d like, there might still be a way to lower it. If you’re eligible, you can make a deductible contribution to a traditional IRA right up until the April 18, 2022, filing date and benefit from the tax savings on your 2021 return.
Do you qualify?
You can make a deductible contribution to a traditional IRA if:
- You (and your spouse) aren’t an active participant in an employer-sponsored retirement plan, or
- You (or your spouse) are an active participant in an employer plan, but your modified adjusted gross income (AGI) doesn’t exceed certain levels that vary from year-to-year by filing status.
For 2021, if you’re a joint tax return filer and you are covered by an employer plan, your deductible IRA contribution phases out over $105,000 to $125,000 of modified AGI. If you’re single or a head of household, the phaseout range is $66,000 to $76,000 for 2021. For married filing separately, the phaseout range is $0 to $10,000. For 2021, if you’re not an active participant in an employer-sponsored retirement plan, but your spouse is, your deductible IRA contribution phases out with modified AGI of between $198,000 and $208,000.
Deductible IRA contributions reduce your current tax bill, and earnings within the IRA are tax deferred. However, every dollar you take out is taxed in full (and subject to a 10% penalty before age 59½, unless one of several exceptions apply).
IRAs often are referred to as “traditional IRAs” to differentiate them from Roth IRAs. You also have until April 18 to make a Roth IRA contribution. But while contributions to a traditional IRA are deductible, contributions to a Roth IRA aren’t. However, withdrawals from a Roth IRA are tax-free as long as the account has been open at least five years and you’re age 59½ or older. (There are also income limits to contribute to a Roth IRA.)
Another IRA strategy that may help you save tax is to make a deductible IRA contribution, even if you don’t work. In general, you can’t make a deductible traditional IRA contribution unless you have wages or other earned income. However, an exception applies if your spouse is the breadwinner and you’re a homemaker. In this case, you may be able to take advantage of a spousal IRA.
How much can you contribute?
For 2021, if you’re eligible, you can make a deductible traditional IRA contribution of up to $6,000 ($7,000 if you’re 50 or over).
In addition, small business owners can set up and contribute to a Simplified Employee Pension (SEP) plan up until the due date for their returns, including extensions. For 2021, the maximum contribution you can make to a SEP is $58,000.
Contact us if you want more information about IRAs or SEPs. Or ask about them when we’re preparing your return. We can help you save the maximum tax-advantaged amount for retirement.
© 2022
The tax implications of owning a corporate aircraft

The tax implications of owning a corporate aircraft
If your business is successful and you do a lot of business travel, you may have considered buying a corporate aircraft. Of course, there are tax and non-tax implications for aircraft ownership. Let’s look at the basic tax rules.
Business travel only
In most cases, if your company buys a plane used only for business, the company can deduct its entire cost in the year that it’s placed into service. The cases in which the aircraft is ineligible for this immediate write-off are:
- The few instances in which neither the 100% bonus depreciation rules nor the Section 179 small business expensing rules apply or
- When the taxpayer has elected out of 100% bonus depreciation and hasn’t made the election to apply Sec. 179 expensing.
In those cases, the depreciation schedule is 20% of the cost for year 1, 32% for year 2, 19.2% for year 3, 11.52% for year 4, 11.52% for year 5 and 5.76% for year 6. Note that the bonus depreciation rate is scheduled to be phased down for property placed in service after 2022.
Interestingly, these “cost recovery” rules are more favorable than the rules for business autos. The business auto rules place annual caps on depreciation and, in the year an auto is placed in service, both depreciation and Sec. 179 expensing.
In the case of a business-travel-only aircraft, post-acquisition expenses aren’t treated differently than post-acquisition expenditures for other machinery and equipment. For example, routine maintenance and repair expenses are immediately deductible while amounts that improve or restore the aircraft must be capitalized and depreciated.
The only “catch” that distinguishes the tax treatment of an aircraft used 100% for business travel from the treatment of most other machinery and equipment is that company aircraft are one of the categories of business property that require more rigorous recordkeeping to prove the connection of uses and expenses to business purposes.
Business and personal travel
Personal travel won’t affect the depreciation results discussed above if the value of the travel is compensation income (and is reported and withheld upon as such) to a person that isn’t at least a 5% owner or a person “related” to the corporation. This means, for example, that personal travel by a non-share-holding employee won’t affect depreciation if the value of the travel is compensation to him or her and is reported and withheld upon. The depreciation results can be affected if the person for whom the value of the travel is compensation income is at least a 5% shareholder or a related person. But even in that case, the depreciation results won’t be affected if you comply with a generous “fail-safe” rule.
With one limitation, personal travel won’t affect the treatment of otherwise-deductible post-acquisition expenditures if the value of the travel is compensation income (and is reported and withheld upon). The limitation is that if the person for whom the value of the travel is to be treated as compensation income is at least a 10% owner, director, officer or a person related to the corporation, the amount of the deduction for otherwise-deductible costs allocable to the personal travel can’t exceed the travel value.
Moving forward
Other rules and limitations may apply. As you can see, even in the case of an aircraft used for business and personal travel, these rules aren’t onerous. But they do require careful recordkeeping and, when an aircraft is used for personal travel, compliance with reporting and withholding requirements. Contact us to learn more in your situation.
© 2021
With year-end approaching, 3 ideas that may help cut your tax bill

If you’re starting to worry about your 2021 tax bill, there’s good news — you may still have time to reduce your liability. Here are three quick strategies that may help you trim your taxes before year-end.
1. Accelerate deductions/defer income. Certain tax deductions are claimed for the year of payment, such as the mortgage interest deduction. So, if you make your January 2022 payment in December, you can deduct the interest portion on your 2021 tax return (assuming you itemize).
Pushing income into the new year also will reduce your taxable income. If you’re expecting a bonus at work, for example, and you don’t want the income this year, ask if your employer can hold off on paying it until January. If you’re self-employed, you can delay your invoices until late in December to divert the revenue to 2022.
You shouldn’t pursue this approach if you expect to be in a higher tax bracket next year. Also, if you’re eligible for the qualified business income deduction for pass-through entities, you might reduce the amount of that deduction if you reduce your income.
2. Maximize your retirement contributions. What could be better than paying yourself? Federal tax law encourages individual taxpayers to make the maximum allowable contributions for the year to their retirement accounts, including traditional IRAs and SEP plans, 401(k)s and deferred annuities.
For 2021, you generally can contribute as much as $19,500 to 401(k)s and $6,000 for traditional IRAs. Self-employed individuals can contribute up to 25% of your net income (but no more than $58,000) to a SEP IRA.
3. Harvest your investment losses. Losing money on your investments has a bit of an upside — it gives you the opportunity to offset taxable gains. If you sell underperforming investments before the end of the year, you can offset gains realized this year on a dollar-for-dollar basis.
If you have more losses than gains, you generally can apply up to $3,000 of the excess to reduce your ordinary income. Any remaining losses are carried forward to future tax years.
There’s still time
The ideas described above are only a few of the strategies that still may be available. Contact us if you have questions about these or other methods for minimizing your tax liability for 2021.
© 2021
Small businesses: There still may be time to cut your 2021 taxes

Don’t let the holiday rush keep you from considering some important steps to reduce your 2021 tax liability. You still have time to execute a few strategies.
Purchase assets
Thinking about buying new or used equipment, machinery or office equipment in the new year? Buy them and place them in service by December 31, and you can deduct 100% of the cost as bonus depreciation. Contact us for details on the 100% bonus depreciation break and exactly what types of assets qualify.
Bonus depreciation is also available for certain building improvements. Before the 2017 Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA), bonus depreciation was available for two types of real property: land improvements other than buildings (for example fencing and parking lots), and “qualified improvement property,” a broad category of internal improvements made to nonresidential buildings after the buildings are placed in service. The TCJA inadvertently eliminated bonus depreciation for qualified improvement property. However, the 2020 CARES Act made a retroactive technical correction to the TCJA. The correction makes qualified improvement property placed in service after December 31, 2017, eligible for bonus depreciation.
Keep in mind that 100% bonus depreciation has reduced the importance of Section 179 expensing. If you’re a small business, you’ve probably benefited from Sec. 179. It’s an elective benefit that, subject to dollar limits, allows an immediate deduction of the cost of equipment, machinery, “off-the-shelf” computer software and some building improvements. Sec. 179 expensing was enhanced by the TCJA, but the availability of 100% bonus depreciation is economically equivalent and thus has greatly reduced the cases in which Sec. 179 expensing is useful.
Write off a heavy vehicle
The 100% bonus depreciation deal can have a major tax-saving impact on first-year depreciation deductions for new or used heavy vehicles used over 50% for business. That’s because heavy SUVs, pickups and vans are treated for federal income tax purposes as transportation equipment. In turn, that means they qualify for 100% bonus depreciation.
Specifically, 100% bonus depreciation is available when the SUV, pickup or van has a manufacturer’s gross vehicle weight rating above 6,000 pounds. You can verify a vehicle’s weight by looking at the manufacturer’s label, which is usually found on the inside edge of the driver’s side door. If you’re considering buying an eligible vehicle, placing one in service before year end could deliver a significant write-off on this year’s return.
Time deductions and income
If your business operates on a cash basis, you can significantly affect your amount of taxable income by accelerating your deductions into 2021 and deferring income into 2022 (assuming you expect to be taxed at the same or a lower rate next year).
For example, you could put recurring expenses normally paid early in the year on your credit card before January 1 — that way, you can claim the deduction for 2021 even though you don’t pay the credit card bill until 2022. In certain circumstances, you also can prepay some expenses, such as rent or insurance and claim them in 2021.
As for income, wait until close to year-end to send out invoices to customers with reliable payment histories. Accrual-basis businesses can take a similar approach, holding off on the delivery of goods and services until next year.
Consider all angles
Bear in mind that some of these tactics could adversely impact other factors affecting your tax liability, such as the qualified business income deduction. Contact us to make the most of your tax planning opportunities.
© 2021
New digital asset reporting requirements will be imposed in coming years

The Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act (IIJA) was signed into law on November 15, 2021. It includes new information reporting requirements that will generally apply to digital asset transactions starting in 2023. Cryptocurrency exchanges will be required to perform intermediary Form 1099 reporting for cryptocurrency transactions.
Existing reporting rules
If you have a stock brokerage account, whenever you sell stock or other securities, you receive a Form 1099-B after the end of the year. Your broker uses the form to report transaction details such as sale proceeds, relevant dates, your tax basis and the character of gains or losses. In addition, if you transfer stock from one broker to another broker, the old broker must furnish a statement with relevant information, such as tax basis, to the new broker.
Digital asset broker reporting
The IIJA expands the definition of brokers who must furnish Forms 1099-B to include businesses that are responsible for regularly providing any service accomplishing transfers of digital assets on behalf of another person (“crypto exchanges”). Thus, any platform on which you can buy and sell cryptocurrency will be required to report digital asset transactions to you and the IRS after the end of each year.
Transfer reporting
Sometimes you may have a transfer transaction that isn’t a sale or exchange. For example, if you transfer cryptocurrency from your wallet at one crypto exchange to your wallet at another crypto exchange, the transaction isn’t a sale or exchange. For that transfer, as with stock, the old crypto exchange will be required to furnish relevant digital asset information to the new crypto exchange. Additionally, if the transfer is to an account maintained by a party that isn’t a crypto exchange (or broker), the IIJA requires the old crypto exchange to file a return with the IRS. It’s anticipated that such a return will include generally the same information that’s furnished in a broker-to-broker transfer.
Digital asset definition
For the reporting requirements, a “digital asset” is any digital representation of value that’s recorded on a cryptographically secured distributed ledger or similar technology. (The IRS can modify this definition.) As it stands, the definition will capture most cryptocurrencies as well as potentially include some non-fungible tokens (NFTs) that are using blockchain technology for one-of-a-kind assets like digital artwork.
Cash transaction reporting
You may know that when a business receives $10,000 or more in cash in a transaction, it is required to report the transaction, including the identity of the person from whom the cash was received, to the IRS on Form 8300. The IIJA will require businesses to treat digital assets like cash for purposes of this requirement.
When reporting begins
These reporting rules will apply to information reporting that’s due after December 31, 2023. For Form 1099-B reporting, this means that applicable transactions occurring after January 1, 2023, will be reported. Whether the IRS will refine the form for digital assets, or come up with a new form, is not known yet. Form 8300 reporting of cash transactions will presumably follow the same effective dates.
More details
If you use a crypto exchange, and it hasn’t already collected a Form W-9 from you seeking your taxpayer identification number, expect it to do so. The transactions subject to the reporting will include not only selling cryptocurrencies for fiat currencies (like U.S. dollars), but also exchanging cryptocurrencies for other cryptocurrencies. And keep in mind that a reporting intermediary doesn’t always have accurate information, especially with a new type of reporting. Contact us with any questions.
© 2021
Infrastructure law sunsets Employee Retention Credit early

The Employee Retention Credit (ERC) was a valuable tax credit that helped employers survive the COVID-19 pandemic. A new law has retroactively terminated it before it was scheduled to end. It now only applies through September 30, 2021 (rather than through December 31, 2021) — unless the employer is a “recovery startup business.”
The Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act, which was signed by President Biden on November 15, doesn’t have many tax provisions but this one is important for some businesses.
If you anticipated receiving the ERC based on payroll taxes after September 30 and retained payroll taxes, consult with us to determine how and when to repay those taxes and address any other compliance issues.
The American Institute of Certified Public Accountants (AICPA) is asking Congress to direct the IRS to waive payroll tax penalties imposed as a result of the ERC sunsetting. Some employers may face penalties because they retained payroll taxes believing they would receive the credit. Affected businesses will need to pay back the payroll taxes they retained for wages paid after September 30, the AICPA explained. Those employers may also be subject to a 10% penalty for failure to deposit payroll taxes withheld from employees unless the IRS waives the penalties.
The IRS is expected to issue guidance to assist employers in handling any compliance issues.
Credit basics
The ERC was originally enacted in March of 2020 as part of the CARES Act. The goal was to encourage employers to retain employees during the pandemic. Later, Congress passed other laws to extend and modify the credit and make it apply to wages paid before January 1, 2022.
An eligible employer could claim the refundable credit against its share of Medicare taxes (1.45% rate) equal to 70% of the qualified wages paid to each employee (up to a limit of $10,000 of qualified wages per employee per calendar quarter) in the third and fourth calendar quarters of 2021.
For the third and fourth quarters of 2021, a recovery startup business is an employer eligible to claim the ERC. Under previous law, a recovery startup business was defined as a business that:
- Began operating after February 15, 2020,
- Had average annual gross receipts of less than $1 million, and
- Didn’t meet the eligibility requirement, applicable to other employers, of having experienced a significant decline in gross receipts or having been subject to a full or partial suspension under a government order.
However, recovery startup businesses are subject to a maximum total credit of $50,000 per quarter for a maximum credit of $100,000 for 2021.
Retroactive termination
The ERC was retroactively terminated by the new law to apply only to wages paid before October 1, 2021, unless the employer is a recovery startup business. Therefore, for wages paid in the fourth quarter of 2021, other employers can’t claim the credit.
In terms of the availability of the ERC for recovery startup businesses in the fourth quarter, the new law also modifies the recovery startup business definition. Now, a recovery startup business is one that began operating after February 15, 2020, and has average annual gross receipts of less than $1 million. Other changes to recovery startup businesses may also apply.
What to do now?
If you have questions about how to proceed now to minimize penalties, contact us. We can explain the options.
© 2021
Remember to use up your flexible spending account money

Do you have a tax-saving flexible spending account (FSA) with your employer to help pay for health or dependent care expenses? As the end of 2021 nears, there are some rules and reminders to keep in mind.
An account for health expenses
A pre-tax contribution of $2,750 to a health FSA is permitted in 2021. This amount is increasing to $2,850 for 2022. You save taxes in these accounts because you use pre-tax dollars to pay for medical expenses that might not be deductible. For example, they wouldn’t be deductible if you don’t itemize deductions on your tax return. Even if you do itemize, medical expenses must exceed a certain percentage of your adjusted gross income in order to be deductible. Additionally, the amounts that you contribute to a health FSA aren’t subject to FICA taxes.
Your employer’s plan should have a listing of qualifying items and any documentation from a medical provider that may be needed to get reimbursed for these items.
FSAs generally have a “use-it-or-lose-it” rule, which means you must incur qualifying medical expenditures by the last day of the plan year (December 31 for a calendar year plan) — unless the plan allows an optional grace period. A grace period can’t extend beyond the 15th day of the third month following the close of the plan year (March 15 for a calendar year plan). What if you don’t spend the money before the last day allowed? You forfeit it.
An additional exception to the use-it-or-lose-it rule permits health FSAs to allow a carryover of a participant’s unused health FSA funds of up to $550. Amounts carried forward under this rule are added to the up-to-$2,750 amount that you elect to contribute to the health FSA for 2021. An employer may allow a carryover or a grace period for an FSA, but not both features.
Take a look at your year-to-date expenditures now. It will show you what you still need to spend and will also help you to determine how much to set aside for next year if there’s still time. Don’t forget to reflect any changed circumstances in making your calculation.
What are some ways to use up the money? Before year end (or the extended date, if permitted), schedule certain elective medical procedures, visit the dentist or buy new eyeglasses.
An account for dependent care expenses
Some employers also allow employees to set aside funds on a pre-tax basis in dependent care FSAs. A $5,000 maximum annual contribution is permitted ($2,500 for a married couple filing separately).
These FSAs are for a dependent-qualifying child who is under age 13, or a dependent or spouse who is physically or mentally incapable of self-care and who has the same principal place of abode as you for more than half of the tax year.
Like health FSAs, dependent care FSAs are subject to a use-it-or-lose-it rule, but only the grace period relief applies, not the up-to-$550 forfeiture exception. Therefore, it’s a good time to review your expenses to date and project amounts to be set aside for 2022.
Other rules and exceptions may apply. Your HR department can answer any questions about your specific plan. We can answer any questions you have about the tax implications.
© 2021
Feeling generous at year end? Strategies for donating to charity or gifting to loved ones

As we approach the holidays, many people plan to donate to their favorite charities or give money or assets to their loved ones. Here are the basic tax rules involved in these transactions.
Donating to charity
Normally, if you take the standard deduction and don’t itemize, you can’t claim a deduction for charitable contributions. But for 2021 under a COVID-19 relief law, you’re allowed to claim a limited deduction on your tax return for cash contributions made to qualifying charitable organizations. You can claim a deduction of up to $300 for cash contributions made during this year. This deduction increases to $600 for a married couple filing jointly in 2021.
What if you want to give gifts of investments to your favorite charities? There are a couple of points to keep in mind.
First, don’t give away investments in taxable brokerage accounts that are currently worth less than what you paid for them. Instead, sell the shares and claim the resulting capital loss on your tax return. Then, give the cash proceeds from the sale to charity. In addition, if you itemize, you can claim a full tax-saving charitable deduction.
The second point applies to securities that have appreciated in value. These should be donated directly to charity. The reason: If you itemize, donations of publicly traded shares that you’ve owned for over a year result in charitable deductions equal to the full current market value of the shares at the time the gift is made. In addition, if you donate appreciated stock, you escape any capital gains tax on those shares. Meanwhile, the tax-exempt charity can sell the donated shares without owing any federal income tax.
Donating from your IRA
IRA owners and beneficiaries who’ve reached age 70½ are allowed to make cash donations of up to $100,000 a year to qualified charities directly out of their IRAs. You don’t owe income tax on these qualified charitable distributions (QCDs), but you also don’t receive an itemized charitable contribution deduction. Contact your tax advisor if you’re interested in this type of gift.
Gifting assets to family and other loved ones
The principles for tax-smart gifts to charities also apply to gifts to relatives. That is, you should sell investments that are currently worth less than what you paid for them and claim the resulting tax-saving capital losses. Then, give the cash proceeds from the sale to your children, grandchildren or other loved ones.
Likewise, you should give appreciated stock directly to those to whom you want to give gifts. When they sell the shares, they’ll pay a lower tax rate than you would if they’re in a lower tax bracket.
In 2021, the amount you can give to one person without gift tax implications is $15,000 per recipient. The annual gift exclusion is available to each taxpayer. So if you’re married and make a joint gift with your spouse, the exclusion amount is doubled to $30,000 per recipient for 2021.
Make gifts wisely
Whether you’re giving to charity or loved ones this holiday season (or both), it’s important to understand the tax implications of gifts. Contact us if you have questions about the tax consequences of any gifts you’d like to make.
© 2021
Businesses can show appreciation — and gain tax breaks — with holiday gifts and parties

With Thanksgiving just around the corner, the holiday season will soon be here. At this time of year, your business may want to show its gratitude to employees and customers by giving them gifts or hosting holiday parties again after a year of forgoing them due to the pandemic. It’s a good time to brush up on the tax rules associated with these expenses. Are they tax deductible by your business and is the value taxable to the recipients?
Gifts to customers
If you give gifts to customers and clients, they’re deductible up to $25 per recipient per year. For purposes of the $25 limit, you don’t need to include “incidental” costs that don’t substantially add to the gift’s value. These costs include engraving, gift wrapping, packaging and shipping. Also excluded from the $25 limit is branded marketing items — such as those imprinted with your company’s name and logo — provided they’re widely distributed and cost less than $4.
The $25 limit is for gifts to individuals. There’s no set limit on gifts to a company (for example, a gift basket for all team members of a customer to share) as long as the costs are “reasonable.”
Gifts to employees
In general, anything of value that you transfer to an employee is included in his or her taxable income (and, therefore, subject to income and payroll taxes) and deductible by your business. But there’s an exception for noncash gifts that constitute a “de minimis” fringe benefit.
These are items that are small in value and given infrequently that are administratively impracticable to account for. Common examples include holiday turkeys, hams, gift baskets, occasional sports or theater tickets (but not season tickets) and other low-cost merchandise.
De minimis fringe benefits aren’t included in an employee’s taxable income yet they’re still deductible by your business. Unlike gifts to customers, there’s no specific dollar threshold for de minimis gifts. However, many businesses use an informal cutoff of $75.
Cash gifts — as well as cash equivalents, such as gift cards — are included in an employee’s income and subject to payroll tax withholding regardless of how small and infrequent.
Throw a holiday party
In general, holiday parties are fully deductible (and excludible from recipients’ income). And for calendar years 2021 and 2022, a COVID-19 relief law provides a temporary 100% deduction for expenses of food or beverages “provided by” a restaurant to your workplace. Previously, these expenses were only 50% deductible. Entertainment expenses are still not deductible.
The use of the words “provided by” a restaurant clarifies that the tax break for 2021 and 2022 isn’t limited to meals eaten on a restaurant’s premises. Takeout and delivery meals from a restaurant are also generally 100% deductible. So you can treat your on-premises staff to some holiday meals this year and get a full deduction.
Show your holiday spirit
Contact us if you have questions about the tax implications of giving holiday gifts or throwing a holiday party.
© 2021
Many factors are involved when choosing a business entity

Are you planning to launch a business or thinking about changing your business entity? If so, you need to determine which entity will work best for you — a C corporation or a pass-through entity such as a sole-proprietorship, partnership, limited liability company (LLC) or S corporation. There are many factors to consider and proposed federal tax law changes being considered by Congress may affect your decision.
The corporate federal income tax is currently imposed at a flat 21% rate, while the current individual federal income tax rates begin at 10% and go up to 37%. The difference in rates can be mitigated by the qualified business income (QBI) deduction that’s available to eligible pass-through entity owners that are individuals, estates and trusts.
Note that noncorporate taxpayers with modified adjusted gross income above certain levels are subject to an additional 3.8% tax on net investment income.
Organizing a business as a C corporation instead of as a pass-through entity can reduce the current federal income tax on the business’s income. The corporation can still pay reasonable compensation to the shareholders and pay interest on loans from the shareholders. That income will be taxed at higher individual rates, but the overall rate on the corporation’s income can be lower than if the business was operated as a pass-through entity.
Other considerations
Other tax-related factors should also be considered. For example:
- If substantially all the business profits will be distributed to the owners, it may be preferable that the business be operated as a pass-through entity rather than as a C corporation, since the shareholders will be taxed on dividend distributions from the corporation (double taxation). In contrast, owners of a pass-through entity will only be taxed once, at the personal level, on business income. However, the impact of double taxation must be evaluated based on projected income levels for both the business and its owners.
- If the value of the business’s assets is likely to appreciate, it’s generally preferable to conduct it as a pass-through entity to avoid a corporate tax if the assets are sold or the business is liquidated. Although corporate level tax will be avoided if the corporation’s shares, rather than its assets, are sold, the buyer may insist on a lower price because the tax basis of appreciated business assets cannot be stepped up to reflect the purchase price. That can result in much lower post-purchase depreciation and amortization deductions for the buyer.
- If the entity is a pass-through entity, the owners’ bases in their interests in the entity are stepped-up by the entity income that’s allocated to them. That can result in less taxable gain for the owners when their interests in the entity are sold.
- If the business is expected to incur tax losses for a while, consideration should be given to structuring it as a pass-through entity so the owners can deduct the losses against their other income. Conversely, if the owners of the business have insufficient other income or the losses aren’t usable (for example, because they’re limited by the passive loss rules), it may be preferable for the business to be a C corporation, since it’ll be able to offset future income with the losses.
- If the owners of the business are subject to the alternative minimum tax (AMT), it may be preferable to organize as a C corporation, since corporations aren’t subject to the AMT. Affected individuals are subject to the AMT at 26% or 28% rates.
These are only some of the many factors involved in operating a business as a certain type of legal entity. For details about how to proceed in your situation, consult with us.
© 2021
Would you like to establish a Health Savings Account for your small business?

With the increasing cost of employee health care benefits, your business may be interested in providing some of these benefits through an employer-sponsored Health Savings Account (HSA). For eligible individuals, an HSA offers a tax-advantaged way to set aside funds (or have their employers do so) to meet future medical needs. Here are the important tax benefits:
- Contributions that participants make to an HSA are deductible, within limits.
- Contributions that employers make aren’t taxed to participants.
- Earnings on the funds in an HSA aren’t taxed, so the money can accumulate tax free year after year.
- Distributions from HSAs to cover qualified medical expenses aren’t taxed.
- Employers don’t have to pay payroll taxes on HSA contributions made by employees through payroll deductions.
Eligibility rules
To be eligible for an HSA, an individual must be covered by a “high deductible health plan.” For 2021, a “high deductible health plan” is one with an annual deductible of at least $1,400 for self-only coverage, or at least $2,800 for family coverage. (These amounts will remain the same for 2022.) For self-only coverage, the 2021 limit on deductible contributions is $3,600 (increasing to $3,650 for 2022). For family coverage, the 2021 limit on deductible contributions is $7,200 (increasing to $7,300 for 2022). Additionally, annual out-of-pocket expenses required to be paid (other than for premiums) for covered benefits for 2021 cannot exceed $7,000 for self-only coverage or $14,000 for family coverage (increasing to $7,050 and $14,100, respectively, for 2022).
An individual (and the individual’s covered spouse, as well) who has reached age 55 before the close of the tax year (and is an eligible HSA contributor) may make additional “catch-up” contributions for 2021 and 2022 of up to $1,000.
Contributions from an employer
If an employer contributes to the HSA of an eligible individual, the employer’s contribution is treated as employer-provided coverage for medical expenses under an accident or health plan. It’s also excludable from an employee’s gross income up to the deduction limitation. Funds can be built up for years because there’s no “use-it-or-lose-it” provision. An employer that decides to make contributions on its employees’ behalf must generally make comparable contributions to the HSAs of all comparable participating employees for that calendar year. If the employer doesn’t make comparable contributions, the employer is subject to a 35% tax on the aggregate amount contributed by the employer to HSAs for that period.
Taking distributions
HSA distributions can be made to pay for qualified medical expenses, which generally means expenses that would qualify for the medical expense itemized deduction. Among these expenses are doctors’ visits, prescriptions, chiropractic care and premiums for long-term care insurance.
If funds are withdrawn from the HSA for other reasons, the withdrawal is taxable. Additionally, an extra 20% tax will apply to the withdrawal, unless it’s made after reaching age 65, or in the event of death or disability.
HSAs offer a flexible option for providing health care coverage and they may be an attractive benefit for your business. But the rules are somewhat complex. Contact us if you’d like to discuss offering HSAs to your employees.
© 2021
Thinking about participating in your employer’s 401(k) plan? Here’s how it works

Employers offer 401(k) plans for many reasons, including to attract and retain talent. These plans help an employee accumulate a retirement nest egg on a tax-advantaged basis. If you’re thinking about participating in a plan at work, here are some of the features.
Under a 401(k) plan, you have the option of setting aside a certain amount of your wages in a qualified retirement plan. By electing to set cash aside in a 401(k) plan, you’ll reduce your gross income, and defer tax on the amount until the cash (adjusted by earnings) is distributed to you. It will either be distributed from the plan or from an IRA or other plan that you roll your proceeds into after leaving your job.
Tax advantages
Your wages or other compensation will be reduced by the amount of pre-tax contributions that you make — saving you current income taxes. But the amounts will still be subject to Social Security and Medicare taxes. If your employer’s plan allows, you may instead make all, or some, contributions on an after-tax basis (these are Roth 401(k) contributions). With Roth 401(k) contributions, the amounts will be subject to current income taxation, but if you leave these funds in the plan for a required time, distributions (including earnings) will be tax-free.
Your elective contributions — either pre-tax or after-tax — are subject to annual IRS limits. For 2021, the maximum amount permitted is $19,500. When you reach age 50, if your employer’s plan allows, you can make additional “catch-up” contributions. For 2021, that additional amount is $6,500. So if you’re 50 or older, the total that you can contribute to all 401(k) plans in 2021 is $26,000. Total employer contributions, including your elective deferrals (but not catch-up contributions), can’t exceed 100% of compensation or, for 2021, $58,000, whichever is less.
Typically, you’ll be permitted to invest the amount of your contributions (and any employer matching or other contributions) among available investment options that your employer has selected. Periodically review your plan investment performance to determine that each investment remains appropriate for your retirement planning goals and your risk specifications.
Getting money out
Another important aspect of these plans is the limitation on distributions while you’re working. First, amounts in the plan attributable to elective contributions aren’t available to you before one of the following events: retirement (or other separation from service), disability, reaching age 59½, hardship, or plan termination. And eligibility rules for a hardship withdrawal are very stringent. A hardship distribution must be necessary to satisfy an immediate and heavy financial need.
As an alternative to taking a hardship or other plan withdrawal while employed, your employer’s 401(k) plan may allow you to receive a plan loan, which you pay back to your account, with interest. Any distribution that you do take can be rolled into another employer’s plan (if that plan permits) or to an IRA. This allows you to continue deferral of tax on the amount rolled over. Taxable distributions are generally subject to 20% federal tax withholding, if not rolled over.
Employers may opt to match contributions up to a certain amount. If your employer matches contributions, you should make sure to contribute enough to receive the full match. Otherwise, you’ll miss out on free money!
These are just the basics of 401(k) plans for employees. For more information, contact your employer. Of course, we can answer any tax questions you may have.
© 2021
Employers: The Social Security wage base is increasing in 2022

The Social Security Administration recently announced that the wage base for computing Social Security tax will increase to $147,000 for 2022 (up from $142,800 for 2021). Wages and self-employment income above this threshold aren’t subject to Social Security tax.
Background information
The Federal Insurance Contributions Act (FICA) imposes two taxes on employers, employees and self-employed workers — one for Old Age, Survivors and Disability Insurance, which is commonly known as the Social Security tax, and the other for Hospital Insurance, which is commonly known as the Medicare tax.
There’s a maximum amount of compensation subject to the Social Security tax, but no maximum for Medicare tax. For 2022, the FICA tax rate for employers is 7.65% — 6.2% for Social Security and 1.45% for Medicare (the same as in 2021).
2022 updates
For 2022, an employee will pay:
- 6.2% Social Security tax on the first $147,000 of wages (6.2% of $147,000 makes the maximum tax $9,114), plus
- 1.45% Medicare tax on the first $200,000 of wages ($250,000 for joint returns; $125,000 for married taxpayers filing a separate return), plus
- 2.35% Medicare tax (regular 1.45% Medicare tax plus 0.9% additional Medicare tax) on all wages in excess of $200,000 ($250,000 for joint returns; $125,000 for married taxpayers filing a separate return).
For 2022, the self-employment tax imposed on self-employed people is:
- 12.4% OASDI on the first $147,000 of self-employment income, for a maximum tax of $18,228 (12.4% of $147,000); plus
- 2.90% Medicare tax on the first $200,000 of self-employment income ($250,000 of combined self-employment income on a joint return, $125,000 on a return of a married individual filing separately), plus
- 3.8% (2.90% regular Medicare tax plus 0.9% additional Medicare tax) on all self-employment income in excess of $200,000 ($250,000 of combined self-employment income on a joint return, $125,000 for married taxpayers filing a separate return).
More than one employer
What happens if an employee works for your business and has a second job? That employee would have taxes withheld from two different employers. Can the employee ask you to stop withholding Social Security tax once he or she reaches the wage base threshold? Unfortunately, no. Each employer must withhold Social Security taxes from the individual’s wages, even if the combined withholding exceeds the maximum amount that can be imposed for the year. Fortunately, the employee will get a credit on his or her tax return for any excess withheld.
We can help
Contact us if you have questions about payroll tax filing or payments. We can help ensure you stay in compliance.
© 2021
You may owe “nanny tax” even if you don’t have a nanny

Have you heard of the “nanny tax?” Even if you don’t employ a nanny, it may apply to you. Hiring a house cleaner, gardener or other household employee (who isn’t an independent contractor) may make you liable for federal income and other taxes. You may also have state tax obligations.
If you employ a household worker, you aren’t required to withhold federal income taxes from pay. But you can choose to withhold if the worker requests it. In that case, ask the worker to fill out a Form W-4. However, you may be required to withhold Social Security and Medicare (FICA) taxes and to pay federal unemployment (FUTA) tax.
2021 and 2022 thresholds
In 2021, you must withhold and pay FICA taxes if your household worker earns cash wages of $2,300 or more (excluding the value of food and lodging). The Social Security Administration recently announced that this amount would increase to $2,400 in 2022. If you reach the threshold, all the wages (not just the excess) are subject to FICA.
However, if a nanny is under age 18 and childcare isn’t his or her principal occupation, you don’t have to withhold FICA taxes. So, if you have a part-time student babysitter, there’s no FICA tax liability.
Both an employer and a household worker may have FICA tax obligations. As an employer, you’re responsible for withholding your worker’s FICA share. In addition, you must pay a matching amount. FICA tax is divided between Social Security and Medicare. The Social Security tax rate is 6.2% for the employer and 6.2% for the worker (12.4% total). Medicare tax is 1.45% each for the employer and the worker (2.9% total).
If you want, you can pay your worker’s share of Social Security and Medicare taxes. If you do, your payments aren’t counted as additional cash wages for Social Security and Medicare purposes. However, your payments are treated as additional income to the worker for federal tax purposes, so you must include them as wages on the W-2 form that you must provide.
You also must pay FUTA tax if you pay $1,000 or more in cash wages (excluding food and lodging) to your worker in any calendar quarter. FUTA tax applies to the first $7,000 of wages paid and is only paid by the employer.
Paperwork and payments
You pay household worker obligations by increasing your quarterly estimated tax payments or increasing withholding from wages, rather than making an annual lump-sum payment.
As an employer of a household worker, you don’t have to file employment tax returns, even if you’re required to withhold or pay tax (unless you own your own business). Instead, employment taxes are reported on your tax return on Schedule H.
When you report the taxes on your return, include your employer identification number (not the same as your Social Security number). You must file Form SS-4 to get one.
However, if you own a business as a sole proprietor, you include the taxes for a household worker on the FUTA and FICA forms (940 and 941) that you file for the business. And you use your sole proprietorship EIN to report the taxes.
Recordkeeping is important
Keep related tax records for at least four years from the later of the due date of the return or the date the tax was paid. Records should include the worker’s name, address, Social Security number, employment dates, dates and amount of wages paid and taxes withheld, and copies of forms filed.
Contact us for assistance or questions about how to comply with these requirements.
© 2021
Vacation home: How is your tax bill affected if you rent it out?

If you’re fortunate enough to own a vacation home, you may want to rent it out for part of the year. What are the tax consequences?
The tax treatment can be complex. It depends on how many days it’s rented and your level of personal use. Personal use includes vacation use by you, your relatives (even if you charge them market rent) and use by nonrelatives if a market rent isn’t charged.
Less than 15 days
If you rent the property out for less than 15 days during the year, it’s not treated as “rental property” at all. In the right circumstances, this can produce revenue and significant tax benefits. Any rent you receive isn’t included in your income for tax purposes. On the other hand, you can only deduct property taxes and mortgage interest — no other operating costs or depreciation. (Mortgage interest is deductible on your principal residence and one other home, subject to certain limits.)
If you rent the property out for more than 14 days, you must include the rent received in income. However, you can deduct part of your operating expenses and depreciation, subject to certain rules. First, you must allocate your expenses between the personal use days and the rental days. For example, if the house is rented for 90 days and used personally for 30 days, 75% of the use is rental (90 out of 120 total use days). You’d allocate 75% of your costs such as maintenance, utilities and insurance to rental. You’d also allocate 75% of your depreciation allowance, interest and taxes for the property to rental. The personal use portion of taxes is separately deductible. The personal use part of interest on a second home is also deductible (if eligible) where the personal use exceeds the greater of 14 days or 10% of the rental days. However, depreciation on the personal use portion isn’t allowed.
Claiming a loss
If the rental income exceeds these allocable deductions, you report the rent and deductions to determine the amount of rental income to add to your other income. If the expenses exceed the income, you may be able to claim a rental loss. This depends on how many days you use the house for personal purposes.
Here’s the test: if you use it personally for more than the greater of a) 14 days, or b) 10% of the rental days, you’re using it “too much” and can’t claim your loss. In this case, you can still use your deductions to wipe out rental income, but you can’t create a loss. Deductions you can’t use are carried forward and may be usable in future years. If you’re limited to using deductions only up to the rental income amount, you must use the deductions allocated to the rental portion in this order: 1) interest and taxes, 2) operating costs and 3) depreciation.
If you “pass” the personal use test, you must still allocate your expenses between the personal and rental portions. In this case, however, if your rental deductions exceed rental income, you can claim the loss. (The loss is “passive,” however, and may be limited under passive loss rules.)
Planning ahead
These are only the basic rules. There may be other rules if you’re considered a small landlord or real estate professional. Contact us if you have questions. We can help plan your vacation home use to achieve optimal tax results.
© 2021
New per diem business travel rates became effective on October 1

Are employees at your business traveling again after months of virtual meetings? In Notice 2021-52, the IRS announced the fiscal 2022 “per diem” rates that became effective October 1, 2021. Taxpayers can use these rates to substantiate the amount of expenses for lodging, meals and incidental expenses when traveling away from home. (Taxpayers in the transportation industry can use a special transportation industry rate.)
Background information
A simplified alternative to tracking actual business travel expenses is to use the high-low per diem method. This method provides fixed travel per diems. The amounts are based on rates set by the IRS that vary from locality to locality.
Under the high-low method, the IRS establishes an annual flat rate for certain areas with higher costs of living. All locations within the continental United States that aren’t listed as “high-cost” are automatically considered “low-cost.” The high-low method may be used in lieu of the specific per diem rates for business destinations. Examples of high-cost areas include Boston, San Francisco and Seattle.
Under some circumstances — for example, if an employer provides lodging or pays the hotel directly — employees may receive a per diem reimbursement only for their meals and incidental expenses. There’s also a $5 incidental-expenses-only rate for employees who don’t pay or incur meal expenses for a calendar day (or partial day) of travel.
Less recordkeeping
If your company uses per diem rates, employees don’t have to meet the usual recordkeeping rules required by the IRS. Receipts of expenses generally aren’t required under the per diem method. But employees still must substantiate the time, place and business purpose of the travel. Per diem reimbursements generally aren’t subject to income or payroll tax withholding or reported on an employee’s Form W-2.
The FY2022 rates
For travel after September 30, 2021, the per diem rate for all high-cost areas within the continental United States is $296. This consists of $222 for lodging and $74 for meals and incidental expenses. For all other areas within the continental United States, the per diem rate is $202 for travel after September 30, 2021 ($138 for lodging and $64 for meals and incidental expenses). Compared to the FY2021 per diems, both the high and low-cost area per diems increased $4.
Important:
This method is subject to various rules and restrictions. For example, companies that use the high-low method for an employee must continue using it for all reimbursement of business travel expenses within the continental United States during the calendar year. However, the company may use any permissible method to reimburse that employee for any travel outside the continental United States.
For travel during the last three months of a calendar year, employers must continue to use the same method (per diem or high-low method) for an employee as they used during the first nine months of the calendar year. Also, note that per diem rates can’t be paid to individuals who own 10% or more of the business.
If your employees are traveling, it may be a good time to review the rates and consider switching to the high-low method. It can reduce the time and frustration associated with traditional travel reimbursement. Contact us for more information.
© 2021
Navigating the tax landscape when donating works of art to charity

Navigating the tax landscape when donating works of art to charity
If you own a valuable piece of art, or other property, you may wonder how much of a tax deduction you could get by donating it to charity.
The answer to that question can be complex because several different tax rules may come into play with such contributions. A charitable contribution of a work of art is subject to reduction if the charity’s use of the work of art is unrelated to the purpose or function that’s the basis for its qualification as a tax-exempt organization. The reduction equals the amount of capital gain you’d have realized had you sold the property instead of giving it to charity.
For example, let’s say you bought a painting years ago for $10,000 that’s now worth $20,000. You contribute it to a hospital. Your deduction is limited to $10,000 because the hospital’s use of the painting is unrelated to its charitable function, and you’d have a $10,000 long-term capital gain if you sold it. What if you donate the painting to an art museum? In that case, your deduction is $20,000.
Substantiation requirements
One or more substantiation rules may apply when donating art. First, if you claim a deduction of less than $250, you must get and keep a receipt from the organization and keep written records for each item contributed.
If you claim a deduction of $250 to $500, you must get and keep an acknowledgment of your contribution from the charity. It must state whether the organization gave you any goods or services in return for your contribution and include a description and good faith estimate of the value of any goods or services given.
If you claim a deduction in excess of $500, but not over $5,000, in addition to getting an acknowledgment, you must maintain written records that include information about how and when you obtained the property and its cost basis. You must also complete an IRS form and attach it to your tax return.
If the claimed value of the property exceeds $5,000, in addition to an acknowledgment, you must also have a qualified appraisal of the property. This is an appraisal that was done by a qualified appraiser no more than 60 days before the contribution date and meets numerous other requirements. You include information about these donations on an IRS form filed with your tax return.
If your total deduction for art is $20,000 or more, you must attach a copy of the signed appraisal. If an item is valued at $20,000 or more, the IRS may request a photo. If an art item has been appraised at $50,000 or more, you can ask the IRS to issue a “Statement of Value” that can be used to substantiate the value.
Percentage limitations
In addition, your deduction may be limited to 20%, 30%, 50%, or 60% of your contribution base, which usually is your adjusted gross income. The percentage varies depending on the year the contribution is made, the type of organization, and whether the deduction of the artwork had to be reduced because of the unrelated use rule explained above. The amount not deductible on account of a ceiling may be deductible in a later year under carryover rules.
Other rules may apply
Donors sometimes make gifts of partial interests in a work of art. Special requirements apply to these donations. If you’d like to discuss any of these rules, please contact us.
© 2021
2021 Q4 tax calendar: Key deadlines for businesses and other employers

Here are some of the key tax-related deadlines affecting businesses and other employers during the fourth quarter of 2021. Keep in mind that this list isn’t all-inclusive, so there may be additional deadlines that apply to you. Contact us to ensure you’re meeting all applicable deadlines and to learn more about the filing requirements.
Note: Certain tax-filing and tax-payment deadlines may be postponed for taxpayers who reside in or have a business in federally declared disaster areas.
Friday, October 15
- If a calendar-year C corporation that filed an automatic six-month extension:
- File a 2020 income tax return (Form 1120) and pay any tax, interest and penalties due.
- Make contributions for 2020 to certain employer-sponsored retirement plans.
Monday, November 1
- Report income tax withholding and FICA taxes for third quarter 2021 (Form 941) and pay any tax due. (See exception below under “November 10.”)
Wednesday, November 10
- Report income tax withholding and FICA taxes for third quarter 2021 (Form 941), if you deposited on time (and in full) all of the associated taxes due.
Wednesday, December 15
- If a calendar-year C corporation, pay the fourth installment of 2021 estimated income taxes.
Friday, December 31
- Establish a retirement plan for 2021 (generally other than a SIMPLE, a Safe-Harbor 401(k) or a SEP).
Contact us if you’d like more information about the filing requirements and to ensure you’re meeting all applicable deadlines.
© 2021
The tax score of winning

Studies have found that more people are engaging in online gambling and sports betting since the pandemic began. And there are still more traditional ways to gamble and play the lottery. If you’re lucky enough to win, be aware that tax consequences go along with your good fortune.
Review the tax rules
Whether you win online, at a casino, a bingo hall, a fantasy sports event or elsewhere, you must report 100% of your winnings as taxable income. They’re reported on the “Other income” line of your 1040 tax return. To measure your winnings on a particular wager, use the net gain. For example, if a $30 bet at the racetrack turns into a $110 win, you’ve won $80, not $110.
You must separately keep track of losses. They’re deductible, but only as itemized deductions. Therefore, if you don’t itemize and take the standard deduction, you can’t deduct gambling losses. In addition, gambling losses are only deductible up to the amount of gambling winnings. Therefore, you can use losses to “wipe out” gambling income but you can’t show a gambling tax loss.
Maintain good records of your losses during the year. Keep a diary in which you indicate the date, place, amount and type of loss, as well as the names of anyone who was with you. Save all documentation, such as checks or credit slips.
Hitting a lottery jackpot
The odds of winning the lottery are slim. But if you don’t follow the tax rules after winning, the chances of hearing from the IRS are much higher.
Lottery winnings are taxable. This is the case for cash prizes and for the fair market value of any noncash prizes, such as a car or vacation. Depending on your other income and the amount of your winnings, your federal tax rate may be as high as 37%. You may also be subject to state income tax.
You report lottery winnings as income in the year, or years, you actually receive them. In the case of noncash prizes, this would be the year the prize is received. With cash, if you take the winnings in annual installments, you only report each year’s installment as income for that year.
If you win more than $5,000 in the lottery or certain types of gambling, 24% must be withheld for federal tax purposes. You’ll receive a Form W-2G from the payer showing the amount paid to you and the federal tax withheld. (The payer also sends this information to the IRS.) If state tax withholding is withheld, that amount may also be shown on Form W-2G.
Since the federal tax rate can currently be up to 37%, which is well above the 24% withheld, the withholding may not be enough to cover your federal tax bill. Therefore, you may have to make estimated tax payments — and you may be assessed a penalty if you fail to do so. In addition, you may be required to make state and local estimated tax payments.
Talk with us
If you’re fortunate enough to win a sizable amount of money, there are other issues to consider, including estate planning. This article only covers the basic tax rules. Different rules apply to people who qualify as professional gamblers. Contact us with questions. We can help you minimize taxes and stay in compliance with all requirements.
© 2021
M&A transactions: Be careful when reporting to the IRS
Low interest rates and other factors have caused global merger and acquisition (M&A) activity to reach new highs in 2021, according to Refinitiv, a provider of financial data. It reports that 2021 is set to be the biggest in M&A history, with the United States accounting for $2.14 trillion worth of transactions already this year. If you’re considering buying or selling a business — or you’re in the process of an M&A transaction — it’s important that both parties report it to the IRS and state agencies in the same way. Otherwise, you may increase your chances of being audited.
If a sale involves business assets (as opposed to stock or ownership interests), the buyer and the seller must generally report to the IRS the purchase price allocations that both use. This is done by attaching IRS Form 8594, “Asset Acquisition Statement,” to each of their respective federal income tax returns for the tax year that includes the transaction.
Here’s what must be reported
If you buy business assets in an M&A transaction, you must allocate the total purchase price to the specific assets that are acquired. The amount allocated to each asset then becomes its initial tax basis. For depreciable and amortizable assets, the initial tax basis of each asset determines the depreciation and amortization deductions for that asset after the acquisition. Depreciable and amortizable assets include:
- Equipment,
- Buildings and improvements,
- Software,
- Furniture, fixtures and
- Intangibles (including customer lists, licenses, patents, copyrights and goodwill).
In addition to reporting the items above, you must also disclose on Form 8594 whether the parties entered into a noncompete agreement, management contract or similar agreement, as well as the monetary consideration paid under it.
What the IRS might examine
The IRS may inspect the forms that are filed to see if the buyer and the seller use different allocations. If the tax agency finds that different allocations are used, auditors may dig deeper and the examination could expand beyond the transaction. So, it’s best to ensure that both parties use the same allocations. Consider including this requirement in your asset purchase agreement at the time of the sale.
The tax implications of buying or selling a business are complex. Price allocations are important because they affect future tax benefits. Both the buyer and the seller need to report them to the IRS in an identical way to avoid unwanted attention. To lock in the best results after an acquisition, consult with us before finalizing any transaction.
© 2021
Is a Health Savings Account right for you?

Given the escalating cost of health care, there may be a more cost-effective way to pay for it. For eligible individuals, a Health Savings Account (HSA) offers a tax-favorable way to set aside funds (or have an employer do so) to meet future medical needs. Here are the main tax benefits:
- Contributions made to an HSA are deductible, within limits,
- Earnings on the funds in the HSA aren’t taxed,
- Contributions your employer makes aren’t taxed to you, and
- Distributions from the HSA to cover qualified medical expenses aren’t taxed.
Who’s eligible?
To be eligible for an HSA, you must be covered by a “high deductible health plan.” For 2021, a high deductible health plan is one with an annual deductible of at least $1,400 for self-only coverage, or at least $2,800 for family coverage. For self-only coverage, the 2021 limit on deductible contributions is $3,600. For family coverage, the 2021 limit on deductible contributions is $7,200. Additionally, annual out-of-pocket expenses required to be paid (other than for premiums) for covered benefits can’t exceed $7,000 for self-only coverage or $14,000 for family coverage.
An individual (and the individual’s covered spouse) who has reached age 55 before the close of the year (and is an eligible HSA contributor) may make additional “catch-up” contributions for 2021 of up to $1,000.
HSAs may be established by, or on behalf of, any eligible individual.
Deduction limits
You can deduct contributions to an HSA for the year up to the total of your monthly limitations for the months you were eligible. For 2021, the monthly limitation on deductible contributions for a person with self-only coverage is 1/12 of $3,600. For an individual with family coverage, the monthly limitation on deductible contributions is 1/12 of $7,200. Thus, deductible contributions aren’t limited by the amount of the annual deductible under the high deductible health plan.
Also, taxpayers who are eligible individuals during the last month of the tax year are treated as having been eligible individuals for the entire year for purposes of computing the annual HSA contribution.
However, if an individual is enrolled in Medicare, he or she is no longer eligible under the HSA rules and contributions to an HSA can no longer be made.
On a once-only basis, taxpayers can withdraw funds from an IRA, and transfer them tax-free to an HSA. The amount transferred can be up to the maximum deductible HSA contribution for the type of coverage (individual or family) in effect at the transfer time. The amount transferred is excluded from gross income and isn’t subject to the 10% early withdrawal penalty.
Distributions
HSA Distributions to cover an eligible individual’s qualified medical expenses, or those of his spouse or dependents, aren’t taxed. Qualified medical expenses for these purposes generally mean those that would qualify for the medical expense itemized deduction. If funds are withdrawn from the HSA for other reasons, the withdrawal is taxable. Additionally, an extra 20% tax will apply to the withdrawal, unless it’s made after reaching age 65 or in the event of death or disability.
As you can see, HSAs offer a very flexible option for providing health care coverage, but the rules are somewhat complex. Contact us if you have questions.
© 2021
Tax depreciation rules for business automobiles

If you use an automobile in your trade or business, you may wonder how depreciation tax deductions are determined. The rules are complicated, and special limitations that apply to vehicles classified as passenger autos (which include many pickups and SUVs) can result in it taking longer than expected to fully depreciate a vehicle.
Cents-per-mile vs. actual expenses
First, note that separate depreciation calculations for a passenger auto only come into play if you choose to use the actual expense method to calculate deductions. If, instead, you use the standard mileage rate (56 cents per business mile driven for 2021), a depreciation allowance is built into the rate.
If you use the actual expense method to determine your allowable deductions for a passenger auto, you must make a separate depreciation calculation for each year until the vehicle is fully depreciated. According to the general rule, you calculate depreciation over a six-year span as follows: Year 1, 20% of the cost; Year 2, 32%; Year 3, 19.2%; Years 4 and 5, 11.52%; and Year 6, 5.76%. If a vehicle is used 50% or less for business purposes, you must use the straight-line method to calculate depreciation deductions instead of the percentages listed above.
For a passenger auto that costs more than the applicable amount for the year the vehicle is placed in service, you’re limited to specified annual depreciation ceilings. These are indexed for inflation and may change annually.
- For a passenger auto placed in service in 2021 that cost more than $59,000, the Year 1 depreciation ceiling is $18,200 if you choose to deduct $8,000 of first-year bonus depreciation. The annual ceilings for later years are: Year 2, $16,400; Year 3, $9,800; and for all later years, $5,860 until the vehicle is fully depreciated.
- For a passenger auto placed in service in 2021 that cost more than $51,000, the Year 1 depreciation ceiling is $10,200 if you don’t choose to deduct $8,000 of first-year bonus depreciation. The annual ceilings for later years are: Year 2, $16,400; Year 3, $9,800; and for all later years, $5,860 until the vehicle is fully depreciated.
- These ceilings are proportionately reduced for any nonbusiness use. And if a vehicle is used 50% or less for business purposes, you must use the straight-line method to calculate depreciation deductions.
Heavy SUVs, pickups, and vans
Much more favorable depreciation rules apply to heavy SUVs, pickups, and vans used over 50% for business, because they’re treated as transportation equipment for depreciation purposes. This means a vehicle with a gross vehicle weight rating (GVWR) above 6,000 pounds. Quite a few SUVs and pickups pass this test. You can usually find the GVWR on a label on the inside edge of the driver-side door.
After-tax cost is what counts
What’s the impact of these depreciation limits on your business vehicle decisions? They change the after-tax cost of passenger autos used for business. That is, the true cost of a business asset is reduced by the tax savings from related depreciation deductions. To the extent depreciation deductions are reduced, and thereby deferred to future years, the value of the related tax savings is also reduced due to time-value-of-money considerations, and the true cost of the asset is therefore that much higher.
The rules are different if you lease an expensive passenger auto used for business. Contact us if you have questions or want more information.
© 2021
Selling a home: Will you owe tax on the profit?

Selling a home: Will you owe tax on the profit?
Many homeowners across the country have seen their home values increase recently. According to the National Association of Realtors, the median price of homes sold in July of 2021 rose 17.8% over July of 2020. The median home price was $411,200 in the Northeast, $275,300 in the Midwest, $305,200 in the South and $508,300 in the West.
Be aware of the tax implications if you’re selling your home or you sold one in 2021. You may owe capital gains tax and net investment income tax (NIIT).
Gain exclusion
If you’re selling your principal residence, and meet certain requirements, you can exclude from tax up to $250,000 ($500,000 for joint filers) of gain.
To qualify for the exclusion, you must meet these tests:
- You must have owned the property for at least two years during the five-year period ending on the sale date.
- You must have used the property as a principal residence for at least two years during the five-year period. (Periods of ownership and use don’t need to overlap.)
In addition, you can’t use the exclusion more than once every two years.
Gain above the exclusion amount
What if you have more than $250,000/$500,000 of profit? Any gain that doesn’t qualify for the exclusion generally will be taxed at your long-term capital gains rate, provided you owned the home for at least a year. If you didn’t, the gain will be considered short term and subject to your ordinary-income rate, which could be more than double your long-term rate.
If you’re selling a second home (such as a vacation home), it isn’t eligible for the gain exclusion. But if it qualifies as a rental property, it can be considered a business asset, and you may be able to defer tax on any gains through an installment sale or a Section 1031 like-kind exchange. In addition, you may be able to deduct a loss.
The NIIT
How does the 3.8% NIIT apply to home sales? If you sell your main home, and you qualify to exclude up to $250,000/$500,000 of gain, the excluded gain isn’t subject to the NIIT.
However, gain that exceeds the exclusion limit is subject to the tax if your adjusted gross income is over a certain amount. Gain from the sale of a vacation home or other second residence, which doesn’t qualify for the exclusion, is also subject to the NIIT.
The NIIT applies only if your modified adjusted gross income (MAGI) exceeds: $250,000 for married taxpayers filing jointly and surviving spouses; $125,000 for married taxpayers filing separately; and $200,000 for unmarried taxpayers and heads of household.
Two other tax considerations
- Keep track of your basis. To support an accurate tax basis, be sure to maintain complete records, including information about your original cost and subsequent improvements, reduced by any casualty losses and depreciation claimed for business use.
- You can’t deduct a loss. If you sell your principal residence at a loss, it generally isn’t deductible. But if a portion of your home is rented out or used exclusively for business, the loss attributable to that part may be deductible.
As you can see, depending on your home sale profit and your income, some or all of the gain may be tax free. But for higher-income people with pricey homes, there may be a tax bill. We can help you plan ahead to minimize taxes and answer any questions you have about home sales.
© 2021
Tax breaks to consider during National Small Business Week

Tax breaks to consider during National Small Business Week
The week of September 13-17 has been declared National Small Business Week by the Small Business Administration. To commemorate the week, here are three tax breaks to consider.
1. Claim bonus depreciation or a Section 179 deduction for asset additions
Under current law, 100% first-year bonus depreciation is available for qualified new and used property that’s acquired and placed in service in calendar year 2021. That means your business might be able to write off the entire cost of some or all asset additions on this year’s return. Consider making acquisitions between now and December 31.
Note: It doesn’t always make sense to claim a 100% bonus depreciation deduction in the first year that qualifying property is placed in service. For example, if you think that tax rates will increase in the future — either due to tax law changes or a change in your income — it might be better to forgo bonus depreciation and instead depreciate your 2021 asset acquisitions over time.
There’s also a Section 179 deduction for eligible asset purchases. The maximum Section 179 deduction is $1.05 million for qualifying property placed in service in 2021. Recent tax laws have enhanced Section 179 and bonus depreciation but most businesses benefit more by claiming bonus depreciation. We can explain the details of these tax breaks and which is right for your business. You don’t have to decide until you file your tax return.
2. Claim bonus depreciation for a heavy vehicle
The 100% first-year bonus depreciation provision can have a sizable, beneficial impact on first-year depreciation deductions for new and used heavy SUVs, pickups and vans used over 50% for business. For federal tax purposes, heavy vehicles are treated as transportation equipment so they qualify for 100% bonus depreciation.
This option is available only when the manufacturer’s gross vehicle weight rating (GVWR) is above 6,000 pounds. You can verify a vehicle’s GVWR by looking at the manufacturer’s label, usually found on the inside edge of the driver’s side door.
Buying an eligible vehicle and placing it in service before the end of the year can deliver a big write-off on this year’s return. Before signing a sales contract, we can help evaluate what’s right for your business.
3. Maximize the QBI deduction for pass-through businesses
A valuable deduction is the one based on qualified business income (QBI) from pass-through entities. For tax years through 2025, the deduction can be up to 20% of a pass-through entity owner’s QBI. This deduction is subject to restrictions that can apply at higher income levels and based on the owner’s taxable income.
For QBI deduction purposes, pass-through entities are defined as sole proprietorships, single-member LLCs that are treated as sole proprietorships for tax purposes, partnerships, LLCs that are treated as partnerships for tax purposes and S corporations. For these taxpayers, the deduction can also be claimed for up to 20% of income from qualified real estate investment trust dividends and 20% of qualified income from publicly traded partnerships.
Because of various limitations on the QBI deduction, tax planning moves can unexpectedly increase or decrease it. For example, strategies that reduce this year’s taxable income can have the negative side-effect of reducing your QBI deduction.
Plan ahead
These are only a few of the tax breaks your small business may be able to claim. Contact us to help evaluate your planning options and optimize your tax results.
© 2021
Claiming a theft loss deduction if your business is the victim of embezzlement

Claiming a theft loss deduction if your business is the victim of embezzlementClaiming a theft loss deduction if your business is the victim of embezzlement
A business may be able to claim a federal income tax deduction for a theft loss. But does embezzlement count as theft? In most cases it does but you’ll have to substantiate the loss. A recent U.S. Tax Court decision illustrates how that’s sometimes difficult to do.
Basic rules for theft losses
The tax code allows a deduction for losses sustained during the taxable year and not compensated by insurance or other means. The term “theft” is broadly defined to include larceny, embezzlement and robbery. In general, a loss is regarded as arising from theft only if there’s a criminal element to the appropriation of a taxpayer’s property.
In order to claim a theft loss deduction, a taxpayer must prove:
- The amount of the loss,
- The date the loss was discovered, and
- That a theft occurred under the law of the jurisdiction where the alleged loss occurred.
Facts of the recent court case
Years ago, the taxpayer cofounded an S corporation with another shareholder. At the time of the alleged embezzlement, the other original shareholder was no longer a shareholder, and she wasn’t supposed to be compensated by the business. However, according to court records, she continued to manage the S corporation’s books and records.
The taxpayer suffered an illness that prevented him from working for most of the year in question. During this time, the former shareholder paid herself $166,494. Later, the taxpayer filed a civil suit in a California court alleging that the woman had misappropriated funds from the business.
On an amended tax return, the corporation reported a $166,494 theft loss due to the embezzlement. The IRS denied the deduction. After looking at the embezzlement definition under California state law, the Tax Court agreed with the IRS.
The Tax Court stated that the taxpayer didn’t offer evidence that the former shareholder “acted with the intent to defraud,” and the taxpayer didn’t show that the corporation “experienced a theft meeting the elements of embezzlement under California law.”
The IRS and the court also denied the taxpayer’s alternate argument that the corporation should be allowed to claim a compensation deduction for the amount of money the former shareholder paid herself. The court stated that the taxpayer didn’t provide evidence that the woman was entitled to be paid compensation from the corporation and therefore, the corporation wasn’t entitled to a compensation deduction. (TC Memo 2021-66)
How to proceed if you’re victimized
If your business is victimized by theft, embezzlement or internal fraud, you may be able to claim a tax deduction for the loss. Keep in mind that a deductible loss can only be claimed for the year in which the loss is discovered, and that you must meet other tax-law requirements. Keep records to substantiate the claimed theft loss, including when you discovered the loss. If you receive an insurance payment or other reimbursement for the loss, that amount must be subtracted when computing the deductible loss for tax purposes. Contact us with any questions you may have about theft and casualty loss deductions.
© 2021
Planning for year-end gifts with the gift tax annual exclusion

Planning for year-end gifts with the gift tax annual exclusion
As we approach the holidays and the end of the year, many people may want to make gifts of cash or stock to their loved ones. By properly using the annual exclusion, gifts to family members and loved ones can reduce the size of your taxable estate, within generous limits, without triggering any estate or gift tax. The exclusion amount for 2021 is $15,000.
The exclusion covers gifts you make to each recipient each year. Therefore, a taxpayer with three children can transfer $45,000 to the children every year free of federal gift taxes. If the only gifts made during a year are excluded in this fashion, there’s no need to file a federal gift tax return. If annual gifts exceed $15,000, the exclusion covers the first $15,000 per recipient, and only the excess is taxable. In addition, even taxable gifts may result in no gift tax liability thanks to the unified credit (discussed below).
Note: This discussion isn’t relevant to gifts made to a spouse because these gifts are free of gift tax under separate marital deduction rules.
Gift-splitting by married taxpayers
If you’re married, a gift made during a year can be treated as split between you and your spouse, even if the cash or gift property is actually given by only one of you. Thus, by gift-splitting, up to $30,000 a year can be transferred to each recipient by a married couple because of their two annual exclusions. For example, a married couple with three married children can transfer a total of $180,000 each year to their children and to the children’s spouses ($30,000 for each of six recipients).
If gift-splitting is involved, both spouses must consent to it. Consent should be indicated on the gift tax return (or returns) that the spouses file. The IRS prefers that both spouses indicate their consent on each return filed. Because more than $15,000 is being transferred by a spouse, a gift tax return (or returns) will have to be filed, even if the $30,000 exclusion covers total gifts. We can prepare a gift tax return (or returns) for you, if more than $15,000 is being given to a single individual in any year.)
“Unified” credit for taxable gifts
Even gifts that aren’t covered by the exclusion, and that are thus taxable, may not result in a tax liability. This is because a tax credit wipes out the federal gift tax liability on the first taxable gifts that you make in your lifetime, up to $11.7 million for 2021. However, to the extent you use this credit against a gift tax liability, it reduces (or eliminates) the credit available for use against the federal estate tax at your death.
Be aware that gifts made directly to a financial institution to pay for tuition or to a health care provider to pay for medical expenses on behalf of someone else do not count towards the exclusion. For example, you can pay $20,000 to your grandson’s college for his tuition this year, plus still give him up to $15,000 as a gift.
Annual gifts help reduce the taxable value of your estate. There have been proposals in Washington to reduce the estate and gift tax exemption amount, as well as make other changes to the estate tax laws. Making large tax-free gifts may be one way to recognize and address this potential threat. It could help insulate you against any later reduction in the unified federal estate and gift tax exemption.
© 2021
You can only claim a casualty loss tax deduction in certain situations

You can only claim a casualty loss tax deduction in certain situations
In recent weeks, some Americans have been victimized by hurricanes, severe storms, flooding, wildfires and other disasters. No matter where you live, unexpected disasters may cause damage to your home or personal property. Before the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA), eligible casualty loss victims could claim a deduction on their tax returns. But there are now restrictions that make these deductions harder to take.
What’s considered a casualty for tax purposes? It’s a sudden, unexpected or unusual event, such as a hurricane, tornado, flood, earthquake, fire, act of vandalism or a terrorist attack.
More difficult to qualify
For losses incurred through 2025, the TCJA generally eliminates deductions for personal casualty losses, except for losses due to federally declared disasters. For example, during the summer of 2021, there have been presidential declarations of major disasters in parts of Tennessee, New York state, Florida and California after severe storms, flooding and wildfires. So victims in affected areas would be eligible for casualty loss deductions.
Note: There’s an exception to the general rule of allowing casualty loss deductions only in federally declared disaster areas. If you have personal casualty gains because your insurance proceeds exceed the tax basis of the damaged or destroyed property, you can deduct personal casualty losses that aren’t due to a federally declared disaster up to the amount of your personal casualty gains.
Special election to claim a refund
If your casualty loss is due to a federally declared disaster, a special election allows you to deduct the loss on your tax return for the preceding year and claim a refund. If you’ve already filed your return for the preceding year, you can file an amended return to make the election and claim the deduction in the earlier year. This can potentially help you get extra cash when you need it.
This election must be made by no later than six months after the due date (without considering extensions) for filing your tax return for the year in which the disaster occurs. However, the election itself must be made on an original or amended return for the preceding year.
How to calculate the deduction
You must take the following three steps to calculate the casualty loss deduction for personal-use property in an area declared a federal disaster:
- Subtract any insurance proceeds.
- Subtract $100 per casualty event.
- Combine the results from the first two steps and then subtract 10% of your adjusted gross income (AGI) for the year you claim the loss deduction.
Important: Another factor that now makes it harder to claim a casualty loss than it used to be years ago is that you must itemize deductions to claim one. Through 2025, fewer people will itemize, because the TCJA significantly increased the standard deduction amounts. For 2021, they’re $12,550 for single filers, $18,800 for heads of households, and $25,100 for married joint-filing couples.
So even if you qualify for a casualty deduction, you might not get any tax benefit, because you don’t have enough itemized deductions.
Contact us
These are the rules for personal property. Keep in mind that the rules for business or income-producing property are different. (It’s easier to get a deduction for business property casualty losses.) If you are a victim of a disaster, we can help you understand the complex rules.
© 2021
Want to find out what IRS auditors know about your business industry?

Want to find out what IRS auditors know about your business industry?
In order to prepare for a business audit, an IRS examiner generally does research about the specific industry and issues on the taxpayer’s return. Examiners may use IRS “Audit Techniques Guides (ATGs).” A little-known secret is that these guides are available to the public on the IRS website. In other words, your business can use the same guides to gain insight into what the IRS is looking for in terms of compliance with tax laws and regulations.
Many ATGs target specific industries or businesses, such as construction, aerospace, art galleries, architecture and veterinary medicine. Others address issues that frequently arise in audits, such as executive compensation, passive activity losses and capitalization of tangible property.
Unique issues
IRS auditors need to examine different types of businesses, as well as individual taxpayers and tax-exempt organizations. Each type of return might have unique industry issues, business practices and terminology. Before meeting with taxpayers and their advisors, auditors do their homework to understand various industries or issues, the accounting methods commonly used, how income is received, and areas where taxpayers might not be in compliance.
By using a specific ATG, an auditor may be able to reconcile discrepancies when reported income or expenses aren’t consistent with what’s normal for the industry or to identify anomalies within the geographic area in which the business is located.
Updates and revisions
Some guides were written several years ago and others are relatively new. There is not a guide for every industry. Here are some of the guide titles that have been revised or added this year:
- Retail Industry (March 2021),
- Construction Industry (April 2021),
- Nonqualified Deferred Compensation (June 2021), and
- Real Estate Property Foreclosure and Cancellation of Debt (August 2021).
Although ATGs were created to help IRS examiners uncover common methods of hiding income and inflating deductions, they also can help businesses ensure they aren’t engaging in practices that could raise audit red flags. For a complete list of ATGs, visit the IRS website here: https://www.checkpointmarketing.net/newsletter/linkShimRadar.cfm?key=89521358G3971J9375127&l=72457
© 2021
Does your employer provide life insurance? Here are the tax consequences

Does your employer provide life insurance? Here are the tax consequences
Employer-provided life insurance is a coveted fringe benefit. However, if group term life insurance is part of your benefit package, and the coverage is higher than $50,000, there may be undesirable income tax implications.
Tax on income you don’t receive
The first $50,000 of group term life insurance coverage that your employer provides is excluded from taxable income and doesn’t add anything to your income tax bill. But the employer-paid cost of group term coverage in excess of $50,000 is taxable income to you. It’s included in the taxable wages reported on your Form W-2 — even though you never actually receive it. In other words, it’s “phantom income.”
What’s worse, the cost of group term insurance must be determined under a table prepared by the IRS even if the employer’s actual cost is less than the cost figured under the table. With these determinations, the amount of taxable phantom income attributed to an older employee is often higher than the premium the employee would pay for comparable coverage under an individual term policy. This tax trap gets worse as an employee gets older and as the amount of his or her compensation increases.
Your W-2 has answers
What should you do if you think the tax cost of employer-provided group term life insurance is higher than you’d like? First, you should establish if this is actually the case. If a specific dollar amount appears in Box 12 of your Form W-2 (with code “C”), that dollar amount represents your employer’s cost of providing you with group term life insurance coverage in excess of $50,000, less any amount you paid for the coverage. You’re responsible for federal, state and local taxes on the amount that appears in Box 12 and for the associated Social Security and Medicare taxes as well.
But keep in mind that the amount in Box 12 is already included as part of your total “Wages, tips and other compensation” in Box 1 of the W-2, and it’s the Box 1 amount that’s reported on your tax return.
Possible options
If you decide that the tax cost is too high for the benefit you’re getting in return, find out whether your employer has a “carve-out” plan (a plan that carves out selected employees from group term coverage) or, if not, whether it would be willing to create one. There are different types of carve-out plans that employers can offer to their employees.
For example, the employer can continue to provide $50,000 of group term insurance (since there’s no tax cost for the first $50,000 of coverage). Then, the employer can either provide the employee with an individual policy for the balance of the coverage, or give the employee the amount the employer would have spent for the excess coverage as a cash bonus that the employee can use to pay the premiums on an individual policy.
Contact us if you have questions about group term coverage or whether it’s adding to your tax bill.
© 2021
Getting a divorce? Be aware of tax implications if you own a business

If you’re a business owner and you’re getting a divorce, tax issues can complicate matters. Your business ownership interest is one of your biggest personal assets and in many cases, your marital property will include all or part of it.
Tax-free property transfers
You can generally divide most assets, including cash and business ownership interests, between you and your soon-to-be ex-spouse without any federal income or gift tax consequences. When an asset falls under this tax-free transfer rule, the spouse who receives the asset takes over its existing tax basis (for tax gain or loss purposes) and its existing holding period (for short-term or long-term holding period purposes).
Let’s say that under the terms of your divorce agreement, you give your house to your spouse in exchange for keeping 100% of the stock in your business. That asset swap would be tax-free. And the existing basis and holding periods for the home and the stock would carry over to the person who receives them.
Tax-free transfers can occur before a divorce or at the time it becomes final. Tax-free treatment also applies to post-divorce transfers as long as they’re made “incident to divorce.” This means transfers that occur within:
- A year after the date the marriage ends, or
- Six years after the date the marriage ends if the transfers are made pursuant to your divorce agreement.
More tax issues
Later on, there will be tax implications for assets received tax-free in a divorce settlement. The ex-spouse who winds up owning an appreciated asset — when the fair market value exceeds the tax basis — generally must recognize taxable gain when it’s sold (unless an exception applies).
What if your ex-spouse receives 49% of your highly appreciated small business stock? Thanks to the tax-free transfer rule, there’s no tax impact when the shares are transferred. Your ex will continue to apply the same tax rules as if you had continued to own the shares, including carryover basis and carryover holding period. When your ex-spouse ultimately sells the shares, he or she will owe any capital gains taxes. You will owe nothing.
Note that the person who winds up owning appreciated assets must pay the built-in tax liability that comes with them. From a net-of-tax perspective, appreciated assets are worth less than an equal amount of cash or other assets that haven’t appreciated. That’s why you should always take taxes into account when negotiating your divorce agreement.
In addition, the beneficial tax-free transfer rule is now extended to ordinary-income assets, not just to capital-gains assets. For example, if you transfer business receivables or inventory to your ex-spouse in a divorce, these types of ordinary-income assets can also be transferred tax-free. When the asset is later sold, converted to cash or exercised (in the case of nonqualified stock options), the person who owns the asset at that time must recognize the income and pay the tax liability.
Plan ahead to avoid surprises
Like many major life events, divorce can have major tax implications. For example, you may receive an unexpected tax bill if you don’t carefully handle the splitting up of qualified retirement plan accounts (such as a 401(k) plan) and IRAs. And if you own a business, the stakes are higher. We can help you minimize the adverse tax consequences of settling your divorce.
ABLE accounts may help disabled or blind family members

ABLE accounts may help disabled or blind family members
There may be a tax-advantaged way for people to save for the needs of family members with disabilities — without having them lose eligibility for government benefits to which they’re entitled. It can be done though an Achieving a Better Life Experience (ABLE) account, which is a tax-free account that can be used for disability-related expenses.
Who is eligible?
ABLE accounts can be created by eligible individuals to support themselves, by family members to support their dependents, or by guardians for the benefit of the individuals for whom they’re responsible. Anyone can contribute to an ABLE account. While contributions aren’t tax-deductible, the funds in the account are invested and grow free of tax.
Eligible individuals must be blind or disabled — and must have become so before turning age 26. They also must be entitled to benefits under the Supplemental Security Income (SSI) or Social Security Disability Insurance (SSDI) programs. Alternatively, an individual can become eligible if a disability certificate is filed with the IRS for him or her.
Distributions from an ABLE account are tax-free if used to pay for expenses that maintain or improve the beneficiary’s health, independence or quality of life. These expenses include education, housing, transportation, employment support, health and wellness costs, assistive technology, personal support services, and other IRS-approved expenses.
If distributions are used for nonqualified expenses, the portion of the distribution that represents earnings on the account is subject to income tax — plus a 10% penalty.
More details
Here are some other key factors:
- An eligible individual can have only one ABLE account. Contributions up to the annual gift-tax exclusion amount, currently $15,000, may be made to an ABLE account each year for the benefit of an eligible person. If the beneficiary works, the beneficiary can also contribute part, or all, of their income to their account. (This additional contribution is limited to the poverty-line amount for a one-person household.)
- There’s also a limit on the total account balance. This limit, which varies from state to state, is equal to the limit imposed by that state on qualified tuition (Section 529) plans.
- ABLE accounts have no impact on an individual’s Medicaid eligibility. However, ABLE account balances in excess of $100,000 are counted toward the SSI program’s $2,000 individual resource limit. Therefore, an individual’s SSI benefits are suspended, but not terminated, when his or her ABLE account balance exceeds $102,000 (assuming the individual has no other assets). In addition, distributions from an ABLE account to pay housing expenses count toward the SSI income limit.
- For contributions made before 2026, the designated beneficiary can claim the saver’s credit for contributions made to his or her ABLE account.
States establish programs
There are many choices. ABLE accounts are established under state programs. An account may be opened under any state’s program (if the state allows out-of-state participants). The funds in an account can be invested in a variety of options and the account’s investment directions can be changed up to twice a year. Contact us if you’d like more details about setting up or maintaining an ABLE account.
© 2021
There may be a tax-advantaged way for people to save for the needs of family members with disabilities, without having them lose eligibility for their government benefits. It’s done though an ABLE account, which is a tax-free account that can be used for disability-related expenses. Eligible individuals must have become blind or disabled before turning age 26. ABLE accounts can be created by eligible individuals to support themselves, by family members to support their dependents, or by guardians. Contributions up to the annual gift-tax exclusion amount ($15,000 in 2021), can be made to an account each year. Contact us if you have questions about setting up or maintaining an ABLE account.
Possible tax consequences of guaranteeing a loan to your corporation

What if you decide to, or are asked to, guarantee a loan to your corporation? Before agreeing to act as a guarantor, endorser or indemnitor of a debt obligation of your closely held corporation, be aware of the possible tax consequences. If your corporation defaults on the loan and you’re required to pay principal or interest under the guarantee agreement, you don’t want to be blindsided.
Business vs. nonbusiness
If you’re compelled to make good on the obligation, the payment of principal or interest in discharge of the obligation generally results in a bad debt deduction. This may be either a business or a nonbusiness bad debt deduction. If it’s a business bad debt, it’s deductible against ordinary income. A business bad debt can be either totally or partly worthless. If it’s a nonbusiness bad debt, it’s deductible as a short-term capital loss, which is subject to certain limitations on deductions of capital losses. A nonbusiness bad debt is deductible only if it’s totally worthless.
In order to be treated as a business bad debt, the guarantee must be closely related to your trade or business. If the reason for guaranteeing the corporation loan is to protect your job, the guarantee is considered closely related to your trade or business as an employee. But employment must be the dominant motive. If your annual salary exceeds your investment in the corporation, this tends to show that the dominant motive for the guarantee was to protect your job. On the other hand, if your investment in the corporation substantially exceeds your annual salary, that’s evidence that the guarantee was primarily to protect your investment rather than your job.
Except in the case of job guarantees, it may be difficult to show the guarantee was closely related to your trade or business. You’d have to show that the guarantee was related to your business as a promoter, or that the guarantee was related to some other trade or business separately carried on by you.
If the reason for guaranteeing your corporation’s loan isn’t closely related to your trade or business and you’re required to pay off the loan, you can take a nonbusiness bad debt deduction if you show that your reason for the guarantee was to protect your investment, or you entered the guarantee transaction with a profit motive.
In addition to satisfying the above requirements, a business or nonbusiness bad debt is deductible only if:
- You have a legal duty to make the guaranty payment, although there’s no requirement that a legal action be brought against you;
- The guaranty agreement was entered into before the debt becomes worthless; and
- You received reasonable consideration (not necessarily cash or property) for entering into the guaranty agreement.
Any payment you make on a loan you guaranteed is deductible as a bad debt in the year you make it, unless the agreement (or local law) provides for a right of subrogation against the corporation. If you have this right, or some other right to demand payment from the corporation, you can’t take a bad debt deduction until the rights become partly or totally worthless.
These are only a few of the possible tax consequences of guaranteeing a loan to your closely held corporation. Contact us to learn all the implications in your situation.
© 2021
Large cash transactions with your business must be reported to the IRS

If your business receives large amounts of cash or cash equivalents, you may be required to report these transactions to the IRS.
What are the requirements?
Each person who, in the course of operating a trade or business, receives more than $10,000 in cash in one transaction (or two or more related transactions), must file Form 8300. What is considered a “related transaction?” Any transactions conducted in a 24-hour period. Transactions can also be considered related even if they occur over a period of more than 24 hours if the recipient knows, or has reason to know, that each transaction is one of a series of connected transactions.
To complete a Form 8300, you’ll need personal information about the person making the cash payment, including a Social Security or taxpayer identification number.
Why does the government require reporting?
Although many cash transactions are legitimate, the IRS explains that “information reported on (Form 8300) can help stop those who evade taxes, profit from the drug trade, engage in terrorist financing and conduct other criminal activities. The government can often trace money from these illegal activities through the payments reported on Form 8300 and other cash reporting forms.”
You should keep a copy of each Form 8300 for five years from the date you file it, according to the IRS.
What’s considered “cash” and “cash equivalents?”
For Form 8300 reporting purposes, cash includes U.S. currency and coins, as well as foreign money. It also includes cash equivalents such as cashier’s checks (sometimes called bank checks), bank drafts, traveler’s checks and money orders.
Money orders and cashier’s checks under $10,000, when used in combination with other forms of cash for a single transaction that exceeds $10,000, are defined as cash for Form 8300 reporting purposes.
Note: Under a separate reporting requirement, banks and other financial institutions report cash purchases of cashier’s checks, treasurer’s checks and/or bank checks, bank drafts, traveler’s checks and money orders with a face value of more than $10,000 by filing currency transaction reports.
Can the forms be filed electronically?
Businesses required to file reports of large cash transactions on Form 8300 should know that in addition to filing on paper, e-filing is an option. The form is due 15 days after a transaction and there’s no charge for the e-file option. Businesses that file electronically get an automatic acknowledgment of receipt when they file.
The IRS also reminds businesses that they can “batch file” their reports, which is especially helpful to those required to file many forms.
How can we set up an electronic account?
To file Form 8300 electronically, a business must set up an account with FinCEN’s Bank Secrecy Act E-Filing System. For more information, visit: https://bsaefiling.fincen.treas.gov/AboutBsa.html. Interested businesses can also call the BSA E-Filing Help Desk at 866-346-9478 (Monday through Friday from 8 am to 6 pm EST). Contact us with any questions or for assistance.
5 possible tax aspects of a parent moving into a nursing home

|
There’s currently a “stepped-up basis” if you inherit property — but will it last?

|
Getting a new business off the ground: How start-up expenses are handled on your tax return

|
Can taxpayers who manage their own investment portfolios deduct related expenses? It depends

|
Who in a small business can be hit with the “Trust Fund Recovery Penalty?”

|
10 facts about the pass-through deduction for qualified business income

|
IRS audits may be increasing, so be prepared

|
Are you a nonworking spouse? You may still be able to contribute to an IRA

|
Eligible Businesses: Claim the Employee Retention Tax Credit

|
Traveling for business again? What can you deduct?

|
Tax-favored ways to build up a college fund

|
2021 Q3 tax calendar: Key deadlines for businesses and other employers

|
Retiring soon? 4 tax issues you may face

If you’re getting ready to retire, you’ll soon experience changes in your lifestyle and income sources that may have numerous tax implications.
Here's a brief rundown of four tax and financial issues you may deal with when you retire:
Taking required minimum distributions.
This is the minimum amount you must withdraw from your retirement accounts. You generally must start taking withdrawals from your IRA, SEP, SIMPLE, and other retirement plan accounts when you reach age 72 (70½ before January 1, 2020). Roth IRAs don’t require withdrawals until after the death of the owner.
You can withdraw more than the minimum required amount. Your withdrawals will be included in your taxable income except for any part that was taxed before or that can be received tax-free (such as qualified distributions from Roth accounts).
Selling your principal residence
Many retirees want to downsize to smaller homes. If you’re one of them and you have a gain from the sale of your principal residence, you may be able to exclude up to $250,000 of that gain from your income. If you file a joint return, you may be able to exclude up to $500,000.
To claim the exclusion, you must meet certain requirements. During a five-year period ending on the date of the sale, you must have owned the home and lived in it as your main home for at least two years.
If you're thinking of selling your home, make sure you’ve identified all items that should be included in its basis, which can save you tax.
Engaging in new work activities.
After retirement, many people continue to work as consultants or start new businesses. Here are some tax-related questions to ask:
Should the business be a sole proprietorship, S corporation, C corporation, partnership, or limited liability company?
Are you familiar with how to elect to amortize start-up expenditures and make payroll tax deposits?
What expenses can you deduct and can you claim home office deductions?
How should you finance the business?
Taking Social Security benefits.
If you continue to work, it may have an impact on your Social Security benefits. If you retire before reaching full Social Security retirement age (65 years of age for people born before 1938, rising to 67 years of age for people born after 1959) and the sum of your wages plus self-employment income is over the Social Security annual exempt amount ($18,960 for 2021), you must give back $1 of Social Security benefits for each $2 of excess earnings.
If you reach full retirement age this year, your benefits will be reduced by $1 for every $3 you earn over a different annual limit ($50,520 in 2021) until the month you reach full retirement age. Then, your earnings will no longer affect the amount of your monthly benefits, no matter how much you earn.
Speaking of Social Security, you may have to pay federal (and possibly state) tax on your benefits. Depending on how much income you have from other sources, you may have to report up to 85% of your benefits as income on your tax return and pay the resulting federal income tax.
Many decisions
As you can see, tax planning is still important after you retire. We can help maximize the tax breaks you’re entitled to so you can keep more of your hard-earned money.
© 2021
Recordkeeping DOs and DON’Ts for business meal and vehicle expenses

If you're claiming deductions for business meals or auto expenses, expect the IRS to closely review them. In some cases, taxpayers have incomplete documentation or try to create records months (or years) later. In doing so, they fail to meet the strict substantiation requirements set forth under tax law. Tax auditors are adept at rooting out inconsistencies, omissions, and errors in taxpayers' records, as illustrated by one recent U.S. Tax Court case.
Facts of the case
In this case, the taxpayer ran a notary and paralegal business. She deducted business meals and vehicle expenses that she allegedly incurred in connection with her business.
The deductions were denied by the IRS and the court. Does tax law establish higher substantiation requirements for these and certain other expenses, the court noted. No deduction is generally allowed unless the taxpayer substantiates the amount, time and place, business purpose, and business relationship to the taxpayer of the person receiving the benefit for each expense with adequate records or sufficient evidence.
The taxpayer in this case didn't provide adequate records or other sufficient evidence to prove the business purpose of her meal expenses. She gave vague testimony that she deducted expenses for meals where she talked strategies with people who wanted her to do some work. The court found this was insufficient to show the connection between the meals and her business.
When it came to the taxpayer's vehicle expense deductions, she failed to offer credible evidence showing where she drove her vehicle, the purpose of each trip and her business relationship to the places visited. She also conceded that she used her car for both business and personal activities. (TC Memo 2021-50)
Best practices for business expenses
This case is an example of why it's critical to maintain meticulous records to support business expenses for meals and vehicle deductions. Here's a list of DOs and DON'Ts to help meet the strict IRS and tax law substantiation requirements for these items:
DO keep detailed, accurate records. For each expense, record the amount, the time and place, the business purpose, and the business relationship of any person to whom you provided a meal. If you have employees who you reimburse for meals and auto expenses, make sure they're complying with all the rules.
DONT reconstruct expense logs at year-end or wait until you receive a notice from the IRS. Take a moment to record the details in a log or diary or on a receipt at the time of the event or soon after. Require employees to submit monthly expense reports.
DO respect the fine line between personal and business expenses. Be careful about combining business and pleasure. Your business checking account shouldn't be used for personal expenses.
DONT be surprised if the IRS asks you to prove your deductions. Meal and auto expenses are a magnet for attention. Be prepared for a challenge.
With organization and guidance from us, your tax records can stand up to scrutiny from the IRS. There may be ways to substantiate your deductions that you haven't thought of, and there may be a way to estimate certain deductions (the Cohan rule), if your records are lost due to a fire, theft, flood, or other disasters.
If you're claiming deductions for business meals or auto expenses, expect the IRS to closely review them. It's important to comply with the strict tax law substantiation requirements for these items. DO keep detailed, accurate records. For each expense, record the amount, the time and place, the business purpose, and the business relationship of anyone to whom you provided a meal. If you have employees who you reimburse for meals and auto expenses, make sure they're complying with all the rules. DONT reconstruct expense logs at year-end or wait until you receive an IRS. Take a moment to record the details in a log or diary or on a receipt at the time of the event or soon after.
© 2021
Hiring your minor children this summer? Reap tax and nontax benefits
|
Plan ahead for the 3.8% Net Investment Income Tax
|
Many parents will receive advance tax credit payments beginning July 15

Eligible parents will soon begin receiving payments from the federal government. The IRS announced that the 2021 advance child tax credit (CTC) payments, which were created in the American Rescue Plan Act (ARPA), will begin being made on July 15, 2021.
How have child tax credits changed?
The ARPA temporarily expanded and made CTCs refundable for 2021. The law increased the maximum CTC — for 2021 only — to $3,600 for each qualifying child under age 6 and to $3,000 per child for children ages 6 to 17, provided their parents’ income is below a certain threshold.
Advance payments will receive up to $300 monthly for each child under 6, and up to $250 monthly for each child 6 and older. The increased credit amount will be reduced or phased out, for households with modified adjusted gross income above the following thresholds:
- $150,000 for married taxpayers filing jointly and qualifying widows and widowers;
- $112,500 for heads of household; and
- $75,000 for other taxpayers.
Under prior law, the maximum annual CTC for 2018 through 2025 was $2,000 per qualifying child but the income thresholds were higher and some of the qualification rules were different.
Important: If your income is too high to receive the increased advance CTC payments, you may still qualify to claim the $2,000 CTC on your tax return for 2021.
What is a qualifying child?
For 2021, a “qualifying child” with respect to a taxpayer is defined as one who is under age 18 and who the taxpayer can claim as a dependent. That means a child related to the taxpayer who, generally, lived with the taxpayer for at least six months during the year. The child also must be a U.S. citizen or national or a U.S. resident.
How and when will advance payments be sent out?
Under the ARPA, the IRS is required to establish a program to make periodic advance payments which in total equal 50% of IRS’s estimate of the eligible taxpayer’s 2021 CTCs, during the period July 2021 through December 2021. The payments will begin on July 15, 2021. After that, they’ll be made on the 15th of each month unless the 15th falls on a weekend or holiday. Parents will receive the monthly payments through direct deposit, paper check or debit card.
Who will benefit from these payments and do they have to do anything to receive them?
According to the IRS, about 39 million households covering 88% of children in the U.S. “are slated to begin receiving monthly payments without any further action required.” Contact us if you have questions about the child tax credit.
© 2021
Home sales: How to determine your “basis”

The housing market in many parts of the country is strong this spring. If you’re buying or selling a home, you should know how to determine your “basis.”
How it works
You can claim an itemized deduction on your tax return for real estate taxes and home mortgage interest. Most other home ownership costs can’t be deducted currently. However, these costs may increase your home’s “basis” (your cost for tax purposes). And a higher basis can save taxes when you sell.
The law allows an exclusion from income for all or part of the gain realized on the sale of your home. The general exclusion limit is $250,000 ($500,000 for married taxpayers). You may feel the exclusion amount makes keeping track of the basis relatively unimportant. Many homes today sell for less than $500,000. However, that reasoning doesn’t take into account what may happen in the future. If history is any indication, a home that’s owned for 20 or 30 years appreciates greatly. Thus, you want your basis to be as high as possible in order to avoid or reduce the tax that may result when you eventually sell.
Good recordkeeping
To prove the amount of your basis, keep accurate records of your purchase price, closing costs, and other expenses that increase your basis. Save receipts and other records for improvements and additions you make to the home. When you eventually sell, your basis will establish the amount of your gain. Keep the supporting documentation for at least three years after you file your return for the sale year.
Start with the purchase price
The main element in your home’s basis is the purchase price. This includes your down payment and any debt, such as a mortgage. It also includes certain settlement or closing costs. If you had your house built on land you own, your basis is the cost of the land plus certain costs to complete the house.
You add to the cost of your home expenses that you paid in connection with the purchase, including attorney’s fees, abstract fees, owner’s title insurance, recording fees and transfer taxes. The basis of your home is affected by expenses after a casualty to restore damaged property and depreciation if you used your home for business or rental purposes,
Over time, you may make additions and improvements to your home. Add the cost of these improvements to your basis. Improvements that add to your home’s basis include:
- A room addition,
- Finishing the basement,
- A fence,
- Storm windows or doors,
- A new heating or central air conditioning system,
- Flooring,
- A new roof, and
- Driveway paving.
Home expenses that don’t add much to the value or the property’s life are considered repairs, not improvements. Therefore, you can’t add them to the property’s basis. Repairs include painting, fixing gutters, repairing leaks and replacing broken windows. However, an entire job is considered an improvement if items that would otherwise be considered repairs are done as part of extensive remodeling.
The cost of appliances purchased for your home generally don’t add to your basis unless they are considered attached to the house. Thus, the cost of a built-in oven or range would increase basis. But an appliance that can be easily removed wouldn’t.
Plan for best results
Other rules and requirements may apply. We can help you plan for the best tax results involving your home’s basis.
© 2021
Simple retirement savings options for your small business

|
Who qualifies for “head of household” tax filing status?

|
Tax advantages of hiring your child at your small business
|
How to ensure life insurance isn’t part of your taxable estate
|
Need a new business vehicle? Consider a heavy SUV

Are you considering buying or replacing a vehicle that you’ll use in your business? If you choose a heavy sport utility vehicle (SUV), you may be able to benefit from lucrative tax rules for those vehicles.
Bonus depreciation
Under current law, 100% first-year bonus depreciation is available for qualified new and used property that’s acquired and placed in service in a calendar year. New and pre-owned heavy SUVs, pickups and vans acquired and put to business use in 2021 are eligible for 100% first-year bonus depreciation. The only requirement is that you must use the vehicle more than 50% for business. If your business usage is between 51% and 99%, you can deduct that percentage of the cost in the first year the vehicle is placed in service. This generous tax break is available for qualifying vehicles that are acquired and placed in service through December 31, 2022.
The 100% first-year bonus depreciation write-off will reduce your federal income tax bill and self-employment tax bill, if applicable. You might get a state tax income deduction, too.
Weight requirement
This option is available only if the manufacturer’s gross vehicle weight rating (GVWR) is above 6,000 pounds. You can verify a vehicle’s GVWR by looking at the manufacturer’s label, usually found on the inside edge of the driver’s side door where the door hinges meet the frame.
Note: These tax benefits are subject to adjustment for non-business use. And if business use of an SUV doesn’t exceed 50% of total use, the SUV won’t be eligible for the expensing election, and would have to be depreciated on a straight-line method over a six-tax-year period.
Detailed, contemporaneous expense records are essential — in case the IRS questions your heavy vehicle’s claimed business-use percentage.
That means you’ll need to keep track of the miles you’re driving for business purposes, compared to the vehicle’s total mileage for the year. Recordkeeping is much simpler today, now that there are apps and mobile technology you can use. Or simply keep a small calendar or mileage log in your car and record details as business trips occur.
If you’re considering buying an eligible vehicle, doing so and placing it in service before the end of this tax year could deliver a big write-off on your 2021 tax return. Before signing a sales contract, consult with us to help evaluate the right tax moves for your business.
© 2021
New law tax break may make child care less expensive

The new American Rescue Plan Act (ARPA) provides eligible families with an enhanced child and dependent care credit for 2021. This is the credit available for expenses a taxpayer pays for the care of qualifying children under the age of 13 so that the taxpayer can be gainfully employed.
Note that a credit reduces your tax bill dollar for dollar.
Who qualifies?
For care to qualify for the credit, the expenses must be “employment-related.” In other words, they must enable you and your spouse to work. In addition, they must be for the care of your child, stepchild, foster child, brother, sister or step-sibling (or a descendant of any of these), who’s under 13, lives in your home for over half the year, and doesn’t provide over half of his or her own support for the year. The expenses can also be for the care of your spouse or dependent who’s handicapped and lives with you for over half the year.
The typical expenses that qualify for the credit are payments to a day care center, nanny or nursery school. Sleep-away camp doesn’t qualify. The cost of kindergarten or higher grades doesn’t qualify because it’s an education expense. However, the cost of before and after school programs may qualify.
To claim the credit, married couples must file a joint return. You must also provide the caregiver’s name, address and Social Security number (or tax ID number for a day care center or nursery school). You also must include on the return the Social Security number(s) of the children receiving the care.
The 2021 credit is refundable as long as either you or your spouse has a principal residence in the U.S. for more than half of the tax year.
What are the limits?
When calculating the credit, several limits apply. First, qualifying expenses are limited to the income you or your spouse earn from work, self-employment, or certain disability and retirement benefits — using the figure for whichever of you earns less. Under this limitation, if one of you has no earned income, you aren’t entitled to any credit. However, in some cases, if one spouse has no actual earned income and that spouse is a full-time student or disabled, the spouse is considered to have monthly income of $250 (for one qualifying individual) or $500 (for two or more qualifying individuals).
For 2021, the first $8,000 of care expenses generally qualifies for the credit if you have one qualifying individual, or $16,000 if you have two or more. (These amounts have increased significantly from $3,000 and $6,000, respectively.) However, if your employer has a dependent care assistance program under which you receive benefits excluded from gross income, the qualifying expense limits ($8,000 or $16,000) are reduced by the excludable amounts you receive.
How much is the credit worth?
If your AGI is $125,000 or less, the maximum credit amount is $4,000 for taxpayers with one qualifying individual and $8,000 for taxpayers with two or more qualifying individuals. The credit phases out under a complicated formula. For taxpayers with an AGI greater than $440,000, it’s phased out completely.
These are the essential elements of the enhanced child and dependent care credit in 2021 under the new law. Contact us if you have questions.
© 2021
Is an S corporation the best choice of entity for your business?
|
New law: Parents and other eligible Americans to receive direct payments

The American Rescue Plan Act, signed into law on March 11, provides a variety of tax and financial relief to help mitigate the effects of the COVID-19 pandemic. Among the many initiatives are direct payments that will be made to eligible individuals. And parents under certain income thresholds will also receive additional payments in the coming months through a greatly revised Child Tax Credit.
Here are some answers to questions about these payments.
What are the two types of payments?
Under the new law, eligible individuals will receive advance direct payments of a tax credit. The law calls these payments “recovery rebates.” The law also includes advance Child Tax Credit payments to eligible parents later this year.
How much are the recovery rebates?
An eligible individual is allowed a 2021 income tax credit, which will generally be paid in advance through direct bank deposit or a paper check. The full amount is $1,400 ($2,800 for eligible married joint filers) plus $1,400 for each dependent.
Who is eligible?
There are several requirements but the most important is income on your most recently filed tax return. Full payments are available to those with adjusted gross incomes (AGIs) of less than $75,000 ($150,000 for married joint filers and $112,500 for heads of households). Your AGI can be found on page 1 of Form 1040.
The credit phases out and is no longer available to taxpayers with AGIs of more than $80,000 ($160,000 for married joint filers and $120,000 for heads of households).
Who isn’t eligible?
Among those who aren’t eligible are nonresident aliens, individuals who are the dependents of other taxpayers, estates and trusts.
How has the Child Tax Credit changed?
Before the new law, the Child Tax Credit was $2,000 per “qualifying child.” Under the new law, the credit is increased to $3,000 per child ($3,600 for children under age 6 as of the end of the year). But the increased 2021 credit amounts are phased out at modified AGIs of over $75,000 for singles ($150,000 for joint filers and $112,500 for heads of households).
A qualifying child before the new law was defined as an under-age-17 child, whom the taxpayer could claim as a dependent. The $2,000 Child Tax Credit was phased out for taxpayers with modified AGIs of over $400,000 for joint filers, and $200,000 for other filers.
Under the new law, for 2021, the definition of a qualifying child for purposes of the Child Tax Credit includes one who hasn’t turned 18 by the end of this year. So 17-year-olds qualify for the credit for 2021 only.
How are parents going to receive direct payments of the Child Tax Credit this year?
Unlike in the past, you don’t have to wait to file your tax return to fully benefit from the credit. The new law directs the IRS to establish a program to make monthly advance payments equal to 50% of eligible taxpayers’ 2021 Child Tax Credits. These payments will be made from July through December 2021.
What if my income is above the amounts listed above?
Taxpayers who aren’t eligible to claim an increased Child Tax Credit, because their incomes are too high, may be able to claim a regular credit of up to $2,000 on their 2021 tax returns, subject to the existing phaseout rules.
Much more
There are other rules and requirements involving these payments. This article only describes the basics. Stay tuned for additional details about other tax breaks in the new law.
© 2021
Business highlights in the new American Rescue Plan Act
|
Estimated tax payments: The deadline for the first 2021 installment is coming ups
|
Launching a small business? Here are some tax considerations
|
Retiring soon? Recent law changes may have an impact on your retirement savings

If you’re approaching retirement, you probably want to ensure the money you’ve saved in retirement plans lasts as long as possible. If so, be aware that a law was recently enacted that makes significant changes to retirement accounts. The SECURE Act, which was signed into law in late 2019, made a number of changes of interest to those nearing retirement.
You can keep making traditional IRA contributions if you’re still working
Before 2020, traditional IRA contributions weren’t allowed once you reached age 70½. But now, an individual of any age can make contributions to a traditional IRA, as long as he or she has compensation, which generally means earned income from wages or self-employment. So if you work part time after retiring, or do some work as an independent contractor, you may be able to continue saving in your IRA if you’re otherwise eligible.
The required minimum distribution (RMD) age was raised from 70½ to 72.
Before 2020, retirement plan participants and IRA owners were generally required to begin taking RMDs from their plans by April 1 of the year following the year they reached age 70½. The age 70½ requirement was first applied in the early 1960s and, until recently, hadn’t been adjusted to account for increased life expectancies.
For distributions required to be made after December 31, 2019, for individuals who attain age 70½ after that date, the age at which individuals must begin taking distributions from their retirement plans or IRAs is increased from 70½ to 72.
“Stretch IRAs” have been partially eliminated
If a plan participant or IRA owner died before 2020, their beneficiaries (spouses and non-spouses) were generally allowed to stretch out the tax-deferral advantages of the plan or IRA by taking distributions over the life or life expectancy of the beneficiaries. This was sometimes called a “stretch IRA.”
However, for deaths of plan participants or IRA owners beginning in 2020 (later for some participants in collectively bargained plans and governmental plans), distributions to most non-spouse beneficiaries are generally required to be distributed within 10 years following a plan participant’s or IRA owner’s death. Therefore, the “stretch” strategy is no longer allowed for those beneficiaries.
There are some exceptions to the 10-year rule. For example, it’s still allowed for: the surviving spouse of a plan participant or IRA owner; a child of a plan participant or IRA owner who hasn’t reached the age of majority; a chronically ill individual; and any other individual who isn’t more than 10 years younger than a plan participant or IRA owner. Those beneficiaries who qualify under this exception may generally still take their distributions over their life expectancies.
More changes may be ahead
These are only some of the changes included in the SECURE Act. In addition, there’s bipartisan support in Congress to make even more changes to promote retirement saving. Last year, a law dubbed the SECURE Act 2.0 was introduced in the U.S. House of Representatives. At this time, it’s unclear if or when it could be enacted. We’ll let you know about any new opportunities. In the meantime, if you have questions about your situation, don’t hesitate to contact us.
© 2020
Didn’t contribute to an IRA last year? There still may be time
|
If you run a business from home, you could qualify for home office deductions

During the COVID-19 pandemic, many people are working from home. If you’re self-employed and run your business from your home or perform certain functions there, you might be able to claim deductions for home office expenses against your business income. There are two methods for claiming this tax break: the actual expenses method and the simplified method.
Who qualifies?
In general, you qualify for home office deductions if part of your home is used “regularly and exclusively” as your principal place of business.
If your home isn’t your principal place of business, you may still be able to deduct home office expenses if 1) you physically meet with patients, clients or customers on your premises, or 2) you use a storage area in your home (or a separate free-standing structure, such as a garage) exclusively and regularly for business.
What can you deduct?
Many eligible taxpayers deduct actual expenses when they claim home office deductions. Deductible home office expenses may include:
- Direct expenses, such as the cost of painting and carpeting a room used exclusively for business,
- A proportionate share of indirect expenses, including mortgage interest, rent, property taxes, utilities, repairs and insurance, and
- Depreciation.
But keeping track of actual expenses can take time and require organization.
How does the simpler method work?
Fortunately, there’s a simplified method: You can deduct $5 for each square foot of home office space, up to a maximum total of $1,500.
The cap can make the simplified method less valuable for larger home office spaces. But even for small spaces, taxpayers may qualify for bigger deductions using the actual expense method. So, tracking your actual expenses can be worth it.
Can I switch?
When claiming home office deductions, you’re not stuck with a particular method. For instance, you might choose the actual expense method on your 2020 return, use the simplified method when you file your 2021 return next year and then switch back to the actual expense method for 2022. The choice is yours.
What if I sell the home?
If you sell — at a profit — a home that contains (or contained) a home office, there may be tax implications. We can explain them to you.
Also be aware that the amount of your home office deductions is subject to limitations based on the income attributable to your use of the office. Other rules and limitations may apply. But any home office expenses that can’t be deducted because of these limitations can be carried over and deducted in later years.
Do employees qualify?
Unfortunately, the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act suspended the business use of home office deductions from 2018 through 2025 for employees. Those who receive a paycheck or a W-2 exclusively from their employers aren’t eligible for deductions, even if they’re currently working from home.
We can help you determine if you’re eligible for home office deductions and how to proceed in your situation.
© 2021
What are the tax implications of buying or selling a business?

Merger and acquisition activity in many industries slowed during 2020 due to COVID-19. But analysts expect it to improve in 2021 as the country comes out of the pandemic. If you are considering buying or selling another business, it’s important to understand the tax implications.
Two ways to arrange a deal
Under current tax law, a transaction can basically be structured in two ways:
1. Stock (or ownership interest). A buyer can directly purchase a seller’s ownership interest if the target business is operated as a C or S corporation, a partnership, or a limited liability company (LLC) that’s treated as a partnership for tax purposes.
The current 21% corporate federal income tax rate makes buying the stock of a C corporation somewhat more attractive. Reasons: The corporation will pay less tax and generate more after-tax income. Plus, any built-in gains from appreciated corporate assets will be taxed at a lower rate when they’re eventually sold.
The current law’s reduced individual federal tax rates have also made ownership interests in S corporations, partnerships and LLCs more attractive. Reason: The passed-through income from these entities also is taxed at lower rates on a buyer’s personal tax return. However, current individual rate cuts are scheduled to expire at the end of 2025, and, depending on actions taken in Washington, they could be eliminated earlier.
Keep in mind that President Biden has proposed increasing the tax rate on corporations to 28%. He has also proposed increasing the top individual income tax rate from 37% to 39.6%. With Democrats in control of the White House and Congress, business and individual tax changes are likely in the next year or two.
2. Assets. A buyer can also purchase the assets of a business. This may happen if a buyer only wants specific assets or product lines. And it’s the only option if the target business is a sole proprietorship or a single-member LLC that’s treated as a sole proprietorship for tax purposes.
Preferences of buyers
For several reasons, buyers usually prefer to buy assets rather than ownership interests. In general, a buyer’s primary goal is to generate enough cash flow from an acquired business to pay any acquisition debt and provide an acceptable return on the investment. Therefore, buyers are concerned about limiting exposure to undisclosed and unknown liabilities and minimizing taxes after a transaction closes.
A buyer can step up (increase) the tax basis of purchased assets to reflect the purchase price. Stepped-up basis lowers taxable gains when certain assets, such as receivables and inventory, are sold or converted into cash. It also increases depreciation and amortization deductions for qualifying assets.
Preferences of sellers
In general, sellers prefer stock sales for tax and nontax reasons. One of their objectives is to minimize the tax bill from a sale. That can usually be achieved by selling their ownership interests in a business (corporate stock or partnership or LLC interests) as opposed to selling assets
With a sale of stock or other ownership interest, liabilities generally transfer to the buyer and any gain on sale is generally treated as lower-taxed long-term capital gain (assuming the ownership interest has been held for more than one year).
Obtain professional advice
Be aware that other issues, such as employee benefits, can also cause tax issues in M&A transactions. Buying or selling a business may be the largest transaction you’ll ever make, so it’s important to seek professional assistance. After a transaction is complete, it may be too late to get the best tax results. Contact us about how to proceed.
© 2021
Did you make donations in 2020? There’s still time to get substantiation

If you’re like many Americans, letters from your favorite charities may be appearing in your mailbox acknowledging your 2020 donations. But what happens if you haven’t received such a letter — can you still claim a deduction for the gift on your 2020 income tax return? It depends.
What is required
To support a charitable deduction, you need to comply with IRS substantiation requirements. This generally includes obtaining a contemporaneous written acknowledgment from the charity stating the amount of the donation, whether you received any goods or services in consideration for the donation and the value of any such goods or services.
“Contemporaneous” means the earlier of:
- The date you file your tax return, or
- The extended due date of your return.
So if you made a donation in 2020 but haven’t yet received substantiation from the charity, it’s not too late — as long as you haven’t filed your 2020 return. Contact the charity and request a written acknowledgment.
Keep in mind that, if you made a cash gift of under $250 with a check or credit card, generally a canceled check, bank statement or credit card statement is sufficient. However, if you received something in return for the donation, you generally must reduce your deduction by its value — and the charity is required to provide you a written acknowledgment as described earlier.
New deduction for non-itemizers
In general, taxpayers who don’t itemize their deductions (and instead claim the standard deduction) can’t claim a charitable deduction. Under the CARES Act, individuals who don’t itemize deductions can claim a federal income tax write-off for up to $300 of cash contributions to IRS-approved charities for the 2020 tax year. The same $300 limit applies to both unmarried taxpayers and married joint-filing couples.
Even better, this tax break was extended to cover $300 of cash contributions made in 2021 under the Consolidated Appropriations Act. The new law doubles the deduction limit to $600 for married joint-filing couples for cash contributions made in 2021.
2020 and 2021 deductions
Additional substantiation requirements apply to some types of donations. We can help you determine whether you have sufficient substantiation for the donations you hope to deduct on your 2020 income tax return — and guide you on the substantiation you’ll need for gifts you’re planning this year to ensure you can enjoy the desired deductions on your 2021 return.
© 2021
2021 individual taxes: Answers to your questions about limits

Many people are more concerned about their 2020 tax bills right now than they are about their 2021 tax situations. That’s understandable because your 2020 individual tax return is due to be filed in less than three months (unless you file an extension).
However, it’s a good idea to acquaint yourself with tax amounts that may have changed for 2021. Below are some Q&As about tax amounts for this year.
Be aware that not all tax figures are adjusted annually for inflation and even if they are, they may be unchanged or change only slightly due to low inflation. In addition, some amounts only change with new legislation.
How much can I contribute to an IRA for 2021?
If you’re eligible, you can contribute $6,000 a year to a traditional or Roth IRA, up to 100% of your earned income. If you’re 50 or older, you can make another $1,000 “catch up” contribution. (These amounts were the same for 2020.)
I have a 401(k) plan through my job. How much can I contribute to it?
For 2021, you can contribute up to $19,500 (unchanged from 2020) to a 401(k) or 403(b) plan. You can make an additional $6,500 catch-up contribution if you’re age 50 or older.
I sometimes hire a babysitter and a cleaning person. Do I have to withhold and pay FICA tax on the amounts I pay them?
In 2021, the threshold when a domestic employer must withhold and pay FICA for babysitters, house cleaners, etc., is $2,300 (up from $2,200 in 2020).
How much do I have to earn in 2021 before I can stop paying Social Security on my salary?
The Social Security tax wage base is $142,800 for this year (up from $137,700 last year). That means that you don’t owe Social Security tax on amounts earned above that. (You must pay Medicare tax on all amounts that you earn.)
I didn’t qualify to itemize deductions on my last tax return. Will I qualify for 2021?
A 2017 tax law eliminated the tax benefit of itemizing deductions for many people by increasing the standard deduction and reducing or eliminating various deductions. For 2021, the standard deduction amount is $25,100 for married couples filing jointly (up from $24,800). For single filers, the amount is $12,550 (up from $12,400) and for heads of households, it’s $18,800 (up from $18,650). If the amount of your itemized deductions (such as mortgage interest) are less than the applicable standard deduction amount, you won’t itemize for 2021.
If I don’t itemize, can I claim charitable deductions on my 2021 return?
Generally, taxpayers who claim the standard deduction on their federal tax returns can’t deduct charitable donations. But thanks to the CARES Act that was enacted last year, single and married joint filing taxpayers can deduct up to $300 in donations to qualified charities on their 2020 federal returns, even if they claim the standard deduction. The Consolidated Appropriations Act extended this tax break into 2021 and increased the amount that married couples filing jointly can claim to $600.
How much can I give to one person without triggering a gift tax return in 2021?
The annual gift exclusion for 2021 is $15,000 (unchanged from 2020). This amount is only adjusted in $1,000 increments, so it typically only increases every few years.
Your tax situation
These are only some of the tax amounts that may apply to you. Contact us for more information about your tax situation, or if you have questions
© 2021
Many tax amounts affecting businesses have increased for 2021

A number of tax-related limits that affect businesses are annually indexed for inflation, and many have increased for 2021. Some stayed the same due to low inflation. And the deduction for business meals has doubled for this year after a new law was enacted at the end of 2020. Here’s a rundown of those that may be important to you and your business.
Social Security tax
The amount of employees’ earnings that are subject to Social Security tax is capped for 2021 at $142,800 (up from $137,700 for 2020).
Deductions
- Section 179 expensing:
- Limit: $1.05 million (up from $1.04 million for 2020)
- Phaseout: $2.62 million (up from $2.59 million)
- Income-based phase-out for certain limits on the Sec. 199A qualified business income deduction begins at:
- Married filing jointly: $329,800 (up from $326,600)
- Married filing separately: $164,925 (up from $163,300)
- Other filers: $164,900 (up from $163,300)
Business meals
Deduction for eligible business-related food and beverage expenses provided by a restaurant: 100% (up from 50%)
Retirement plans
- Employee contributions to 401(k) plans: $19,500 (unchanged from 2020)
- Catch-up contributions to 401(k) plans: $6,500 (unchanged)
- Employee contributions to SIMPLEs: $13,500 (unchanged)
- Catch-up contributions to SIMPLEs: $3,000 (unchanged)
- Combined employer/employee contributions to defined contribution plans: $58,000 (up from $57,000)
- Maximum compensation used to determine contributions: $290,000 (up from $285,000)
- Annual benefit for defined benefit plans: $230,000 (up from $225,000)
- Compensation defining a highly compensated employee: $130,000 (unchanged)
- Compensation defining a “key” employee: $185,000 (unchanged)
Other employee benefits
- Qualified transportation fringe-benefits employee income exclusion: $270 per month (unchanged)
- Health Savings Account contributions:
- Individual coverage: $3,600 (up from $3,550)
- Family coverage: $7,200 (up from $7,100)
- Catch-up contribution: $1,000 (unchanged)
- Flexible Spending Account contributions:
- Health care: $2,750 (unchanged)
- Dependent care: $5,000 (unchanged)
These are only some of the tax limits that may affect your business and additional rules may apply. If you have questions, please contact us.
© 2021
The power of the tax credit for buying an electric vehicle

Although electric vehicles (or EVs) are a small percentage of the cars on the road today, they’re increasing in popularity all the time. And if you buy one, you may be eligible for a federal tax break.
The tax code provides a credit to purchasers of qualifying plug-in electric drive motor vehicles including passenger vehicles and light trucks. The credit is equal to $2,500 plus an additional amount, based on battery capacity, that can’t exceed $5,000. Therefore, the maximum credit allowed for a qualifying EV is $7,500.
The EV definition
For purposes of the tax credit, a qualifying vehicle is defined as one with four wheels that’s propelled to a significant extent by an electric motor, which draws electricity from a battery. The battery must have a capacity of not less than four kilowatt hours and be capable of being recharged from an external source of electricity.
The credit may not be available because of a per-manufacturer cumulative sales limitation. Specifically, it phases out over six quarters beginning when a manufacturer has sold at least 200,000 qualifying vehicles for use in the United States (determined on a cumulative basis for sales after December 31, 2009). For example, Tesla and General Motors vehicles are no longer eligible for the tax credit.
The IRS provides a list of qualifying vehicles on its website and it recently added a number of models that are eligible. You can access the list here: https://bit.ly/2Yrhg5Z.
Here are some additional points about the plug-in electric vehicle tax credit:
- It’s allowed in the year you place the vehicle in service.
- The vehicle must be new.
- An eligible vehicle must be used predominantly in the U.S. and have a gross weight of less than 14,000 pounds.
Electric motorcycles
There’s a separate 10% federal income tax credit for the purchase of qualifying electric two-wheeled vehicles manufactured primarily for use on public thoroughfares and capable of at least 45 miles per hour (in other words, electric-powered motorcycles). It can be worth up to $2,500. This electric motorcycle credit was recently extended to cover qualifying 2021 purchases.
These are only the basic rules. There may be additional incentives provided by your state. Contact us if you’d like to receive more information about the federal plug-in electric vehicle tax break.
© 2021
The cents-per-mile rate for business miles decreases again for 2021

This year, the optional standard mileage rate used to calculate the deductible costs of operating an automobile for business decreased by one-and-one-half cents, to 56 cents per mile. As a result, you might claim a lower deduction for vehicle-related expenses for 2021 than you could for 2020 or 2019. This is the second year in a row that the cents-per-mile rate has decreased.
Deducting actual expenses vs. cents-per-mile
In general, businesses can deduct the actual expenses attributable to business use of vehicles. This includes gas, oil, tires, insurance, repairs, licenses and vehicle registration fees. In addition, you can claim a depreciation allowance for the vehicle. However, in many cases, certain limits apply to depreciation write-offs on vehicles that don’t apply to other types of business assets.
The cents-per-mile rate is useful if you don’t want to keep track of actual vehicle-related expenses. With this method, you don’t have to account for all your actual expenses. However, you still must record certain information, such as the mileage for each business trip, the date and the destination.
Using the cents-per-mile rate is also popular with businesses that reimburse employees for business use of their personal vehicles. These reimbursements can help attract and retain employees who drive their personal vehicles extensively for business purposes. Why? Under current law, employees can no longer deduct unreimbursed employee business expenses, such as business mileage, on their own income tax returns.
If you do use the cents-per-mile rate, be aware that you must comply with various rules. If you don’t comply, the reimbursements could be considered taxable wages to the employees.
The 2021 rate
Beginning on January 1, 2021, the standard mileage rate for the business use of a car (van, pickup or panel truck) is 56 cents per mile. It was 57.5 cents for 2020 and 58 cents for 2019.
The business cents-per-mile rate is adjusted annually. It’s based on an annual study commissioned by the IRS about the fixed and variable costs of operating a vehicle, such as gas, maintenance, repair and depreciation. The rate partly reflects the current price of gas, which is down from a year ago. According to AAA Gas Prices, the average nationwide price of a gallon of unleaded regular gas was $2.42 recently, compared with $2.49 a year ago. Occasionally, if there’s a substantial change in average gas prices, the IRS will change the cents-per-mile rate midyear.
When this method can’t be used
There are some situations when you can’t use the cents-per-mile rate. In some cases, it partly depends on how you’ve claimed deductions for the same vehicle in the past. In other cases, it depends on if the vehicle is new to your business this year or whether you want to take advantage of certain first-year depreciation tax breaks on it.
As you can see, there are many factors to consider in deciding whether to use the mileage rate to deduct vehicle expenses. We can help if you have questions about tracking and claiming such expenses in 2021 — or claiming them on your 2020 income tax return.
© 2021
Don’t forget to take required minimum distributions this year

If you have a traditional IRA or tax-deferred retirement plan account, you probably know that you must take required minimum distributions (RMDs) when you reach a certain age — or you’ll be penalized. The CARES Act, which passed last March, allowed people to skip taking these withdrawals in 2020 but now that we’re in 2021, RMDs must be taken again.
The basics
Once you attain age 72 (or age 70½ before 2020), you must begin taking RMDs from your traditional IRAs and certain retirement accounts, including 401(k) plans. In general, RMDs are calculated using life expectancy tables published by the IRS. If you don’t withdraw the minimum amount each year, you may have to pay a 50% penalty tax on what you should have taken out — but didn’t. (Roth IRAs don’t require withdrawals until after the death of the owner.)
You can always take out more than the required amount. In planning for distributions, your income needs must be weighed against the desirable goal of keeping the tax shelter of the IRA going for as long as possible for both yourself and your beneficiaries.
In order to provide tax relief due to COVID-19, the CARES Act suspended RMDs for calendar year 2020 — but only for that one year. That meant that taxpayers could put off RMDs, not have to pay tax on them and allow their retirement accounts to keep growing tax deferred.
Begin taking RMDs again
Many people hoped that the RMD suspension would be extended into 2021. However, the Consolidated Appropriations Act, which was enacted on December 27, 2020, to provide more COVID-19 relief, didn’t extend the RMD relief. That means if you’re required to take RMDs, you need to take them this year or face a penalty.
Note: The IRS may waive part or all of the penalty if you can prove that you didn’t take RMDs due to reasonable error and you’re taking steps to remedy the shortfall. In these cases, the IRS reviews the information a taxpayer provides and decides whether to grant a request for a waiver.
Keep more of your money
Feel free to contact us if have questions about calculating RMDs or avoiding the penalty for not taking them. We can help make sure you keep more of your money.
© 2021
The new Form 1099-NEC and the revised 1099-MISC are due to recipients soon

There’s a new IRS form for business taxpayers that pay or receive certain types of nonemployee compensation and it must be furnished to most recipients by February 1, 2021. After sending the forms to recipients, taxpayers must file the forms with the IRS by March 1 (March 31 if filing electronically).
The requirement begins with forms for tax year 2020. Payers must complete Form 1099-NEC, “Nonemployee Compensation,” to report any payment of $600 or more to a recipient. February 1 is also the deadline for furnishing Form 1099-MISC, “Miscellaneous Income,” to report certain other payments to recipients.
If your business is using Form 1099-MISC to report amounts in box 8, “substitute payments in lieu of dividends or interest,” or box 10, “gross proceeds paid to an attorney,” there’s an exception to the regular due date. Those forms are due to recipients by February 16, 2021.
1099-MISC changes
Before the 2020 tax year, Form 1099-MISC was filed to report payments totaling at least $600 in a calendar year for services performed in a trade or business by someone who isn’t treated as an employee (in other words, an independent contractor). These payments are referred to as nonemployee compensation (NEC) and the payment amount was reported in box 7.
Form 1099-NEC was introduced to alleviate the confusion caused by separate deadlines for Form 1099-MISC that reported NEC in box 7 and all other Form 1099-MISC for paper filers and electronic filers.
Payers of nonemployee compensation now use Form 1099-NEC to report those payments.
Generally, payers must file Form 1099-NEC by January 31. But for 2020 tax returns, the due date is February 1, 2021, because January 31, 2021, is on a Sunday. There’s no automatic 30-day extension to file Form 1099-NEC. However, an extension to file may be available under certain hardship conditions.
When to file 1099-NEC
If the following four conditions are met, you must generally report payments as nonemployee compensation:
- You made a payment to someone who isn’t your employee,
- You made a payment for services in the course of your trade or business,
- You made a payment to an individual, partnership, estate, or, in some cases, a corporation, and
- You made payments to a recipient of at least $600 during the year.
We can help
If you have questions about filing Form 1099-NEC, Form 1099-MISC or any tax forms, contact us. We can assist you in staying in compliance with all rules.
© 2021
PPP loans have reopened: Let’s review the tax consequences

The Small Business Administration (SBA) announced that the Paycheck Protection Program (PPP) reopened the week of January 11. If you’re fortunate to get a PPP loan to help during the COVID-19 crisis (or you received one last year), you may wonder about the tax consequences.
Background on the loans
In March of 2020, the CARES Act became law. It authorized the SBA to make loans to qualified businesses under certain circumstances. The law established the PPP, which provided up to 24 weeks of cash-flow assistance through 100% federally guaranteed loans to eligible recipients. Taxpayers could apply to have the loans forgiven to the extent their proceeds were used to maintain payroll during the COVID-19 pandemic and to cover certain other expenses.
At the end of 2020, the Consolidated Appropriations Act (CAA) was enacted to provide additional relief related to COVID-19. This law includes funding for more PPP loans, including a “second draw” for businesses that received a loan last year. It also allows businesses to claim a tax deduction for the ordinary and necessary expenses paid from the proceeds of PPP loans.
Second draw loans
The CAA permits certain smaller businesses who received a PPP loan and experienced a 25% reduction in gross receipts to take a PPP second draw loan of up to $2 million.
To qualify for a second draw loan, a taxpayer must have taken out an original PPP Loan. In addition, prior PPP borrowers must now meet the following conditions to be eligible:
- Employ no more than 300 employees per location,
- Have used or will use the full amount of their first PPP loan, and
- Demonstrate at least a 25% reduction in gross receipts in the first, second or third quarter of 2020 relative to the same 2019 quarter. Applications submitted on or after Jan. 1, 2021, are eligible to utilize the gross receipts from the fourth quarter of 2020.
To be eligible for full PPP loan forgiveness, a business must generally spend at least 60% of the loan proceeds on qualifying payroll costs (including certain health care plan costs) and the remaining 40% on other qualifying expenses. These include mortgage interest, rent, utilities, eligible operations expenditures, supplier costs, worker personal protective equipment and other eligible expenses to help comply with COVID-19 health and safety guidelines or equivalent state and local guidelines.
Eligible entities include for-profit businesses, certain non-profit organizations, housing cooperatives, veterans’ organizations, tribal businesses, self-employed individuals, sole proprietors, independent contractors and small agricultural co-operatives.
Deductibility of expenses paid by PPP loans
The CARES Act didn’t address whether expenses paid with the proceeds of PPP loans could be deducted on tax returns. Last year, the IRS took the position that these expenses weren’t deductible. However, the CAA provides that expenses paid from the proceeds of PPP loans are deductible.
Cancellation of debt income
Generally, when a lender reduces or cancels debt, it results in cancellation of debt (COD) income to the debtor. However, the forgiveness of PPP debt is excluded from gross income. Your tax attributes (net operating losses, credits, capital and passive activity loss carryovers, and basis) wouldn’t generally be reduced on account of this exclusion.
Assistance provided
This only covers the basics of applying for PPP loans, as well as the tax implications. Contact us if you have questions or if you need assistance in the PPP loan application or forgiveness process.
© 2021
One reason to file your 2020 tax return early

The IRS announced it is opening the 2020 individual income tax return filing season on February 12. (This is later than in past years because of a new law that was enacted late in December.) Even if you typically don’t file until much closer to the April 15 deadline (or you file for an extension), consider filing earlier this year. Why? You can potentially protect yourself from tax identity theft — and there may be other benefits, too.
How is a person’s tax identity stolen?
In a tax identity theft scheme, a thief uses another individual’s personal information to file a fraudulent tax return early in the filing season and claim a bogus refund.
The real taxpayer discovers the fraud when he or she files a return and is told by the IRS that the return is being rejected because one with the same Social Security number has already been filed for the tax year. While the taxpayer should ultimately be able to prove that his or her return is the legitimate one, tax identity theft can be a hassle to straighten out and significantly delay a refund.
Filing early may be your best defense: If you file first, it will be the tax return filed by a potential thief that will be rejected — not yours.
Note: You can get your individual tax return prepared by us before February 12 if you have all the required documents. It’s just that processing of the return will begin after IRS systems open on that date.
When will you receive your W-2s and 1099s?
To file your tax return, you need all of your W-2s and 1099s. January 31 is the deadline for employers to issue 2020 Form W-2 to employees and, generally, for businesses to issue Form 1099s to recipients of any 2020 interest, dividend or reportable miscellaneous income payments (including those made to independent contractors).
If you haven’t received a W-2 or 1099 by February 1, first contact the entity that should have issued it. If that doesn’t work, you can contact the IRS for help.
How else can you benefit by filing early?
In addition to protecting yourself from tax identity theft, another benefit of early filing is that, if you’re getting a refund, you’ll get it faster. The IRS expects most refunds to be issued within 21 days. The time is typically shorter if you file electronically and receive a refund by direct deposit into a bank account.
Direct deposit also avoids the possibility that a refund check could be lost, stolen, returned to the IRS as undeliverable or caught in mail delays.
If you haven’t received an Economic Impact Payment (EIP), or you didn’t receive the full amount due, filing early will help you to receive the amount sooner. EIPs have been paid by the federal government to eligible individuals to help mitigate the financial effects of COVID-19. Amounts due that weren’t sent to eligible taxpayers can be claimed on your 2020 return.
Do you need help?
If you have questions or would like an appointment to prepare your return, please contact us. We can help you ensure you file an accurate return that takes advantage of all of the breaks available to you.
© 2021
Educate yourself about the revised tax benefits for higher education

Attending college is one of the biggest investments that parents and students ever make. If you or your child (or grandchild) attends (or plans to attend) an institution of higher learning, you may be eligible for tax breaks to help foot the bill.
The Consolidated Appropriations Act, which was enacted recently, made some changes to the tax breaks. Here’s a rundown of what has changed.
Deductions vs. credits
Before the new law, there were tax breaks available for qualified education expenses including the Tuition and Fees Deduction, the Lifetime Learning Credit and the American Opportunity Tax Credit.
Tax credits are generally better than tax deductions. The difference? A tax deduction reduces your taxable income while a tax credit reduces the amount of taxes you owe on a dollar-for-dollar basis.
First, let’s look at the deduction
For 2020, the Tuition and Fees Deduction could be up to $4,000 at lower income levels or up to $2,000 at middle income levels. If your 2020 modified adjusted gross income (MAGI) allows you to be eligible, you can claim the deduction whether you itemize or not. Here are the income thresholds:
- For 2020, a taxpayer with a MAGI of up to $65,000 ($130,000 for married filing jointly) could deduct qualified expenses up to $4,000.
- For 2020, a taxpayer with a MAGI between $65,001 and $80,000 ($130,001 and $160,000 for married filing jointly) could deduct up to $2,000.
- For 2020, the allowable 2020 deduction was phased out and was zero if your MAGI was more than $80,000 ($160,000 for married filing jointly).
As you’ll see below, the Tuition and Fees Deduction is not available after the 2020 tax year.
Two credits aligned
Before the new law, an unfavorable income phase-out rule applied to the Lifetime Learning Credit, which can be worth up to $2,000 per tax return annually. For 2021 and beyond, the new law aligns the phase-out rule for the Lifetime Learning Credit with the more favorable phase-out rule for the American Opportunity Tax Credit, which can be worth up to $2,500 per student each year. The CAA also repeals the Tuition and Fees Deduction for 2021 and later years. Basically, the law trades the old-law write-off for the more favorable new-law Lifetime Learning Credit phase-out rule.
Under the CAA, both the Lifetime Learning Credit and the American Opportunity Tax Credit are phased out for 2021 and beyond between a MAGI of $80,001 and $90,000 for unmarried individuals ($160,001 and $180,000 for married couples filing jointly). Before the new law, the Lifetime Learning Credit was phased out for 2020 between a MAGI of $59,001 and $69,000 for unmarried individuals ($118,001 and $138,000 married couples filing jointly).
Best for you
Talk with us about which of the two remaining education tax credits is the most beneficial in your situation. Each of them has its own requirements. There are also other education tax opportunities you may be able to take advantage of, including a Section 529 tuition plan and a Coverdell Education Savings Account.
© 2021
Can your business benefit from the enhanced Employee Retention Tax Credit?

COVID-19 has shut down many businesses, causing widespread furloughs and layoffs. Fortunately, employers that keep workers on their payrolls are eligible for a refundable Employee Retention Tax Credit (ERTC), which was extended and enhanced in the latest law.
Background on the credit
The CARES Act, enacted in March of 2020, created the ERTC. The credit:
- Equaled 50% of qualified employee wages paid by an eligible employer in an applicable 2020 calendar quarter,
- Was subject to an overall wage cap of $10,000 per eligible employee, and
- Was available to eligible large and small employers.
The Consolidated Appropriations Act, enacted December 27, 2020, extends and greatly enhances the ERTC. Under the CARES Act rules, the credit only covered wages paid between March 13, 2020, and December 31, 2020. The new law now extends the covered wage period to include the first two calendar quarters of 2021, ending on June 30, 2021.
In addition, for the first two quarters of 2021 ending on June 30, the new law increases the overall covered wage ceiling to 70% of qualified wages paid during the applicable quarter (versus 50% under the CARES Act). And it increases the per-employee covered wage ceiling to $10,000 of qualified wages paid during the applicable quarter (versus a $10,000 annual ceiling under the original rules).
Interaction with the PPP
In a change retroactive to March 12, 2020, the new law also stipulates that the employee retention credit can be claimed for qualified wages paid with proceeds from Paycheck Protection Program (PPP) loans that aren’t forgiven.
What’s more, the new law liberalizes an eligibility rule. Specifically, it expands eligibility for the credit by reducing the required year-over-year gross receipts decline from 50% to 20% and provides a safe harbor allowing employers to use prior quarter gross receipts to determine eligibility.
We can help
These are just some of the changes made to the ERTC, which rewards employers that can afford to keep workers on the payroll during the COVID-19 crisis. Contact us for more information about this tax saving opportunity.
© 2020
The COVID-19 relief law: What’s in it for you?

The new COVID-19 relief law that was signed on December 27, 2020, contains a multitude of provisions that may affect you. Here are some of the highlights of the Consolidated Appropriations Act, which also contains two other laws: the COVID-related Tax Relief Act (COVIDTRA) and the Taxpayer Certainty and Disaster Tax Relief Act (TCDTR).
Direct payments
The law provides for direct payments (which it calls recovery rebates) of $600 per eligible individual ($1,200 for a married couple filing a joint tax return), plus $600 per qualifying child. The U.S. Treasury Department has already started making these payments via direct bank deposits or checks in the mail and will continue to do so in the coming weeks.
The credit payment amount is phased out at a rate of $5 per $100 of additional income starting at $150,000 of modified adjusted gross income for marrieds filing jointly and surviving spouses, $112,500 for heads of household, and $75,000 for single taxpayers.
Medical expense tax deduction
The law makes permanent the 7.5%-of-adjusted-gross-income threshold on medical expense deductions, which was scheduled to increase to 10% of adjusted gross income in 2021. The lower threshold will make it easier to qualify for the medical expense deduction.
Charitable deduction for non-itemizers
For 2020, individuals who don’t itemize their deductions can take up to a $300 deduction per tax return for cash contributions to qualified charitable organizations. The new law extends this $300 deduction through 2021 for individuals and increases it to $600 for married couples filing jointly. Taxpayers who overstate their contributions when claiming this deduction are subject to a 50% penalty (previously it was 20%).
Allowance of charitable contributions
In response to the pandemic, the limit on cash charitable contributions by an individual in 2020 was increased to 100% of the individual’s adjusted gross income (AGI). (The usual limit is 60% of adjusted gross income.) The new law extends this rule through 2021.
Energy tax credit
A credit of up to $500 is available for purchases of qualifying energy improvements made to a taxpayer’s main home. However, the $500 maximum allowance must be reduced by any credits claimed in earlier years. The law extends this credit, which was due to expire at the end of 2020, through 2021.
Other energy-efficient provisions
There are a few other energy-related provisions in the new law. For example, the tax credit for a qualified fuel cell motor vehicle and the two-wheeled plug-in electric vehicle were scheduled to expire in 2020 but have been extended through the end of 2021.
There’s also a valuable tax credit for qualifying solar energy equipment expenditures for your home. For equipment placed in service in 2020, the credit rate is 26%. The rate was scheduled to drop to 22% for equipment placed in service in 2021 before being eliminated for 2022 and beyond.
Under the new law, the 26% credit rate is extended to cover equipment placed in service in 2021 and 2022 and the law also extends the 22% rate to cover equipment placed in service in 2023. For 2024 and beyond, the credit is scheduled to vanish.
Maximize tax breaks
These are only a few tax breaks contained in the massive new law. We’ll make sure that you claim all the tax breaks you’re entitled to when we prepare your tax return.
© 2021
New law doubles business meal deductions and makes favorable PPP loan changes

The COVID-19 relief bill, signed into law on December 27, 2020, provides a further response from the federal government to the pandemic. It also contains numerous tax breaks for businesses. Here are some highlights of the Consolidated Appropriations Act of 2021 (CAA), which also includes other laws within it.
Business meal deduction increased
The new law includes a provision that removes the 50% limit on deducting business meals provided by restaurants and makes those meals fully deductible.
As background, ordinary and necessary food and beverage expenses that are incurred while operating your business are generally deductible. However, for 2020 and earlier years, the deduction is limited to 50% of the allowable expenses.
The new legislation adds an exception to the 50% limit for expenses of food or beverages provided by a restaurant. This rule applies to expenses paid or incurred in calendar years 2021 and 2022.
The use of the word “by” (rather than “in”) a restaurant clarifies that the new tax break isn’t limited to meals eaten on a restaurant’s premises. Takeout and delivery meals from a restaurant are also 100% deductible.
Note: Other than lifting the 50% limit for restaurant meals, the legislation doesn’t change the rules for business meal deductions. All the other existing requirements continue to apply when you dine with current or prospective customers, clients, suppliers, employees, partners and professional advisors with whom you deal with (or could engage with) in your business.
Therefore, to be deductible:
- The food and beverages can’t be lavish or extravagant under the circumstances, and
- You or one of your employees must be present when the food or beverages are served.
If food or beverages are provided at an entertainment activity (such as a sporting event or theater performance), either they must be purchased separately from the entertainment or their cost must be stated on a separate bill, invoice or receipt. This is required because the entertainment, unlike the food and beverages, is nondeductible.
PPP loans
The new law authorizes more money towards the Paycheck Protection Program (PPP) and extends it to March 31, 2021. There are a couple of tax implications for employers that received PPP loans:
- Clarifications of tax consequences of PPP loan forgiveness. The law clarifies that the non-taxable treatment of PPP loan forgiveness that was provided by the 2020 CARES Act also applies to certain other forgiven obligations. Also, the law makes clear that taxpayers, whose PPP loans or other obligations are forgiven, are allowed deductions for otherwise deductible expenses paid with the proceeds. In addition, the tax basis and other attributes of the borrower’s assets won’t be reduced as a result of the forgiveness.
- Waiver of information reporting for PPP loan forgiveness. Under the CAA, the IRS is allowed to waive information reporting requirements for any amount excluded from income under the exclusion-from-income rule for forgiveness of PPP loans or other specified obligations. (The IRS had already waived information returns and payee statements for loans that were guaranteed by the Small Business Administration).
Much more
These are just a couple of the provisions in the new law that are favorable to businesses. The CAA also provides extensions and modifications to earlier payroll tax relief, allows changes to employee benefit plans, includes disaster relief and much more. Contact us if you have questions about your situation.
© 2021
The right entity choice: Should you convert from a C to an S corporation?

The best choice of entity can affect your business in several ways, including the amount of your tax bill. In some cases, businesses decide to switch from one entity type to another. Although S corporations can provide substantial tax benefits over C corporations in some circumstances, there are potentially costly tax issues that you should assess before making the decision to convert from a C corporation to an S corporation.
Here are four issues to consider:
- LIFO inventories. C corporations that use last-in, first-out (LIFO) inventories must pay tax on the benefits they derived by using LIFO if they convert to S corporations. The tax can be spread over four years. This cost must be weighed against the potential tax gains from converting to S status.
- Built-in gains tax. Although S corporations generally aren’t subject to tax, those that were formerly C corporations are taxed on built-in gains (such as appreciated property) that the C corporation has when the S election becomes effective, if those gains are recognized within five years after the conversion. This is generally unfavorable, although there are situations where the S election still can produce a better tax result despite the built-in gains tax.
- Passive income. S corporations that were formerly C corporations are subject to a special tax. It kicks in if their passive investment income (including dividends, interest, rents, royalties, and stock sale gains) exceeds 25% of their gross receipts, and the S corporation has accumulated earnings and profits carried over from its C corporation years. If that tax is owed for three consecutive years, the corporation’s election to be an S corporation terminates. You can avoid the tax by distributing the accumulated earnings and profits, which would be taxable to shareholders. Or you might want to avoid the tax by limiting the amount of passive income.
- Unused losses. If your C corporation has unused net operating losses, they can’t be used to offset its income as an S corporation and can’t be passed through to shareholders. If the losses can’t be carried back to an earlier C corporation year, it will be necessary to weigh the cost of giving up the losses against the tax savings expected to be generated by the switch to S status.
Other considerations
When a business switches from C to S status, these are only some of the factors to consider. For example, shareholder-employees of S corporations can’t get all of the tax-free fringe benefits that are available with a C corporation. And there may be issues for shareholders who have outstanding loans from their qualified plans. These factors have to be taken into account in order to understand the implications of converting from C to S status.
If you’re interested in an entity conversion, contact us. We can explain what your options are, how they’ll affect your tax bill and some possible strategies you can use to minimize taxes.
© 2020
Can you qualify for a medical expense tax deduction?

You may be able to deduct some of your medical expenses, including prescription drugs, on your federal tax return. However, the rules make it hard for many people to qualify. But with proper planning, you may be able to time discretionary medical expenses to your advantage for tax purposes.
Itemizers must meet a threshold
For 2020, the medical expense deduction can only be claimed to the extent your unreimbursed costs exceed 7.5% of your adjusted gross income (AGI). This threshold amount is scheduled to increase to 10% of AGI for 2021. You also must itemize deductions on your return in order to claim a deduction.
If your total itemized deductions for 2020 will exceed your standard deduction, moving or “bunching” nonurgent medical procedures and other controllable expenses into 2020 may allow you to exceed the 7.5% floor and benefit from the medical expense deduction. Controllable expenses include refilling prescription drugs, buying eyeglasses and contact lenses, going to the dentist and getting elective surgery.
In addition to hospital and doctor expenses, here are some items to take into account when determining your allowable costs:
- Health insurance premiums. This item can total thousands of dollars a year. Even if your employer provides health coverage, you can deduct the portion of the premiums that you pay. Long-term care insurance premiums are also included as medical expenses, subject to limits based on age.
- Transportation. The cost of getting to and from medical treatments counts as a medical expense. This includes taxi fares, public transportation, or using your own car. Car costs can be calculated at 17¢ a mile for miles driven in 2020, plus tolls and parking. Alternatively, you can deduct certain actual costs, such as for gas and oil.
- Eyeglasses, hearing aids, dental work, prescription drugs and more. Deductible expenses include the cost of glasses, hearing aids, dental work, psychiatric counseling and other ongoing expenses in connection with medical needs. Purely cosmetic expenses don’t qualify. Prescription drugs (including insulin) qualify, but over-the-counter aspirin and vitamins don’t. Neither do amounts paid for treatments that are illegal under federal law (such as medical marijuana), even if state law permits them. The services of therapists and nurses can qualify as long as they relate to a medical condition and aren’t for general health. Amounts paid for certain long-term care services required by a chronically ill individual also qualify.
- Smoking-cessation and weight-loss programs. Amounts paid for participating in smoking-cessation programs and for prescribed drugs designed to alleviate nicotine withdrawal are deductible. However, nonprescription nicotine gum and patches aren’t. A weight-loss program is deductible if undertaken as treatment for a disease diagnosed by a physician. Deductible expenses include fees paid to join a program and attend periodic meetings. However, the cost of food isn’t deductible.
Costs for dependents
You can deduct the medical costs that you pay for dependents, such as your children. Additionally, you may be able to deduct medical costs you pay for other individuals, such as an elderly parent. Contact us if you have questions about medical expense deductions.
© 2020
Drive more savings to your business with the heavy SUV tax break

|
Maximize your 401(k) plan to save for retirement

Contributing to a tax-advantaged retirement plan can help you reduce taxes and save for retirement. If your employer offers a 401(k) or Roth 401(k) plan, contributing to it is a smart way to build a substantial sum of money.
If you’re not already contributing the maximum allowed, consider increasing your contribution rate. Because of tax-deferred compounding (tax-free in the case of Roth accounts), boosting contributions can have a major impact on the size of your nest egg at retirement.
With a 401(k), an employee makes an election to have a certain amount of pay deferred and contributed by an employer on his or her behalf to the plan. The contribution limit for 2020 is $19,500. Employees age 50 or older by year end are also permitted to make additional “catch-up” contributions of $6,500, for a total limit of $26,000 in 2020.
The IRS recently announced that the 401(k) contribution limits for 2021 will remain the same as for 2020.
If you contribute to a traditional 401(k)
A traditional 401(k) offers many benefits, including:
- Contributions are pretax, reducing your modified adjusted gross income (MAGI), which can also help you reduce or avoid exposure to the 3.8% net investment income tax.
- Plan assets can grow tax-deferred — meaning you pay no income tax until you take distributions.
- Your employer may match some or all of your contributions pretax.
If you already have a 401(k) plan, take a look at your contributions. Try to increase your contribution rate to get as close to the $19,500 limit (with an extra $6,500 if you’re age 50 or older) as you can afford. Keep in mind that your paycheck will be reduced by less than the dollar amount of the contribution, because the contributions are pretax — so, income tax isn’t withheld.
If you contribute to a Roth 401(k)
Employers may also include a Roth option in their 401(k) plans. If your employer offers this, you can designate some or all of your contributions as Roth contributions. While such contributions don’t reduce your current MAGI, qualified distributions will be tax-free.
Roth 401(k) contributions may be especially beneficial for higher-income earners, because they don’t have the option to contribute to a Roth IRA. Your ability to make a Roth IRA contribution for 2021 will be reduced if your adjusted gross income (AGI) in 2021 exceeds:
- $198,000 (up from $196,000 for 2020) for married joint-filing couples, or
- $125,000 (up from $124,000 for 2020) for single taxpayers.
Your ability to contribute to a Roth IRA in 2021 will be eliminated entirely if you’re a married joint filer and your 2021 AGI equals or exceeds $208,000 (up from $206,000 for 2020). The 2021 cutoff for single filers is $140,000 or more (up from $139,000 for 2020).
The best mix
Contact us if you have questions about how much to contribute or the best mix between traditional and Roth 401(k) contributions. We can discuss the tax and retirement-saving strategies in your situation.
© 2020
The QBI deduction basics and a year-end tax tip that might help you qualify

|
Small businesses: Cash in on depreciation tax savers

As we approach the end of the year, it’s a good time to think about whether your business needs to buy business equipment and other depreciable property. If so, you may benefit from the Section 179 depreciation tax deduction for business property. The election provides a tax windfall to businesses, enabling them to claim immediate deductions for qualified assets, instead of taking depreciation deductions over time.
Even better, the Sec. 179 deduction isn’t the only avenue for immediate tax write-offs for qualified assets. Under the 100% bonus depreciation tax break, the entire cost of eligible assets placed in service in 2020 can be written off this year.
But to benefit for this tax year, you need to buy and place qualifying assets in service by December 31.
What qualifies?
The Sec. 179 deduction applies to tangible personal property such as machinery and equipment purchased for use in a trade or business, and, if the taxpayer elects, qualified real property. It’s generally available on a tax year basis and is subject to a dollar limit.
The annual deduction limit is $1.04 million for tax years beginning in 2020, subject to a phaseout rule. Under the rule, the deduction is phased out (reduced) if more than a specified amount of qualifying property is placed in service during the tax year. The amount is $2.59 million for tax years beginning in 2020. (Note: Different rules apply to heavy SUVs.)
There’s also a taxable income limit. If your taxable business income is less than the dollar limit for that year, the amount for which you can make the election is limited to that taxable income. However, any amount you can’t immediately deduct is carried forward and can be deducted in later years (to the extent permitted by the applicable dollar limit, the phaseout rule, and the taxable income limit).
In addition to significantly increasing the Sec. 179 deduction, the TCJA also expanded the definition of qualifying assets to include depreciable tangible personal property used mainly in the furnishing of lodging, such as furniture and appliances.
The TCJA also expanded the definition of qualified real property to include qualified improvement property and some improvements to nonresidential real property, such as roofs; heating, ventilation and air-conditioning equipment; fire protection and alarm systems; and security systems.
What about bonus depreciation?
With bonus depreciation, businesses are allowed to deduct 100% of the cost of certain assets in the first year, rather than capitalize them on their balance sheets and gradually depreciate them. (Before the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act, you could deduct only 50% of the cost of qualified new property.)
This tax break applies to qualifying assets placed in service between September 28, 2017, and December 31, 2022 (by December 31, 2023, for certain assets with longer production periods and for aircraft). After that, the bonus depreciation percentage is reduced by 20% per year, until it’s fully phased out after 2026 (or after 2027 for certain assets described above).
Bonus depreciation is allowed for both new and used qualifying assets, which include most categories of tangible depreciable assets other than real estate.
Important: When both 100% first-year bonus depreciation and the Sec. 179 deduction are available for the same asset, it’s generally more advantageous to claim 100% bonus depreciation, because there are no limitations on it.
Need assistance?
These favorable depreciation deductions may deliver tax-saving benefits to your business on your 2020 return. Contact us if you have questions, or you want more information about how your business can maximize the deductions.
© 2020
Steer clear of the wash sale rule if you’re selling stock by year end

Are you thinking about selling stock shares at a loss to offset gains that you’ve realized during 2020? If so, it’s important not to run afoul of the “wash sale” rule.
IRS may disallow the loss
Under this rule, if you sell stock or securities for a loss and buy substantially identical stock or securities back within the 30-day period before or after the sale date, the loss can’t be claimed for tax purposes. The rule is designed to prevent taxpayers from using the tax benefit of a loss without parting with ownership in any significant way. Note that the rule applies to a 30-day period before or after the sale date to prevent “buying the stock back” before it’s even sold. (If you participate in any dividend reinvestment plans, it’s possible the wash sale rule may be inadvertently triggered when dividends are reinvested under the plan, if you’ve separately sold some of the same stock at a loss within the 30-day period.)
The rule even applies if you repurchase the security in a tax-advantaged retirement account, such as a traditional or Roth IRA.
Although the loss can’t be claimed on a wash sale, the disallowed amount is added to the cost of the new stock. So, the disallowed amount can be claimed when the new stock is finally disposed of in the future (other than in a wash sale).
An example to illustrate
Let’s say you bought 500 shares of ABC Inc. for $10,000 and sold them on November 5 for $3,000. On November 30, you buy 500 shares of ABC again for $3,200. Since the shares were “bought back” within 30 days of the sale, the wash sale rule applies. Therefore, you can’t claim a $7,000 loss. Your basis in the new 500 shares is $10,200: the actual cost plus the $7,000 disallowed loss.
If only a portion of the stock sold is bought back, only that portion of the loss is disallowed. So, in the above example, if you’d only bought back 300 of the 500 shares (60%), you’d be able to claim 40% of the loss on the sale ($2,800). The remaining $4,200 loss that’s disallowed under the wash sale rule would be added to your cost of the 300 shares.
If you’ve cashed in some big gains in 2020, you may be looking for unrealized losses in your portfolio so you can sell those investments before year end. By doing so, you can offset your gains with your losses and reduce your 2020 tax liability. But be careful of the wash sale rule. We can answer any questions you may have.
© 2020
Employees: Don’t forget about your FSA funds

Many employees take advantage of the opportunity to save taxes by placing funds in their employer’s health or dependent care flexible spending arrangements (FSAs). As the end of 2020 nears, here are some rules and reminders to keep in mind.
Health FSAs
A pre-tax contribution of $2,750 to a health FSA is permitted in both 2020 and 2021. You save taxes because you use pre-tax dollars to pay for medical expenses that might not be deductible. For example, they wouldn’t be deductible if you don’t itemize deductions on your tax return. Even if you do itemize, medical expenses must exceed a certain percentage of your adjusted gross income in order to be deductible. Additionally, the amounts that you contribute to a health FSA aren’t subject to FICA taxes.
Your plan should have a listing of qualifying items and any documentation from a medical provider that may be needed to get a reimbursement for these items.
To avoid any forfeiture of your health FSA funds because of the “use-it-or-lose-it” rule, you must incur qualifying medical expenditures by the last day of the plan year (Dec. 31 for a calendar year plan), unless the plan allows an optional grace period. A grace period can’t extend beyond the 15th day of the third month following the close of the plan year (March 15 for a calendar year plan).
An additional exception to the use-it-or lose-it rule permits health FSAs to allow a carryover of a participant’s unused health FSA funds of up to $550. Amounts carried forward under this rule are added to the up-to-$2,750 amount that you elect to contribute to the health FSA for 2021. An employer may allow a carryover or a grace period for an FSA, but not both features.
Examining your year-to-date expenditures now will also help you to determine how much to set aside for next year. Don’t forget to reflect any changed circumstances in making your calculation.
Dependent care FSAs
Some employers also allow employees to set aside funds on a pre-tax basis in dependent care FSAs. A $5,000 maximum annual contribution is permitted ($2,500 for a married couple filing separately).
These FSAs are for a dependent-qualifying child under age 13, or a dependent or spouse who is physically or mentally incapable of self-care and who has the same principal place of abode as the taxpayer for more than half of the tax year.
Like health FSAs, dependent care FSAs are subject to a use-it-or-lose-it rule, but only the grace period relief applies, not the up-to-$550 forfeiture exception. Thus, now is a good time to review expenditures to date and to project amounts to be set aside for next year.
Note: Because of COVID-19, the IRS has temporarily allowed employees to take certain actions in 2020 related to their health care and dependent care FSAs. For example, employees may be permitted to make prospective mid-year elections and changes. Ask your HR department if your plan allows these actions if you believe they would be beneficial in your situation. Other rules and exceptions may apply.
Contact us if you’d like to discuss FSAs in greater detail.
© 2020
The importance of S corporation basis and distribution elections

S corporations can provide tax advantages over C corporations in the right circumstances. This is true if you expect that the business will incur losses in its early years because shareholders in a C corporation generally get no tax benefit from such losses. Conversely, as an S corporation shareholder, you can deduct your percentage share of these losses on your personal tax return to the extent of your basis in the stock and any loans you personally make to the entity.
Losses that can’t be deducted because they exceed your basis are carried forward and can be deducted by you when there’s sufficient basis.
Therefore, your ability to use losses that pass through from an S corporation depends on your basis in the corporation’s stock and debt. And, basis is important for other purposes such as determining the amount of gain or loss you recognize if you sell the stock. Your basis in the corporation is adjusted to reflect various events such as distributions from the corporation, contributions you make to the corporation and the corporation’s income or loss.
Adjustments to basis
However, you may not be aware that several elections are available to an S corporation or its shareholders that can affect the basis adjustments caused by distributions and other events. Here is some information about four elections:
- An S corporation shareholder may elect to reverse the normal order of basis reductions and have the corporation’s deductible losses reduce basis before basis is reduced by nondeductible, noncapital expenses. Making this election may permit the shareholder to deduct more pass-through losses.
- An election that can help eliminate the corporation’s accumulated earnings and profits from C corporation years is the “deemed dividend election.” This election can be useful if the corporation isn’t able to, or doesn’t want to, make an actual dividend distribution.
- If a shareholder’s interest in the corporation terminates during the year, the corporation and all affected shareholders can agree to elect to treat the corporation’s tax year as having closed on the date the shareholder’s interest terminated. This election affords flexibility in the allocation of the corporation’s income or loss to the shareholders and it may affect the category of accumulated income out of which a distribution is made.
- An election to terminate the S corporation’s tax year may also be available if there has been a disposition by a shareholder of 20% or more of the corporation’s stock within a 30-day period.
Contact us if you would like to go over how these elections, as well as other S corporation planning strategies, can help maximize the tax benefits of operating as an S corporation.
© 2020
Taking distributions from a traditional IRA

Although planning is needed to help build the biggest possible nest egg in your traditional IRA (including a SEP-IRA and SIMPLE-IRA), it’s even more critical that you plan for withdrawals from these tax-deferred retirement vehicles. There are three areas where knowing the fine points of the IRA distribution rules can make a big difference in how much you and your family will keep after taxes:
Early distributions. What if you need to take money out of a traditional IRA before age 59½? For example, you may need money to pay your child’s education expenses, make a down payment on a new home or meet necessary living expenses if you retire early. In these cases, any distribution to you will be fully taxable (unless nondeductible contributions were made, in which case part of each payout will be tax-free). In addition, distributions before age 59½ may also be subject to a 10% penalty tax. However, there are several ways that the penalty tax (but not the regular income tax) can be avoided, including a method that’s tailor-made for individuals who retire early and need to draw cash from their traditional IRAs to supplement other income.
Naming beneficiaries. The decision concerning who you want to designate as the beneficiary of your traditional IRA is critically important. This decision affects the minimum amounts you must generally withdraw from the IRA when you reach age 72, who will get what remains in the account at your death, and how that IRA balance can be paid out. What’s more, a periodic review of the individual(s) you’ve named as IRA beneficiaries is vital. This helps assure that your overall estate planning objectives will be achieved in light of changes in the performance of your IRAs, as well as in your personal, financial and family situation.
Required minimum distributions (RMDs). Once you attain age 72, distributions from your traditional IRAs must begin. If you don’t withdraw the minimum amount each year, you may have to pay a 50% penalty tax on what should have been paid out — but wasn’t. However, for 2020, the CARES Act suspended the RMD rules — including those for inherited accounts — so you don’t have to take distributions this year if you don’t want to. Beginning in 2021, the RMD rules will kick back in unless Congress takes further action. In planning for required distributions, your income needs must be weighed against the desirable goal of keeping the tax shelter of the IRA going for as long as possible for both yourself and your beneficiaries.
Traditional versus Roth
It may seem easier to put money into a traditional IRA than to take it out. This is one area where guidance is essential, and we can assist you and your family. Contact us to conduct a review of your traditional IRAs and to analyze other aspects of your retirement planning. We can also discuss whether you can benefit from a Roth IRA, which operate under a different set of rules than traditional IRAs.
© 2020
Health Savings Accounts for your small business

Small business owners are well aware of the increasing cost of employee health care benefits. As a result, your business may be interested in providing some of these benefits through an employer-sponsored Health Savings Account (HSA). Or perhaps you already have an HSA. It’s a good time to review how these accounts work since the IRS recently announced the relevant inflation-adjusted amounts for 2021.
The basics of HSAs
For eligible individuals, HSAs offer a tax-advantaged way to set aside funds (or have their employers do so) to meet future medical needs. Here are the key tax benefits:
- Contributions that participants make to an HSA are deductible, within limits.
- Contributions that employers make aren’t taxed to participants.
- Earnings on the funds within an HSA aren’t taxed, so the money can accumulate year after year tax free.
- HSA distributions to cover qualified medical expenses aren’t taxed.
- Employers don’t have to pay payroll taxes on HSA contributions made by employees through payroll deductions.
Key 2020 and 2021 amounts
To be eligible for an HSA, an individual must be covered by a “high deductible health plan.” For 2020, a “high deductible health plan” is one with an annual deductible of at least $1,400 for self-only coverage, or at least $2,800 for family coverage. For 2021, these amounts are staying the same.
For self-only coverage, the 2020 limit on deductible contributions is $3,550. For family coverage, the 2020 limit on deductible contributions is $7,100. For 2021, these amounts are increasing to $3,600 and $7,200, respectively. Additionally, for 2020, annual out-of-pocket expenses required to be paid (other than for premiums) for covered benefits cannot exceed $6,900 for self-only coverage or $13,800 for family coverage. For 2021, these amounts are increasing to $7,000 and $14,000.
An individual (and the individual’s covered spouse, as well) who has reached age 55 before the close of the tax year (and is an eligible HSA contributor) may make additional “catch-up” contributions for 2020 and 2021 of up to $1,000.
Contributing on an employee’s behalf
If an employer contributes to the HSA of an eligible individual, the employer’s contribution is treated as employer-provided coverage for medical expenses under an accident or health plan and is excludable from an employee’s gross income up to the deduction limitation. There’s no “use-it-or-lose-it” provision, so funds can be built up for years. An employer that decides to make contributions on its employees’ behalf must generally make comparable contributions to the HSAs of all comparable participating employees for that calendar year. If the employer doesn’t make comparable contributions, the employer is subject to a 35% tax on the aggregate amount contributed by the employer to HSAs for that period.
Paying for eligible expenses
HSA distributions can be made to pay for qualified medical expenses. This generally means those expenses that would qualify for the medical expense itemized deduction. They include expenses such as doctors’ visits, prescriptions, chiropractic care and premiums for long-term care insurance.
If funds are withdrawn from the HSA for any other reason, the withdrawal is taxable. Additionally, an extra 20% tax will apply to the withdrawal, unless it’s made after reaching age 65, or in the event of death or disability.
As you can see, HSAs offer a flexible option for providing health care coverage, but the rules are somewhat complex. Contact us with questions or if you’d like to discuss offering this benefit to your employees.
© 2020
How Series EE savings bonds are taxed

Many people have Series EE savings bonds that were purchased many years ago. Perhaps they were given to your children as gifts or maybe you bought them yourself and put them away in a file cabinet or safe deposit box. You may wonder: How is the interest you earn on EE bonds taxed? And if they reach final maturity, what action do you need to take to ensure there’s no loss of interest or unanticipated tax consequences?
Fixed or variable interest
Series EE Bonds dated May 2005, and after, earn a fixed rate of interest. Bonds purchased between May 1997 and April 30, 2005, earn a variable market-based rate of return.
Paper Series EE bonds were sold at half their face value. For example, if you own a $50 bond, you paid $25 for it. The bond isn’t worth its face value until it matures. (The U.S. Treasury Department no longer issues EE bonds in paper form.) Electronic Series EE Bonds are sold at face value and are worth their full value when available for redemption.
The minimum term of ownership is one year, but a penalty is imposed if the bond is redeemed in the first five years. The bonds earn interest for 30 years.
Interest generally accrues until redemption
Series EE bonds don’t pay interest currently. Instead, the accrued interest is reflected in the redemption value of the bond. The U.S. Treasury issues tables showing the redemption values.
The interest on EE bonds isn’t taxed as it accrues unless the owner elects to have it taxed annually. If an election is made, all previously accrued but untaxed interest is also reported in the election year. In most cases, this election isn’t made so bond holders receive the benefits of tax deferral.
If the election to report the interest annually is made, it will apply to all bonds and for all future years. That is, the election cannot be made on a bond-by-bond or year-by-year basis. However, there’s a procedure under which the election can be canceled.
If the election isn’t made, all of the accrued interest is finally taxed when the bond is redeemed or otherwise disposed of (unless it was exchanged for a Series HH bond). The bond continues to accrue interest even after reaching its face value, but at “final maturity” (after 30 years) interest stops accruing and must be reported.
Note: Interest on EE bonds isn’t subject to state income tax. And using the money for higher education may keep you from paying federal income tax on your interest.
Reaching final maturity
One of the main reasons for buying EE bonds is the fact that interest can build up without having to currently report or pay tax on it. Unfortunately, the law doesn’t allow for this tax-free buildup to continue indefinitely. When the bonds reach final maturity, they stop earning interest.
Series EE bonds issued in January 1990 reached final maturity after 30 years, in January 2020. That means that not only have they stopped earning interest, but all of the accrued and as yet untaxed interest is taxable in 2020.
If you own EE bonds (paper or electronic), check the issue dates on your bonds. If they’re no longer earning interest, you probably want to redeem them and put the money into something more profitable. Contact us if you have any questions about savings bond taxation, including Series HH and Series I bonds.
© 2020
Do you want to withdraw cash from your closely held corporation at a low tax cost?

Owners of closely held corporations are often interested in easily withdrawing money from their businesses at the lowest possible tax cost. The simplest way is to distribute cash as a dividend. However, a dividend distribution isn’t tax-efficient, since it’s taxable to you to the extent of your corporation’s “earnings and profits.” And it’s not deductible by the corporation.
Other strategies
Fortunately, there are several alternative methods that may allow you to withdraw cash from a corporation while avoiding dividend treatment. Here are five strategies to consider:
- Capital repayments. To the extent that you’ve capitalized the corporation with debt, including amounts that you’ve advanced to the business, the corporation can repay the debt without the repayment being treated as a dividend. Additionally, interest paid on the debt can be deducted by the corporation. This assumes that the debt has been properly documented with terms that characterize debt and that the corporation doesn’t have an excessively high debt-to-equity ratio. If not, the “debt” repayment may be taxed as a dividend. If you make future cash contributions to the corporation, consider structuring them as debt to facilitate later withdrawals on a tax-advantaged basis.
- Compensation. Reasonable compensation that you, or family members, receive for services rendered to the corporation is deductible by the business. However, it’s also taxable to the recipient(s). This same rule applies to any compensation (in the form of rent) that you receive from the corporation for the use of property. In both cases, the compensation amount must be reasonable in terms of the services rendered or the value of the property provided. If it’s considered excessive, the excess will be a nondeductible corporate distribution.
- Loans. You can withdraw cash tax free from the corporation by borrowing money from it. However, to prevent having the loan characterized as a corporate distribution, it should be properly documented in a loan agreement or note. It should also be made on terms that are comparable to those in which an unrelated third party would lend money to you, including a provision for interest and principal. Also, consider what the corporation’s receipt of interest income will mean.
- Fringe benefits. You may want to obtain the equivalent of a cash withdrawal in fringe benefits, which aren’t taxable to you and are deductible by the corporation. Examples include life insurance, certain medical benefits, disability insurance and dependent care. Most of these benefits are tax-free only if provided on a nondiscriminatory basis to other corporation employees. You can also establish a salary reduction plan that allows you (and other employees) to take a portion of your compensation as nontaxable benefits, rather than as taxable compensation.
- Property sales. You can withdraw cash from the corporation by selling property to it. However, certain sales should be avoided. For example, you shouldn’t sell property to a more than 50%-owned corporation at a loss, since the loss will be disallowed. And you shouldn’t sell depreciable property to a more than 50%-owned corporation at a gain, since the gain will be treated as ordinary income, rather than capital gain. A sale should be on terms that are comparable to those in which an unrelated third party would purchase the property. You may need to obtain an independent appraisal to establish the property’s value.
Minimize taxes
If you’re interested in discussing any of these ideas, contact us. We can help you get the most out of your corporation at the lowest tax cost.
© 2020
Disability income: How is it taxed?

Many Americans receive disability income. You may wonder if — and how — it’s taxed. As is often the case with tax questions, the answer is … it depends.
The key factor is who paid for the benefit. If the income is paid directly to you by your employer, it’s taxable to you as ordinary salary would be. (Taxable benefits are also subject to federal income tax withholding, although depending on the employer’s disability plan, in some cases aren’t subject to the Social Security tax.)
Frequently, the payments aren’t made by the employer but by an insurance company under a policy providing disability coverage or, under an arrangement having the effect of accident or health insurance. If this is the case, the tax treatment depends on who paid for the coverage. If your employer paid for it, then the income is taxed to you just as if paid directly to you by the employer. On the other hand, if it’s a policy you paid for, the payments you receive under it aren’t taxable.
Even if your employer arranges for the coverage, (in other words, it’s a policy made available to you at work), the benefits aren’t taxed to you if you pay the premiums. For these purposes, if the premiums are paid by the employer but the amount paid is included as part of your taxable income from work, the premiums are treated as paid by you.
A couple of examples
Let’s say your salary is $1,000 a week ($52,000 a year). Additionally, under a disability insurance arrangement made available to you by your employer, $10 a week ($520 for the year) is paid on your behalf by your employer to an insurance company. You include $52,520 in income as your wages for the year: the $52,000 paid to you plus the $520 in disability insurance premiums. In this case, the insurance is treated as paid for by you. If you become disabled and receive benefits, they aren’t taxable income to you.
Now, let’s look at an example with the same facts as above. Except in this case, you include only $52,000 in income as your wages for the year because the amount paid for the insurance coverage qualifies as excludable under the rules for employer-provided health and accident plans. In this case, the insurance is treated as paid for by your employer. If you become disabled and receive benefits, they are taxable income to you.
Note: There are special rules in the case of a permanent loss (or loss of the use) of a part or function of the body, or a permanent disfigurement.
Social Security benefits
This discussion doesn’t cover the tax treatment of Social Security disability benefits. These benefits may be taxed to you under different rules.
How much coverage is needed?
In deciding how much disability coverage you need to protect yourself and your family, take the tax treatment into consideration. If you’re buying the policy yourself, you only have to replace your after tax, “take-home” income because your benefits won’t be taxed. On the other hand, if your employer pays for the benefit, you’ll lose a percentage to taxes. If your current coverage is insufficient, you may wish to supplement an employer benefit with a policy you take out.
Contact us if you’d like to discuss this in more detail.
© 2020
Tax responsibilities if you business is closing amid the pandemic

Unfortunately, the COVID-19 pandemic has forced many businesses to shut down. If this is your situation, we’re here to assist you in any way we can, including taking care of the various tax obligations that must be met.
Of course, a business must file a final income tax return and some other related forms for the year it closes. The type of return to be filed depends on the type of business you have. Here’s a rundown of the basic requirements.
Sole Proprietorships. You’ll need to file the usual Schedule C, “Profit or Loss from Business,” with your individual return for the year you close the business. You may also need to report self-employment tax.
Partnerships. A partnership must file Form 1065, “U.S. Return of Partnership Income,” for the year it closes. You also must report capital gains and losses on Schedule D. Indicate that this is the final return and do the same on Schedules K-1, “Partner’s Share of Income, Deductions, Credits, Etc.”
All Corporations. Form 966, “Corporate Dissolution or Liquidation,” must be filed if you adopt a resolution or plan to dissolve a corporation or liquidate any of its stock.
C Corporations. File Form 1120, “U.S. Corporate Income Tax Return,” for the year you close. Report capital gains and losses on Schedule D. Indicate this is the final return.
S Corporations. File Form 1120-S, “U.S. Income Tax Return for an S Corporation” for the year of closing. Report capital gains and losses on Schedule D. The “final return” box must be checked on Schedule K-1.
All Businesses. Other forms may need to be filed to report sales of business property and asset acquisitions if you sell your business.
Employees and contract workers
If you have employees, you must pay them final wages and compensation owed, make final federal tax deposits and report employment taxes. Failure to withhold or deposit employee income, Social Security and Medicare taxes can result in full personal liability for what’s known as the Trust Fund Recovery Penalty.
If you’ve paid any contractors at least $600 during the calendar year in which you close your business, you must report those payments on Form 1099-NEC, “Nonemployee Compensation.”
Other tax issues
If your business has a retirement plan for employees, you’ll want to terminate the plan and distribute benefits to participants. There are detailed notice, funding, timing and filing requirements that must be met by a terminating plan. There are also complex requirements related to flexible spending accounts, Health Savings Accounts, and other programs for your employees.
We can assist you with many other complicated tax issues related to closing your business, including Paycheck Protection Plan (PPP) loans, the COVID-19 employee retention tax credit, employment tax deferral, debt cancellation, use of net operating losses, freeing up any remaining passive activity losses, depreciation recapture, and possible bankruptcy issues.
We can advise you on the length of time you need to keep business records. You also must cancel your Employer Identification Number (EIN) and close your IRS business account.
If your business is unable to pay all the taxes it owes, we can explain the available payment options to you. Contact us to discuss these issues and get answers to any questions.
© 2020
Divorcing couples should understand these 4 tax issues

When a couple is going through a divorce, taxes are probably not foremost in their minds. But without proper planning and advice, some people find divorce to be an even more taxing experience. Several tax concerns need to be addressed to ensure that taxes are kept to a minimum and that important tax-related decisions are properly made. Here are four issues to understand if you’re in the midst of a divorce.
Issue 1: Alimony or support payments. For alimony under divorce or separation agreements that are executed after 2018, there’s no deduction for alimony and separation support payments for the spouse making them. And the alimony payments aren’t included in the gross income of the spouse receiving them. (The rules are different for divorce or separation agreements executed before 2019.)
Issue 2: Child support. No matter when a divorce or separation instrument is executed, child support payments aren’t deductible by the paying spouse (or taxable to the recipient).
Issue 3: Your residence. Generally, if a married couple sells their home in connection with a divorce or legal separation, they should be able to avoid tax on up to $500,000 of gain (as long as they’ve owned and used the residence as their principal residence for two of the previous five years). If one spouse continues to live in the home and the other moves out (but they both remain owners of the home), they may still be able to avoid gain on the future sale of the home (up to $250,000 each), but special language may have to be included in the divorce decree or separation agreement to protect the exclusion for the spouse who moves out.
If the couple doesn’t meet the two-year ownership and use tests, any gain from the sale may qualify for a reduced exclusion due to unforeseen circumstances.
Issue 4: Pension benefits. A spouse’s pension benefits are often part of a divorce property settlement. In these cases, the commonly preferred method to handle the benefits is to get a “qualified domestic relations order” (QDRO). This gives one spouse the right to share in the pension benefits of the other and taxes the spouse who receives the benefits. Without a QDRO the spouse who earned the benefits will still be taxed on them even though they’re paid out to the other spouse.
More to consider
These are just some of the issues you may have to deal with if you’re getting a divorce. In addition, you must decide how to file your tax return (single, married filing jointly, married filing separately or head of household). You may need to adjust your income tax withholding and you should notify the IRS of any new address or name change. If you own a business, you may have to pay your spouse a share. There are also estate planning considerations. Contact us to help you work through the financial issues involved in divorce.
© 2020
New business? It’s a good time to start a retirement plan

If you recently launched a business, you may want to set up a tax-favored retirement plan for yourself and your employees. There are several types of qualified plans that are eligible for these tax advantages:
- A current deduction from income to the employer for contributions to the plan, ;
- Tax-free buildup of the value of plan investments, and
- The deferral of income (augmented by investment earnings) to employees until funds are distributed.
There are two basic types of plans.
Defined benefit pension plans
A defined benefit plan provides for a fixed benefit in retirement, based generally upon years of service and compensation. While defined benefit plans generally pay benefits in the form of an annuity (for example, over the life of the participant, or joint lives of the participant and his or her spouse), some defined benefit plans provide for a lump sum payment of benefits. In certain “cash balance plans,” the benefit is typically paid and expressed as a cash lump sum.
Adoption of a defined benefit plan requires a commitment to fund it. These plans often provide the greatest current deduction from income and the greatest retirement benefit, if the business owners are nearing retirement. However, the administrative expenses associated with defined benefit plans (for example, actuarial costs) can make them less attractive than the second type of plan.
Defined contribution plans
A defined contribution plan provides for an individual account for each participant. Benefits are based solely on the amount contributed to the participant’s account and any investment income, expenses, gains, losses and forfeitures (usually from departing employees) that may be allocated to a participant’s account. Profit-sharing plans and 401(k)s are defined contribution plans.;
A 401(k) plan provides for employer contributions made at the direction of an employee under a salary reduction agreement. Specifically, the employee elects to have a certain amount of pay deferred and contributed by the employer on his or her behalf to the plan. Employee contributions can be made either:
- On a pre-tax basis, saving employees current income tax on the amount contributed, or
- On an after-tax basis. This includes Roth 401(k) contributions (if permitted), which will allow distributions (including earnings) to be made to the employee tax-free in retirement, if conditions are satisfied.
Automatic-deferral provisions, if adopted, require employees to opt out of participation.
An employer may, or may not, provide matching contributions on behalf of employees who make elective deferrals to the plan. Matching contributions may be subject to a vesting schedule. While 401(k) plans are subject to testing requirements, so that “highly compensated” employees don’t contribute too much more than non-highly-compensated employees, these tests can be avoided if you adopt a “safe harbor” 401(k) plan. A highly compensated employee in 2020 is defined as one who earned more than $130,000 in the preceding year.
There are other types of tax-favored retirement plans within these general categories, including employee stock ownership plans (ESOPs).
Other plans
Small businesses can also adopt a Simplified Employee Pension (SEP), and receive similar tax advantages to “qualified” plans by making contributions on behalf of employees. And a business with 100 or fewer employees can establish a Savings Incentive Match Plan for Employees (SIMPLE). Under a SIMPLE, generally an IRA is established for each employee and the employer makes matching contributions based on contributions elected by employees.
There may be other options. Contact us to discuss the types of retirement plans available to you.
© 2020
Buying and selling mutual fund shares: Avoid these tax pitfalls

If you invest in mutual funds, be aware of some potential pitfalls involved in buying and selling shares.
Surprise sales
You may already have made taxable “sales” of part of your mutual fund investment without knowing it.
One way this can happen is if your mutual fund allows you to write checks against your fund investment. Every time you write a check against your mutual fund account, you’ve made a partial sale of your interest in the fund. Thus, except for funds such as money market funds, for which share value remains constant, you may have taxable gain (or a deductible loss) when you write a check. And each such sale is a separate transaction that must be reported on your tax return.
Here’s another way you may unexpectedly make a taxable sale. If your mutual fund sponsor allows you to make changes in the way your money is invested — for instance, lets you switch from one fund to another fund — making that switch is treated as a taxable sale of your shares in the first fund.
Recordkeeping
Carefully save all the statements that the fund sends you — not only official tax statements, such as Forms 1099-DIV, but the confirmations the fund sends you when you buy or sell shares or when dividends are reinvested in new shares. Unless you keep these records, it may be difficult to prove how much you paid for the shares, and thus, you won’t be able to establish the amount of gain that’s subject to tax (or the amount of loss you can deduct) when you sell.
You also need to keep these records to prove how long you’ve held your shares if you want to take advantage of favorable long-term capital gain tax rates. (If you get a year-end statement that lists all your transactions for the year, you can just keep that and discard quarterly or other interim statements. But save anything that specifically says it contains tax information.)
Recordkeeping is simplified by rules that require funds to report the customer’s basis in shares sold and whether any gain or loss is short-term or long-term. This is mandatory for mutual fund shares acquired after 2011, and some funds will provide this to shareholders for shares they acquired earlier, if the fund has the information.
Timing purchases and sales
If you’re planning to invest in a mutual fund, there are some important tax consequences to take into account in timing the investment. For instance, an investment shortly before payment of a dividend is something you should generally try to avoid. Your receipt of the dividend (even if reinvested in additional shares) will be treated as income and increase your tax liability. If you’re planning a sale of any of your mutual fund shares near year-end, you should weigh the tax and the non-tax consequences in the current year versus a sale in the next year.
Identify shares you sell
If you sell fewer than all of the shares that you hold in the same mutual fund, there are complicated rules for identifying which shares you’ve sold. The proper application of these rules can reduce the amount of your taxable gain or qualify the gain for favorable long-term capital gain treatment.
Contact us if you’d like to find out more about tax planning for buying and selling mutual fund shares.
© 2020
The 2021 “Social Security wage base” is increasing

If your small business is planning for payroll next year, be aware that the “Social Security wage base” is increasing.
The Social Security Administration recently announced that the maximum earnings subject to Social Security tax will increase from $137,700 in 2020 to $142,800 in 2021.
For 2021, the FICA tax rate for both employers and employees is 7.65% (6.2% for Social Security and 1.45% for Medicare).
For 2021, the Social Security tax rate is 6.2% each for the employer and employee (12.4% total) on the first $142,800 of employee wages. The tax rate for Medicare is 1.45% each for the employee and employer (2.9% total). There’s no wage base limit for Medicare tax so all covered wages are subject to Medicare tax.
In addition to withholding Medicare tax at 1.45%, an employer must withhold a 0.9% additional Medicare tax from wages paid to an employee in excess of $200,000 in a calendar year.
Employees working more than one job
You may have employees who work for your business and who also have a second job. They may ask if you can stop withholding Social Security taxes at a certain point in the year because they’ve already reached the Social Security wage base amount. Unfortunately, you generally can’t stop the withholding, but the employees will get a credit on their tax returns for any excess withheld.
Older employees
If your business has older employees, they may have to deal with the “retirement earnings test.” It remains in effect for individuals below normal retirement age (age 65 to 67 depending on the year of birth) who continue to work while collecting Social Security benefits. For affected individuals, $1 in benefits will be withheld for every $2 in earnings above $18,960 in 2021 (up from $18,240 in 2020).
For working individuals collecting benefits who reach normal retirement age in 2021, $1 in benefits will be withheld for every $3 in earnings above $46,920 (up from $48,600 in 2020), until the month that the individual reaches normal retirement age. After that month, there’s no limit on earnings.
Contact us if you have questions. We can assist you with the details of payroll taxes and keep you in compliance with payroll laws and regulations.
© 2020
What tax records can you throw away?

October 15 is the deadline for individual taxpayers who extended their 2019 tax returns. (The original April 15 filing deadline was extended this year to July 15 due to the COVID-19 pandemic.) If you’re finally done filing last year’s return, you might wonder: Which tax records can you toss once you’re done? Now is a good time to go through old tax records and see what you can discard.
The general rules
At minimum, you should keep tax records for as long as the IRS has the ability to audit your tax return or assess additional taxes, which generally is three years after you file your return. This means you potentially can get rid of most records related to tax returns for 2016 and earlier years.
However, the statute of limitations extends to six years for taxpayers who understate their adjusted gross income (AGI) by more than 25%. What constitutes an understatement may go beyond simply not reporting items of income. So a general rule of thumb is to save tax records for six years from filing, just to be safe.
Keep some records longer
You need to hang on to some tax-related records beyond the statute of limitations. For example:
- Keep the tax returns themselves indefinitely, so you can prove to the IRS that you actually filed a legitimate return. (There’s no statute of limitations for an audit if you didn’t file a return or if you filed a fraudulent one.)
- Retain W-2 forms until you begin receiving Social Security benefits. Questions might arise regarding your work record or earnings for a particular year, and your W-2 helps provide the documentation needed.
- Keep records related to real estate or investments for as long as you own the assets, plus at least three years after you sell them and report the sales on your tax return (or six years if you want extra protection).
- Keep records associated with retirement accounts until you’ve depleted the accounts and reported the last withdrawal on your tax return, plus three (or six) years.
Other reasons to retain records
Keep in mind that these are the federal tax record retention guidelines. Your state and local tax record requirements may differ. In addition, lenders, co-op boards and other private parties may require you to produce copies of your tax returns as a condition to lending money, approving a purchase or otherwise doing business with you.
Contact us if you have questions or concerns about recordkeeping.
© 2020
Understanding the passive activity loss rules

Are you wondering if the passive activity loss rules affect business ventures you’re engaged in — or might engage in?
If the ventures are passive activities, the passive activity loss rules prevent you from deducting expenses that are generated by them in excess of their income. You can’t deduct the excess expenses (losses) against earned income or against other nonpassive income. Nonpassive income for this purpose includes interest, dividends, annuities, royalties, gains and losses from most property dispositions, and income from certain oil and gas property interests. So you can’t deduct passive losses against those income items either.
Any losses that you can’t use aren’t lost. Instead, they’re carried forward, indefinitely, to tax years in which your passive activities generate enough income to absorb the losses. To the extent your passive losses from an activity aren’t used up in this way, you’ll be allowed to use them in the tax year in which you dispose of your interest in the activity in a fully taxable transaction, or in the tax year you die.
Passive vs. material
Passive activities are trades, businesses or income-producing activities in which you don’t “materially participate.” The passive activity loss rules also apply to any items passed through to you by partnerships in which you’re a partner, or by S corporations in which you’re a shareholder. This means that any losses passed through to you by partnerships or S corporations will be treated as passive, unless the activities aren’t passive for you.
For example, let’s say that in addition to your regular professional job, you’re a limited partner in a partnership that cleans offices. Or perhaps you’re a shareholder in an S corp that operates a manufacturing business (but you don’t participate in the operations).
If you don’t materially participate in the partnership or S corporation, those activities are passive. On the other hand, if you “materially participate,” the activities aren’t passive (except for rental activities, discussed below), and the passive activity rules won’t apply to the losses. To materially participate, you must be involved in the operations on a regular, continuous and substantial basis.
The IRS uses several tests to establish material participation. Under the most frequently used test, you’re treated as materially participating in an activity if you participate in it for more than 500 hours in the tax year. While other tests require fewer hours, all the tests require you to establish how you participated and the amount of time spent. You can establish this by any reasonable means such as contemporaneous appointment books, calendars, time reports or logs.
Rental activities
Rental activities are automatically treated as passive, regardless of your participation. This means that, even if you materially participate in them, you can’t deduct the losses against your earned income, interest, dividends, etc. There are two important exceptions:
- You can deduct up to $25,000 of losses from rental real estate activities (even though they’re passive) against earned income, interest, dividends, etc., if you “actively participate” in the activities (requiring less participation than “material participation”) and if your adjusted gross income doesn’t exceed specified levels.
- If you qualify as a “real estate professional” (which requires performing substantial services in real property trades or businesses), your rental real estate activities aren’t automatically treated as passive. So losses from those activities can be deducted against earned income, interest, dividends, etc., if you materially participate.
Contact us if you’d like to discuss how these rules apply to your business.
© 2020
There may be relief from tax liability for “innocent spouses”
|
The easiest way to survive an IRS audit is to get ready in advance

|
Why it’s important to plan for income taxes as part of your estate plan

As a result of the current estate tax exemption amount ($11.58 million in 2020), many estates no longer need to be concerned with federal estate tax. Before 2011, a much smaller amount resulted in estate plans attempting to avoid it. Now, because many estates won’t be subject to estate tax, more planning can be devoted to saving income taxes for your heirs.
While saving both income and transfer taxes has always been a goal of estate planning, it was more difficult to succeed at both when the estate and gift tax exemption level was much lower. Here are some strategies to consider.
Plan gifts that use the annual gift tax exclusion. One of the benefits of using the gift tax annual exclusion to make transfers during life is to save estate tax. This is because both the transferred assets and any post-transfer appreciation generated by those assets are removed from the donor’s estate.
As mentioned, estate tax savings may not be an issue because of the large estate exemption amount. Further, making an annual exclusion transfer of appreciated property carries a potential income tax cost because the recipient receives the donor’s basis upon transfer. Thus, the recipient could face income tax, in the form of capital gains tax, on the sale of the gifted property in the future. If there’s no concern that an estate will be subject to estate tax, even if the gifted property grows in value, then the decision to make a gift should be based on other factors.
For example, gifts may be made to help a relative buy a home or start a business. But a donor shouldn’t gift appreciated property because of the capital gain that could be realized on a future sale by the recipient. If the appreciated property is held until the donor’s death, under current law, the heir will get a step-up in basis that will wipe out the capital gain tax on any pre-death appreciation in the property’s value.
Take spouses’ estates into account. In the past, spouses often undertook complicated strategies to equalize their estates so that each could take advantage of the estate tax exemption amount. Generally, a two-trust plan was established to minimize estate tax. “Portability,” or the ability to apply the decedent’s unused exclusion amount to the surviving spouse’s transfers during life and at death, became effective for estates of decedents dying after 2010. As long as the election is made, portability allows the surviving spouse to apply the unused portion of a decedent’s applicable exclusion amount (the deceased spousal unused exclusion amount) as calculated in the year of the decedent’s death. The portability election gives married couples more flexibility in deciding how to use their exclusion amounts.
Be aware that some estate exclusion or valuation discount strategies to avoid inclusion of property in an estate may no longer be worth pursuing. It may be better to have the property included in the estate or not qualify for valuation discounts so that the property receives a step-up in basis. For example, the special use valuation — the valuation of qualified real property used for farming or in a business on the basis of the property’s actual use, rather than on its highest and best use — may not save enough, or any, estate tax to justify giving up the step-up in basis that would otherwise occur for the property.
Contact us if you want to discuss these strategies and how they relate to your estate plan.
© 2020
Can investors who manage their own portfolios deduct related expenses?

In some cases, investors have significant related expenses, such as the cost of subscriptions to financial periodicals and clerical expenses. Are they tax deductible? Under the Tax Cut and Jobs Act, these expenses aren’t deductible through 2025 if they’re considered expenses for the production of income. But they are deductible if they’re considered trade or business expenses. (For tax years before 2018, production-of-income expenses were deductible, but were included in miscellaneous itemized deductions, which were subject to a 2%-of-adjusted-gross-income floor.)
In order to deduct investment-related expenses as business expenses, you must figure out if you’re an investor or a trader — and be aware that it’s more advantageous (and difficult) to qualify for trader status.
To qualify, you must be engaged in a trade or business. The U.S. Supreme Court held many years ago that an individual taxpayer isn’t engaged in a trade or business merely because the individual manages his or her own securities investments, regardless of the amount of the investments or the extent of the work required.
However, if you can show that your investment activities rise to the level of carrying on a trade or business, you may be considered a trader engaged in a trade or business, rather than an investor. As a trader, you’re entitled to deduct your investment-related expenses as business expenses. A trader is also entitled to deduct home-office expenses if the home office is used exclusively on a regular basis as the trader’s principal place of business. An investor, on the other hand, isn’t entitled to home-office deductions since the investment activities aren’t a trade or business.
Since the Supreme Court’s decision, there has been extensive litigation on the issue of whether a taxpayer is a trader or investor. The U.S. Tax Court has developed a two-part test that must be satisfied in order for a taxpayer to be a trader. Under this two-part test, a taxpayer’s investment activities are considered a trade or business only if both of the following are true:
- The taxpayer’s trading is substantial (in other words, sporadic trading isn’t a trade or business), and
- The taxpayer seeks to profit from short-term market swings, rather than from long-term holding of investments.
So, the fact that a taxpayer’s investment activities are regular, extensive and continuous isn’t in itself sufficient for determining that a taxpayer is a trader. In order to be considered a trader, you must show that you buy and sell securities with reasonable frequency in an effort to profit on a short-term basis. In one case, even a taxpayer who made more than 1,000 trades a year with trading activities averaging about $16 million annually was held to be an investor because the holding periods for stocks sold averaged about one year.
Contact us if you have questions about whether your investment-related expenses are deductible. We can also help explain how to help keep capital gains taxes low when you sell investments.
© 2020
Business website costs: How to handle them for tax purposes
|
Tax implications of working from home and collecting unemployment

COVID-19 has changed our lives in many ways, and some of the changes have tax implications. Here is basic information about two common situations.
1. Working from home.
Many employees have been told not to come into their workplaces due to the pandemic. If you’re an employee who “telecommutes” — that is, you work at home, and communicate with your employer mainly by telephone, videoconferencing, email, etc. — you should know about the strict rules that govern whether you can deduct your home office expenses.
Unfortunately, employee home office expenses aren’t currently deductible, even if your employer requires you to work from home. Employee business expense deductions (including the expenses an employee incurs to maintain a home office) are miscellaneous itemized deductions and are disallowed from 2018 through 2025 under the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act.
However, if you’re self-employed and work out of an office in your home, you can be eligible to claim home office deductions for your related expenses if you satisfy the strict rules.
2. Collecting unemployment
Millions of Americans have lost their jobs due to COVID-19 and are collecting unemployment benefits. Some of these people don’t know that these benefits are taxable and must be reported on their federal income tax returns for the tax year they were received. Taxable benefits include the special unemployment compensation authorized under the Coronavirus Aid, Relief and Economic Security (CARES) Act.
In order to avoid a surprise tax bill when filing a 2020 income tax return next year, unemployment recipients can have taxes withheld from their benefits now. Under federal law, recipients can opt to have 10% withheld from their benefits to cover part or all their tax liability. To do this, complete Form W4-V, Voluntary Withholding Request, and give it to the agency paying benefits. (Don’t send it to the IRS.)
We can help
We can assist you with advice about whether you qualify for home office deductions, and how much of these expenses you can deduct. We can also answer any questions you have about the taxation of unemployment benefits as well as any other tax issues that you encounter as a result of COVID-19.
© 2020
Employers have questions and concerns about deferring employees’ Social Security taxes

The IRS has provided guidance to employers regarding the recent presidential action to allow employers to defer the withholding, deposit and payment of certain payroll tax obligations.
The three-page guidance in Notice 2020-65 was issued to implement President Trump’s executive memorandum signed on August 8.
Private employers still have questions and concerns about whether, and how, to implement the optional deferral. The President’s action only defers the employee’s share of Social Security taxes; it doesn’t forgive them, meaning employees will still have to pay the taxes later unless Congress acts to eliminate the liability. (The payroll services provider for federal employers announced that federal employees will have their taxes deferred.)
Deferral basics
President Trump issued the memorandum in light of the COVID-19 crisis. He directed the U.S. Secretary of the Treasury to use his authority under the tax code to defer the withholding, deposit and payment of certain payroll tax obligations.
For purposes of the Notice, “applicable wages” means wages or compensation paid to an employee on a pay date beginning September 1, 2020, and ending December 31, 2020, but only if the amount paid for a biweekly pay period is less than $4,000, or the equivalent amount with respect to other pay periods.
The guidance postpones the withholding and remittance of the employee share of Social Security tax until the period beginning on January 1, 2021, and ending on April 30, 2021. Penalties, interest and additions to tax will begin to accrue on May 1, 2021, for any unpaid taxes.
“If necessary,” the guidance states, an employer “may make arrangements to collect the total applicable taxes” from an employee. But it doesn’t specify how.
Be aware that under the CARES Act, employers can already defer paying their portion of Social Security taxes through December 31, 2020. All 2020 deferred amounts are due in two equal installments — one at the end of 2021 and the other at the end of 2022.
Many employers opting out
Several business groups have stated that their members won’t participate in the deferral. For example, the U.S. Chamber of Commerce and more than 30 trade associations sent a letter to members of Congress and the U.S. Department of the Treasury calling the deferral “unworkable.”
The Chamber is concerned that employees will get a temporary increase in their paychecks this year, followed by a decrease in take-home pay in early 2021. “Many of our members consider it unfair to employees to make a decision that would force a big tax bill on them next year… Therefore, many of our members will likely decline to implement deferral, choosing instead to continue to withhold and remit to the government the payroll taxes required by law,” the group explained.
Businesses are also worried about having to collect the taxes from employees who may quit or be terminated before April 30, 2021. And since some employees are asking questions about the deferral, many employers are also putting together communications to inform their staff members about whether they’re going to participate. If so, they’re informing employees what it will mean for next year’s paychecks.
How to proceed
Contact us if you have questions about the deferral and how to proceed at your business.
© 2020
Homebuyers: Can you deduct seller-paid points?

Despite the COVID-19 pandemic, the National Association of Realtors (NAR) reports that existing home sales and prices are up nationwide, compared with last year. One of the reasons is the pandemic: “With the sizable shift in remote work, current homeowners are looking for larger homes…” according to NAR’s Chief Economist Lawrence Yun.
If you’re buying a home, or you just bought one, you may wonder if you can deduct mortgage points paid on your behalf by the seller. Yes, you can, subject to some important limitations described below.
Points are upfront fees charged by a mortgage lender, expressed as a percentage of the loan principal. Points, which may be deductible if you itemize deductions, are normally the buyer’s obligation. But a seller will sometimes sweeten a deal by agreeing to pay the points on the buyer’s mortgage loan.
In most cases, points a buyer pays are a deductible interest expense. And IRS says that seller-paid points may also be deductible.
Suppose, for example, that you bought a home for $600,000. In connection with a $500,000 mortgage loan, your bank charged two points, or $10,000. The seller agreed to pay the points in order to close the sale.
You can deduct the $10,000 in the year of sale. The only disadvantage is that your tax basis is reduced to $590,000, which will mean more gain if — and when — you sell the home for more than that amount. But that may not happen until many years later, and the gain may not be taxable anyway. You may qualify for an exclusion for up to $250,000 ($500,000 for a married couple filing jointly) of gain on the sale of a principal residence.
Some limitations
There are some important limitations on the rule allowing a deduction for seller-paid points. The rule doesn’t apply:
- To points that are allocated to the part of a mortgage above $750,000 ($375,000 for marrieds filing separately) for tax years 2018 through 2025 (above $1 million for tax years before 2018 and after 2025);
- To points on a loan used to improve (rather than buy) a home;
- To points on a loan used to buy a vacation or second home, investment property or business property; and
- To points paid on a refinancing, home equity loan or line of credit.
Your situation
We can review with you in more detail whether the points in your home purchase are deductible, as well as discuss other tax aspects of your transaction.
© 2020
Back-to-school tax breaks on the books

Despite the COVID-19 pandemic, students are going back to school this fall, either remotely, in-person or under a hybrid schedule. In any event, parents may be eligible for certain tax breaks to help defray the cost of education.
Here is a summary of some of the tax breaks available for education.
1. Higher education tax credits. Generally, you may be able to claim either one of two tax credits for higher education expenses — but not both.
- With the American Opportunity Tax Credit (AOTC), you can save a maximum of $2,500 from your tax bill for each full-time college or grad school student. This applies to qualified expenses including tuition, room and board, books and computer equipment and other supplies. But the credit is phased out for moderate-to-upper income taxpayers. No credit is allowed if your modified adjusted gross income (MAGI) is over $90,000 ($180,000 for joint filers).
- The Lifetime Learning Credit (LLC) is similar to the AOTC, but there are a few important distinctions. In this case, the maximum credit is $2,000 instead of $2,500. Furthermore, this is the overall credit allowed to a taxpayer regardless of the number of students in the family. However, the LLC is also phased out under income ranges even lower than the AOTC. You can’t claim the credit if your MAGI is $68,000 or more ($136,000 or more if you file a joint return).
For these reasons, the AOTC is generally preferable to the LLC. But parents have still another option.
2. Tuition-and-fees deduction. As an alternative to either of the credits above, parents may claim an above-the-line deduction for tuition and related fees. This deduction is either $4,000 or $2,000, depending on the taxpayer’s MAGI, before it is phased out. No deduction is allowed for MAGI above $80,000 for single filers and $160,000 for joint filers.
The tuition-and-fees deduction, which has been extended numerous times, is currently scheduled to expire after 2020. However, it’s likely to be revived again by Congress.
In addition to these tax breaks, there are other ways to save and pay for college on a tax advantaged basis. These include using Section 529 plans and Coverdell Education Savings Accounts. There are limits on contributions to these saving vehicles.
Note: Thanks to a provision in the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act, a 529 plan can now be used to pay for up to $10,000 annually for a child’s tuition at a private or religious elementary or secondary school.
Final lesson
Typically, parents are able to take advantage of one or more of these tax breaks, even though some benefits are phased out above certain income levels. Contact us to maximize the tax breaks for your children’s education.
© 2020
5 key points about bonus depreciation

You’re probably aware of the 100% bonus depreciation tax break that’s available for a wide range of qualifying property. Here are five important points to be aware of when it comes to this powerful tax-saving tool.
1. Bonus depreciation is scheduled to phase out
Under current law, 100% bonus depreciation will be phased out in steps for property placed in service in calendar years 2023 through 2027. Thus, an 80% rate will apply to property placed in service in 2023, 60% in 2024, 40% in 2025, and 20% in 2026, and a 0% rate will apply in 2027 and later years.
For certain aircraft (generally, company planes) and for the pre-January 1, 2027 costs of certain property with a long production period, the phaseout is scheduled to take place a year later, from 2024 to 2028.
Of course, Congress could pass legislation to extend or revise the above rules.
2. Bonus depreciation is available for new and most used property
In the past, used property didn’t qualify. It currently qualifies unless:
- The taxpayer previously used the property and
- The property was acquired in certain forbidden transactions (generally acquisitions that are tax free or from a related person or entity).
3. Taxpayers should sometimes make the election to turn down bonus depreciation
Taxpayers can elect to reject bonus depreciation for one or more classes of property. The election out may be useful for sole proprietorships, and business entities taxed under the rules for partnerships and S corporations, that want to prevent “wasting” depreciation deductions by applying them against lower-bracket income in the year property was placed in service — instead of against anticipated higher bracket income in later years.
Note that business entities taxed as “regular” corporations (in other words, non-S corporations) are taxed at a flat rate.
4. Bonus depreciation is available for certain building improvements
Before the 2017 Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA), bonus depreciation was available for two types of real property:
- Land improvements other than buildings, for example fencing and parking lots, and
- “Qualified improvement property,” a broad category of internal improvements made to non-residential buildings after the buildings are placed in service.
The TCJA inadvertently eliminated bonus depreciation for qualified improvement property.
However, the 2020 Coronavirus Aid, Relief and Economic Security Act (CARES Act) made a retroactive technical correction to the TCJA. The correction makes qualified improvement property placed in service after December 31, 2017, eligible for bonus depreciation.
5. 100% bonus depreciation has reduced the importance of “Section 179 expensing”
If you own a smaller business, you’ve likely benefited from Sec. 179 expensing. This is an elective benefit that — subject to dollar limits — allows an immediate deduction of the cost of equipment, machinery, off-the-shelf computer software and some building improvements. Sec. 179 has been enhanced by the TCJA, but the availability of 100% bonus depreciation is economically equivalent and has greatly reduced the cases in which Sec. 179 expensing is useful.
We can help
The above discussion touches only on some major aspects of bonus depreciation. This is a complex area with tax implications for transactions other than simple asset acquisitions. Contact us if you have any questions about how to proceed in your situation.
© 2020
Will You Have to Pay Tax on Your Social Security Benefits?

If you’re getting close to retirement, you may wonder: Are my Social Security benefits going to be taxed? And if so, how much will you have to pay?
It depends on your other income. If you’re taxed, between 50% and 85% of your benefits could be taxed. (This doesn’t mean you pay 85% of your benefits back to the government in taxes. It merely that you’d include 85% of them in your income subject to your regular tax rates.)
Crunch the numbers
To determine how much of your benefits are taxed, first determine your other income, including certain items otherwise excluded for tax purposes (for example, tax-exempt interest). Add to that the income of your spouse, if you file joint tax returns. To this, add half of the Social Security benefits you and your spouse received during the year. The figure you come up with is your total income plus half of your benefits. Now apply the following rules:
1. If your income plus half your benefits isn’t above $32,000 ($25,000 for single taxpayers), none of your benefits are taxed.
2. If your income plus half your benefits exceeds $32,000 but isn’t more than $44,000, you will be taxed on one half of the excess over $32,000, or one half of the benefits, whichever is lower.
Here’s an example
For example, let’s say you and your spouse have $20,000 in taxable dividends, $2,400 of tax-exempt interest and combined Social Security benefits of $21,000. So, your income plus half your benefits is $32,900 ($20,000 + $2,400 +1/2 of $21,000). You must include $450 of the benefits in gross income (1/2 ($32,900 − $32,000)). (If your combined Social Security benefits were $5,000, and your income plus half your benefits were $40,000, you would include $2,500 of the benefits in income: 1/2 ($40,000 − $32,000) equals $4,000, but 1/2 the $5,000 of benefits ($2,500) is lower, and the lower figure is used.)
Important: If you aren’t paying tax on your Social Security benefits now because your income is below the floor, or you’re paying tax on only 50% of those benefits, an unplanned increase in your income can have a triple tax cost. You’ll have to pay tax on the additional income, you’ll have to pay tax on (or on more of ) your Social Security benefits (since the higher your income the more of your Social Security benefits that are taxed), and you may get pushed into a higher marginal tax bracket.
For example, this situation might arise if you receive a large distribution from an IRA during the year or you have large capital gains. Careful planning might be able to avoid this negative tax result. You might be able to spread the additional income over more than one year, or liquidate assets other than an IRA account, such as stock showing only a small gain or stock with gain that can be offset by a capital loss on other shares.
If you know your Social Security benefits will be taxed, you can voluntarily arrange to have the tax withheld from the payments by filing a Form W-4V. Otherwise, you may have to make estimated tax payments. Contact us for assistance or more information.
© 2020
CARES Act made changes to excess business losses

The Coronavirus Aid, Relief and Economic Security (CARES) Act made changes to excess business losses. This includes some changes that are retroactive and there may be opportunities for some businesses to file amended tax returns.
If you hold an interest in a business, or may do so in the future, here is more information about the changes.
Deferral of the excess business loss limits
The Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA) provided that net tax losses from active businesses in excess of an inflation-adjusted $500,000 for joint filers, or an inflation-adjusted $250,000 for other covered taxpayers, are to be treated as net operating loss (NOL) carryforwards in the following tax year. The covered taxpayers are individuals, estates and trusts that own businesses directly or as partners in a partnership or shareholders in an S corporation.
The $500,000 and $250,000 limits, which are adjusted for inflation for tax years beginning after calendar year 2018, were scheduled under the TCJA to apply to tax years beginning in calendar years 2018 through 2025. But the CARES Act has retroactively postponed the limits so that they now apply to tax years beginning in calendar years 2021 through 2025.
The postponement means that you may be able to amend:
- Any filed 2018 tax returns that reflected a disallowed excess business loss (to allow the loss in 2018) and
- Any filed 2019 tax returns that reflect a disallowed 2019 loss and/or a carryover of a disallowed 2018 loss (to allow the 2019 loss and/or eliminate the carryover).
Note that the excess business loss limits also don’t apply to tax years that begin in 2020. Thus, such a 2020 year can be a window to start a business with large up-front-deductible items (for example capital items that can be 100% deducted under bonus depreciation or other provisions) and be able to offset the resulting net losses from the business against investment income or income from employment (see below).
Changes to the excess business loss limits
The CARES Act made several retroactive corrections to the excess business loss rules as they were originally stated in the 2017 TCJA.
Most importantly, the CARES Act clarified that deductions, gross income or gain attributable to employment aren’t taken into account in calculating an excess business loss. This means that excess business losses can’t shelter either net taxable investment income or net taxable employment income. Be aware of that if you’re planning a start-up that will begin to generate, or will still be generating, excess business losses in 2021.
Another change provides that an excess business loss is taken into account in determining any NOL carryover but isn’t automatically carried forward to the next year. And a generally beneficial change states that excess business losses don’t include any deduction under the tax code provisions involving the NOL deduction or the qualified business income deduction that effectively reduces income taxes on many businesses.
And because capital losses of non-corporations can’t offset ordinary income under the NOL rules:
- Capital loss deductions aren’t taken into account in computing the excess business loss and
- The amount of capital gain taken into account in computing the loss can’t exceed the lesser of capital gain net income from a trade or business or capital gain net income.
Contact us with any questions you have about this or other tax matters.
© 2020
What happens if an individual can’t pay taxes

|
The President’s action to defer payroll taxes: What does it mean for your business?

On August 8, President Trump signed four executive actions, including a Presidential Memorandum to defer the employee’s portion of Social Security taxes for some people. These actions were taken in an effort to offer more relief due to the COVID-19 pandemic.
The action only defers the taxes, which means they’ll have to be paid in the future. However, the action directs the U.S. Treasury Secretary to “explore avenues, including legislation, to eliminate the obligation to pay the taxes deferred pursuant to the implementation of this memorandum.”
Legislative history
On March 18, 2020, President Trump signed into law the Families First Coronavirus Response Act. A short time later, President Trump signed into law the Coronavirus, Aid, Relief and Economic Security (CARES) Act. Both laws contain economic relief provisions for employers and workers affected by the COVID-19 crisis.
The CARES Act allows employers to defer paying their portion of Social Security taxes through December 31, 2020. All 2020 deferred amounts are due in two equal installments — one at the end of 2021 and the other at the end of 2022.
New bill talks fall apart
Discussions of another COVID-19 stimulus bill between Democratic leaders and White House officials broke down in early August. As a result, President Trump signed the memorandum that provides a payroll tax deferral for many — but not all — employees
The memorandum directs the U.S. Treasury Secretary to defer withholding, deposit and payment of the tax on wages or compensation, as applicable, paid during the period of September 1, 2020, through December 31, 2020. This means that the employee’s share of Social Security tax will be deferred for that time period.
However, the memorandum contains the following two conditions:
- The deferral is available with respect to any employee, the amount of whose wages or compensation, as applicable, payable during any biweekly pay period generally is less than $4,000, calculated on a pretax basis, or the equivalent amount with respect to other pay periods; and
- Amounts will be deferred without any penalties, interest, additional amount, or addition to the tax. The Treasury Secretary was ordered to provide guidance to implement the memorandum.
Legal authority
The memorandum (and the other executive actions signed on August 8) note that they’ll be implemented consistent with applicable law. However, some are questioning President Trump’s legal ability to implement the employee Social Security tax deferral.
Employer questions
Employers have questions and concerns about the payroll tax deferral. For example, since this is only a deferral, will employers have to withhold more taxes from employees’ paychecks to pay the taxes back, beginning January 1, 2021? Without a law from Congress to actually forgive the taxes, will employers be liable for paying them back? What if employers can’t get their payroll software changed in time for the September 1 start of the deferral? Are employers and employees required to take part in the payroll tax deferral or is it optional?
Contact us if you have questions about how to proceed. And stay tuned for more details about this action and any legislation that may pass soon.
© 2020
More parents may owe “nanny tax” this year, due to COVID-19

In the COVID-19 era, many parents are hiring nannies and babysitters because their daycare centers and summer camps have closed. This may result in federal “nanny tax” obligations.
Keep in mind that the nanny tax may apply to all household workers, including housekeepers, babysitters, gardeners or others who aren’t independent contractors.
If you employ someone who’s subject to the nanny tax, you aren’t required to withhold federal income taxes from the individual’s pay. You only must withhold if the worker asks you to and you agree. (In that case, ask the nanny to fill out a Form W-4.) However, you may have other withholding and payment obligations.
Withholding FICA and FUTA
You must withhold and pay Social Security and Medicare taxes (FICA) if your nanny earns cash wages of $2,200 or more (excluding food and lodging) during 2020. If you reach the threshold, all of the wages (not just the excess) are subject to FICA.
However, if your nanny is under 18 and childcare isn’t his or her principal occupation, you don’t have to withhold FICA taxes. Therefore, if your nanny is really a student/part-time babysitter, there’s no FICA tax liability.
Both employers and household workers have an obligation to pay FICA taxes. Employers are responsible for withholding the worker’s share of FICA and must pay a matching employer amount. FICA tax is divided between Social Security and Medicare. Social Security tax is 6.2% for the both the employer and the worker (12.4% total). Medicare tax is 1.45% each for both the employer and the worker (2.9% total).
If you prefer, you can pay your nanny’s share of Social Security and Medicare taxes, instead of withholding it from pay.
Note: It’s unclear how these taxes will be affected by the executive order that President Trump signed on August 8, which allows payroll taxes to be deferred from September 1 through December 31, 2020.
You also must pay federal unemployment (FUTA) tax if you pay $1,000 or more in cash wages (excluding food and lodging) to your worker in any calendar quarter of this year or last year. FUTA tax applies to the first $7,000 of wages. The maximum FUTA tax rate is 6%, but credits reduce it to 0.6% in most cases. FUTA tax is paid only by the employer.
Reporting and paying
You pay nanny tax by increasing your quarterly estimated tax payments or increasing withholding from your wages — rather than making an annual lump-sum payment.
You don’t have to file any employment tax returns, even if you’re required to withhold or pay tax (unless you own a business, see below). Instead, you report employment taxes on Schedule H of your tax return.
On your return, you include your employer identification number (EIN) when reporting employment taxes. The EIN isn’t the same as your Social Security number. If you need an EIN, you must file Form SS-4.
However, if you own a business as a sole proprietor, you must include the taxes for your nanny on the FICA and FUTA forms (940 and 941) that you file for your business. And you use the EIN from your sole proprietorship to report the taxes. You also must provide your nanny with a Form W-2.
Recordkeeping
Maintain careful tax records for each household employee. Keep them for at least four years from the later of the due date of the return or the date the tax was paid. Records include: employee name, address, Social Security number; employment dates; wages paid; withheld FICA or income taxes; FICA taxes paid by you for your worker; and copies of forms filed.
Contact us for help or with questions about how to comply with these requirements
© 2020
The possible tax consequences of PPP loans

|
The tax implications of employer-provided life insurance

Does your employer provide you with group term life insurance? If so, and if the coverage is higher than $50,000, this employee benefit may create undesirable income tax consequences for you.
“Phantom income”
The first $50,000 of group term life insurance coverage that your employer provides is excluded from taxable income and doesn’t add anything to your income tax bill. But the employer-paid cost of group term coverage in excess of $50,000 is taxable income to you. It’s included in the taxable wages reported on your Form W-2 — even though you never actually receive it. In other words, it’s “phantom income.”
What’s worse, the cost of group term insurance must be determined under a table prepared by IRS even if the employer’s actual cost is less than the cost figured under the table. Under these determinations, the amount of taxable phantom income attributed to an older employee is often higher than the premium the employee would pay for comparable coverage under an individual term policy. This tax trap gets worse as the employee gets older and as the amount of his or her compensation increases.
Check your W-2
What should you do if you think the tax cost of employer-provided group term life insurance is undesirably high? First, you should establish if this is actually the case. If a specific dollar amount appears in Box 12 of your Form W-2 (with code “C”), that dollar amount represents your employer’s cost of providing you with group-term life insurance coverage in excess of $50,000, less any amount you paid for the coverage. You’re responsible for federal, state and local taxes on the amount that appears in Box 12 and for the associated Social Security and Medicare taxes as well.
But keep in mind that the amount in Box 12 is already included as part of your total “Wages, tips and other compensation” in Box 1 of the W-2, and it’s the Box 1 amount that’s reported on your tax return
Consider some options
If you decide that the tax cost is too high for the benefit you’re getting in return, you should find out whether your employer has a “carve-out” plan (a plan that carves out selected employees from group term coverage) or, if not, whether it would be willing to create one. There are several different types of carve-out plans that employers can offer to their employees.
For example, the employer can continue to provide $50,000 of group term insurance (since there’s no tax cost for the first $50,000 of coverage). Then, the employer can either provide the employee with an individual policy for the balance of the coverage, or give the employee the amount the employer would have spent for the excess coverage as a cash bonus that the employee can use to pay the premiums on an individual policy.
Contact us if you have questions about group term coverage or how much it is adding to your tax bill.
© 2020
File cash transaction reports for your business — on paper or electronically

Does your business receive large amounts of cash or cash equivalents? You may be required to submit forms to the IRS to report these transactions.
Filing requirements
Each person engaged in a trade or business who, in the course of operating, receives more than $10,000 in cash in one transaction, or in two or more related transactions, must file Form 8300. Any transactions conducted in a 24-hour period are considered related transactions. Transactions are also considered related even if they occur over a period of more than 24 hours if the recipient knows, or has reason to know, that each transaction is one of a series of connected transactions.
To complete a Form 8300, you will need personal information about the person making the cash payment, including a Social Security or taxpayer identification number.
You should keep a copy of each Form 8300 for five years from the date you file it, according to the IRS.
Reasons for the reporting
Although many cash transactions are legitimate, the IRS explains that “information reported on (Form 8300) can help stop those who evade taxes, profit from the drug trade, engage in terrorist financing and conduct other criminal activities. The government can often trace money from these illegal activities through the payments reported on Form 8300 and other cash reporting forms.”
What’s considered “cash”
For Form 8300 reporting, cash includes U.S. currency and coins, as well as foreign money. It also includes cash equivalents such as cashier’s checks (sometimes called bank checks), bank drafts, traveler’s checks and money orders.
Money orders and cashier’s checks under $10,000, when used in combination with other forms of cash for a single transaction that exceeds $10,000, are defined as cash for Form 8300 reporting purposes.
Note: Under a separate reporting requirement, banks and other financial institutions report cash purchases of cashier’s checks, treasurer’s checks and/or bank checks, bank drafts, traveler’s checks and money orders with a face value of more than $10,000 by filing currency transaction reports.
E-filing and batch filing
Businesses required to file reports of large cash transactions on Form 8300 should know that in addition to filing on paper, e-filing is an option. The form is due 15 days after a transaction and there’s no charge for the e-file option. Businesses that file electronically get an automatic acknowledgment of receipt when they file.
The IRS also reminds businesses that they can “batch file” their reports, which is especially helpful to those required to file many forms.
Setting up an account
To file Form 8300 electronically, a business must set up an account with FinCEN’s BSA E-Filing System. For more information, interested businesses can also call the BSA E-Filing Help Desk at 866-346-9478 (Monday through Friday from 8 am to 6 pm EST) or email them at BSAEFilingHelp@fincen.gov. Contact us with any questions or for assistance.
© 2020
Are scholarships tax-free or taxable?

COVID-19 is changing the landscape for many schools this fall. But many children and young adults are going back, even if it’s just for online learning, and some parents will be facing tuition bills. If your child has been awarded a scholarship, that’s cause for celebration! But be aware that there may be tax implications.
Scholarships (and fellowships) are generally tax-free for students at elementary, middle and high schools, as well as those attending college, graduate school or accredited vocational schools. It doesn’t matter if the scholarship makes a direct payment to the individual or reduces tuition.
Tuition and related expenses
However, for a scholarship to be tax-free, certain conditions must be satisfied. A scholarship is tax-free only to the extent it’s used to pay for:
- Tuition and fees required to attend the school and
- Fees, books, supplies and equipment required of all students in a particular course.
For example, if a computer is recommended but not required, buying one wouldn’t qualify. Other expenses that don’t qualify include the cost of room and board, travel, research and clerical help.
To the extent a scholarship award isn’t used for qualifying items, it’s taxable. The recipient is responsible for establishing how much of an award is used for tuition and eligible expenses. Maintain records (such as copies of bills, receipts and cancelled checks) that reflect the use of the scholarship money.
Award can’t be payment for services
Subject to limited exceptions, a scholarship isn’t tax-free if the payments are linked to services that your child performs as a condition for receiving the award, even if the services are required of all degree candidates. Therefore, a stipend your child receives for required teaching, research or other services is taxable, even if the child uses the money for tuition or related expenses.
What if you, or a family member, is an employee of an education institution that provides reduced or free tuition? A reduction in tuition provided to you, your spouse or your dependents by the school at which you work isn’t included in your income and isn’t subject to tax.
Returns and recordkeeping
If a scholarship is tax-free and your child has no other income, the award doesn’t have to be reported on a tax return. However, any portion of an award that’s taxable as payment for services is treated as wages. Estimated tax payments may have to be made if the payor doesn’t withhold enough tax. Your child should receive a Form W-2 showing the amount of these “wages” and the amount of tax withheld, and any portion of the award that’s taxable must be reported, even if no Form W-2 is received.
These are just the basic rules. Other rules and limitations may apply. For example, if your child’s scholarship is taxable, it may limit other higher education tax benefits to which you or your child are entitled. As we approach the new school year, best wishes for your child’s success in school. And please contact us if you wish to discuss these or other tax matters further.
© 2020
Why do partners sometimes report more income on tax returns than they receive in cash?

|
Take advantage of a “stepped-up basis” when you inherit property

If you’re planning your estate, or you’ve recently inherited assets, you may be unsure of the “cost” (or “basis”) for tax purposes.
Fair market value rules
Under the fair market value basis rules (also known as the “step-up and step-down” rules), an heir receives a basis in inherited property equal to its date-of-death value. So, for example, if your grandfather bought ABC Corp. stock in 1935 for $500 and it’s worth $5 million at his death, the basis is stepped up to $5 million in the hands of your grandfather’s heirs — and all of that gain escapes federal income tax forever.
The fair market value basis rules apply to inherited property that’s includible in the deceased’s gross estate, and those rules also apply to property inherited from foreign persons who aren’t subject to U.S. estate tax. It doesn’t matter if a federal estate tax return is filed. The rules apply to the inherited portion of property owned by the inheriting taxpayer jointly with the deceased, but not the portion of jointly held property that the inheriting taxpayer owned before his or her inheritance. The fair market value basis rules also don’t apply to reinvestments of estate assets by fiduciaries.
Step up, step down or carryover
It’s crucial for you to understand the fair market value basis rules so that you don’t pay more tax than you’re legally required to.
For example, in the above example, if your grandfather decides to make a gift of the stock during his lifetime (rather than passing it on when he dies), the “step-up” in basis (from $500 to $5 million) would be lost. Property that has gone up in value acquired by gift is subject to the “carryover” basis rules. That means the person receiving the gift takes the same basis the donor had in it (just $500), plus a portion of any gift tax the donor pays on the gift.
A “step-down” occurs if someone dies owning property that has declined in value. In that case, the basis is lowered to the date-of-death value. Proper planning calls for seeking to avoid this loss of basis. Giving the property away before death won’t preserve the basis. That’s because when property that has gone down in value is the subject of a gift, the person receiving the gift must take the date of gift value as his basis (for purposes of determining his or her loss on a later sale). Therefore, a good strategy for property that has declined in value is for the owner to sell it before death so he or she can enjoy the tax benefits of the loss.
These are the basic rules. Other rules and limits may apply. For example, in some cases, a deceased person’s executor may be able to make an alternate valuation election. Contact us for tax assistance when estate planning or after receiving an inheritance.
© 2020
Even if no money changes hands, bartering is a taxable transaction

During the COVID-19 pandemic, many small businesses are strapped for cash. They may find it beneficial to barter for goods and services instead of paying cash for them. If your business gets involved in bartering, remember that the fair market value of goods that you receive in bartering is taxable income. And if you exchange services with another business, the transaction results in taxable income for both parties.
For example, if a computer consultant agrees to exchange services with an advertising agency, both parties are taxed on the fair market value of the services received. This is the amount they would normally charge for the same services. If the parties agree to the value of the services in advance, that will be considered the fair market value unless there is contrary evidence.
In addition, if services are exchanged for property, income is realized. For example, if a construction firm does work for a retail business in exchange for unsold inventory, it will have income equal to the fair market value of the inventory. Another example: If an architectural firm does work for a corporation in exchange for shares of the corporation’s stock, it will have income equal to the fair market value of the stock.
Joining a club
Many businesses join barter clubs that facilitate barter exchanges. In general, these clubs use a system of “credit units” that are awarded to members who provide goods and services. The credits can be redeemed for goods and services from other members.
Bartering is generally taxable in the year it occurs. But if you participate in a barter club, you may be taxed on the value of credit units at the time they’re added to your account, even if you don’t redeem them for actual goods and services until a later year. For example, let’s say that you earn 2,000 credit units one year, and that each unit is redeemable for $1 in goods and services. In that year, you’ll have $2,000 of income. You won’t pay additional tax if you redeem the units the next year, since you’ve already been taxed once on that income.
If you join a barter club, you’ll be asked to provide your Social Security number or employer identification number. You’ll also be asked to certify that you aren’t subject to backup withholding. Unless you make this certification, the club will withhold tax from your bartering income at a 24% rate.
Forms to file
By January 31 of each year, a barter club will send participants a Form 1099-B, “Proceeds from Broker and Barter Exchange Transactions,” which shows the value of cash, property, services and credits that you received from exchanges during the previous year. This information will also be reported to the IRS.
Many benefits
By bartering, you can trade away excess inventory or provide services during slow times, all while hanging onto your cash. You may also find yourself bartering when a customer doesn’t have the money on hand to complete a transaction. As long as you’re aware of the federal and state tax consequences, these transactions can benefit all parties. Contact us if you need assistance or would like more information.
© 2020
Conduct a “paycheck checkup” to make sure your withholding is adequate
|
Businesses: Get ready for the new Form 1099-NEC

There’s a new IRS form for business taxpayers that pay or receive nonemployee compensation.
Beginning with tax year 2020, payers must complete Form 1099-NEC, Nonemployee Compensation, to report any payment of $600 or more to a payee.
Why the new form?
Prior to 2020, Form 1099-MISC was filed to report payments totaling at least $600 in a calendar year for services performed in a trade or business by someone who isn’t treated as an employee. These payments are referred to as nonemployee compensation (NEC) and the payment amount was reported in box 7.
Form 1099-NEC was reintroduced to alleviate the confusion caused by separate deadlines for Form 1099-MISC that report NEC in box 7 and all other Form 1099-MISC for paper filers and electronic filers. The IRS announced in July 2019 that, for 2020 and thereafter, it will reintroduce the previously retired Form 1099-NEC, which was last used in the 1980s.
What businesses will file?
Payers of nonemployee compensation will now use Form 1099-NEC to report those payments.
Generally, payers must file Form 1099-NEC by January 31. For 2020 tax returns, the due date will be February 1, 2021, because January 31, 2021, is on a Sunday. There’s no automatic 30-day extension to file Form 1099-NEC. However, an extension to file may be available under certain hardship conditions.
Can a business get an extension?
Form 8809 is used to file for an extension for all types of Forms 1099, as well as for other forms. The IRS recently released a draft of Form 8809. The instructions note that there are no automatic extension requests for Form 1099-NEC. Instead, the IRS will grant only one 30-day extension, and only for certain reasons.
Requests must be submitted on paper. Line 7 lists reasons for requesting an extension. The reasons that an extension to file a Form 1099-NEC (and also a Form W-2, Wage and Tax Statement) will be granted are:
- The filer suffered a catastrophic event in a federally declared disaster area that made the filer unable to resume operations or made necessary records unavailable.
- A filer’s operation was affected by the death, serious illness or unavoidable absence of the individual responsible for filing information returns.
- The operation of the filer was affected by fire, casualty or natural disaster.
- The filer was “in the first year of establishment.”
- The filer didn’t receive data on a payee statement such as Schedule K-1, Form 1042-S, or the statement of sick pay required under IRS regulations in time to prepare an accurate information return.
Need help?
If you have questions about filing Form 1099-NEC or any tax forms, contact us. We can assist you in staying in compliance with all rules.
© 2020
After you file your tax return: 3 issues to consider

The tax filing deadline for 2019 tax returns has been extended until July 15 this year, due to the COVID-19 pandemic. After your 2019 tax return has been successfully filed with the IRS, there may still be some issues to bear in mind. Here are three considerations.
1. Some tax records can now be thrown away
You should keep tax records related to your return for as long as the IRS can audit your return or assess additional taxes. In general, the statute of limitations is three years after you file your return. So you can generally get rid of most records related to tax returns for 2016 and earlier years. (If you filed an extension for your 2016 return, hold on to your records until at least three years from when you filed the extended return.)
However, the statute of limitations extends to six years for taxpayers who understate their gross income by more than 25%.
You’ll need to hang on to certain tax-related records longer. For example, keep the actual tax returns indefinitely, so you can prove to the IRS that you filed a legitimate return. (There’s no statute of limitations for an audit if you didn’t file a return or you filed a fraudulent one.)
When it comes to retirement accounts, keep records associated with them until you’ve depleted the account and reported the last withdrawal on your tax return, plus three (or six) years. And retain records related to real estate or investments for as long as you own the asset, plus at least three years after you sell it and report the sale on your tax return. (You can keep these records for six years if you want to be extra safe.)
2. You can check up on your refund
The IRS has an online tool that can tell you the status of your refund. Go to irs.gov and click on “Get Your Refund Status” to find out about yours. You’ll need your Social Security number, filing status and the exact refund amount.
3. You can file an amended return if you forgot to report something
In general, you can file an amended tax return and claim a refund within three years after the date you filed your original return or within two years of the date you paid the tax, whichever is later. So for a 2019 tax return that you file on July 15, 2020, you can generally file an amended return until July 15, 2023.
However, there are a few opportunities when you have longer to file an amended return. For example, the statute of limitations for bad debts is longer than the usual three-year time limit for most items on your tax return. In general, you can amend your tax return to claim a bad debt for seven years from the due date of the tax return for the year that the debt became worthless.
We can help
Contact us if you have questions about tax record retention, your refund or filing an amended return. We’re not just available at tax filing time — we’re here all year!
© 2020
Steer clear of the Trust Fund Recovery Penalty

If you own or manage a business with employees, you may be at risk for a severe tax penalty. It’s called the “Trust Fund Recovery Penalty” because it applies to the Social Security and income taxes required to be withheld by a business from its employees’ wages.
Because the taxes are considered property of the government, the employer holds them in “trust” on the government’s behalf until they’re paid over. The penalty is also sometimes called the “100% penalty” because the person liable and responsible for the taxes will be penalized 100% of the taxes due. Accordingly, the amounts IRS seeks when the penalty is applied are usually substantial, and IRS is very aggressive in enforcing the penalty.
Far-reaching penalty
The Trust Fund Recovery Penalty is among the more dangerous tax penalties because it applies to a broad range of actions and to a wide range of people involved in a business.
Here are some answers to questions about the penalty so you can safely stay clear of it.
Which actions are penalized? The Trust Fund Recovery Penalty applies to any willful failure to collect, or truthfully account for, and pay over Social Security and income taxes required to be withheld from employees’ wages.
Who is at risk? The penalty can be imposed on anyone “responsible” for collection and payment of the tax. This has been broadly defined to include a corporation’s officers, directors and shareholders under a duty to collect and pay the tax as well as a partnership’s partners, or any employee of the business with such a duty. Even voluntary board members of tax-exempt organizations, who are generally excepted from responsibility, can be subject to this penalty under certain circumstances. In addition, in some cases, responsibility has been extended to family members close to the business, and to attorneys and accountants.
IRS says responsibility is a matter of status, duty and authority. Anyone with the power to see that the taxes are (or aren’t) paid may be responsible. There’s often more than one responsible person in a business, but each is at risk for the entire penalty. Although a taxpayer held liable can sue other responsible people for contribution, this is an action he or she must take entirely on his or her own after he or she pays the penalty. It isn’t part of the IRS collection process.
Here’s how broadly the net can be cast: You may not be directly involved with the payroll tax withholding process in your business. But if you learn of a failure to pay over withheld taxes and have the power to pay them but instead make payments to creditors and others, you become a responsible person.
What’s considered “willful?” For actions to be willful, they don’t have to include an overt intent to evade taxes. Simply bending to business pressures and paying bills or obtaining supplies instead of paying over withheld taxes that are due the government is willful behavior. And just because you delegate responsibilities to someone else doesn’t necessarily mean you’re off the hook. Your failure to take care of the job yourself can be treated as the willful element.
Avoiding the penalty
You should never allow any failure to withhold and any “borrowing” from withheld amounts — regardless of the circumstances. All funds withheld must also be paid over to the government. Contact us for information about the penalty and making tax payments.
© 2020
Some people are required to return Economic Impact Payments that were sent erroneously

The IRS and the U.S. Treasury had disbursed 160.4 million Economic Impact Payments (EIPs) as of May 31, 2020, according to a new report. These are the payments being sent to eligible individuals in response to the economic threats caused by COVID-19. The U.S. Government Accountability Office (GAO) reports that $269.3 billion of EIPs have already been sent through a combination of electronic transfers to bank accounts, paper checks and prepaid debit cards.
Eligible individuals receive $1,200 or $2,400 for a married couple filing a joint return. Individuals may also receive up to an additional $500 for each qualifying child. Those with adjusted gross income over a threshold receive a reduced amount.
Deceased individuals
However, the IRS says some payments were sent erroneously and should be returned. For example, the tax agency says an EIP made to someone who died before receipt of the payment should be returned. Instructions for returning the payment can be found here: https://bit.ly/31ioZ8W
The entire EIP should be returned unless it was made to joint filers and one spouse hadn’t died before receipt. In that case, you only need to return the EIP portion made to the decedent. This amount is $1,200 unless your adjusted gross income exceeded $150,000. If you cannot deposit the payment because it was issued to both spouses and one spouse is deceased, return the check as described in the link above. Once the IRS receives and processes your returned payment, an EIP will be reissued.
The GAO report states that almost 1.1 million payments totaling nearly $1.4 billion had been sent to deceased individuals, as of April 30, 2020. However, these figures don’t “reflect returned checks or rejected direct deposits, the amount of which IRS and the Treasury are still determining.”
In addition, the IRS states that EIPs sent to incarcerated individuals should be returned.
Payments that don’t have to be returned
The IRS notes on its website that some people receiving an erroneous payment don’t have to return it. For example, if a child’s parents who aren’t married to each other both get an additional $500 for the same qualifying child, one of them isn’t required to pay it back.
But each parent should keep Notice 1444, which the IRS will mail to them within 15 days after the EIP is made, with their 2020 tax records.
Some individuals still waiting
Be aware that the government is still sending out EIPs. If you believe you’re eligible for one but haven’t received it, you will be able to claim your payment when you file your 2020 tax return.
If you need the payment sooner, you can call the IRS EIP line at 800-919-9835 but the Treasury Department notes that “call volumes are high, so call times may be longer than anticipated.”
© 2020
Haven’t filed your 2019 business tax return yet? There may be ways to chip away at your bill

|
What qualifies as a “coronavirus-related distribution” from a retirement plan?
As you may have heard, the Coronavirus Aid, Relief and Economic Security (CARES) Act allows “qualified” people to take certain “coronavirus-related distributions” from their retirement plans without paying tax.
So how do you qualify? In other words, what’s a coronavirus-related distribution?
Early distribution basics
In general, if you withdraw money from an IRA or eligible retirement plan before you reach age 59½, you must pay a 10% early withdrawal tax. This is in addition to any tax you may owe on the income from the withdrawal. There are several exceptions to the general rule. For example, you don’t owe the additional 10% tax if you become totally and permanently disabled or if you use the money to pay qualified higher education costs or medical expenses
New exception
Under the CARES Act, you can take up to $100,000 in coronavirus-related distributions made from an eligible retirement plan between January 1 and December 30, 2020. These coronavirus-related distributions aren’t subject to the 10% additional tax that otherwise generally applies to distributions made before you reach age 59½.
What’s more, a coronavirus-related distribution can be included in income in installments over a three-year period, and you have three years to repay it to an IRA or plan. If you recontribute the distribution back into your IRA or plan within three years of the withdrawal date, you can treat the withdrawal and later recontribution as a totally tax-free rollover.
In new guidance (Notice 2020-50) the IRS explains who qualifies to take a coronavirus-related distribution. A qualified individual is someone who:
- Is diagnosed (or whose spouse or dependent is diagnosed) with COVID-19 after taking a test approved by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (including a test authorized under the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act); or
- Experiences adverse financial consequences as a result of certain events. To qualify under this test, the individual (or his or her spouse or member of his or her household sharing his or her principal residence) must:
- Be quarantined, be furloughed or laid off, or have work hours reduced due to COVID-19;
- Be unable to work due to a lack of childcare because of COVID-19;
- Experience a business that he or she owns or operates due to COVID-19 close or have reduced hours;
- Have pay or self-employment income reduced because of COVID-19; or
- Have a job offer rescinded or start date for a job delayed due to COVID-19.
Favorable rules
As you can see, the rules allow many people — but not everyone — to take retirement plan distributions under the new exception. If you decide to take advantage of it, be sure to keep good records to show that you qualify. Be careful: You’ll be taxed on the coronavirus-related distribution amount that you don’t recontribute within the three-year window. But you won’t have to worry about owing the 10% early withdrawal penalty if you’re under 59½. Other rules and restrictions apply. Contact us if you have questions or need assistance.
© 2020
Launching a business? How to treat start-up expenses on your tax return

While the COVID-19 crisis has devastated many existing businesses, the pandemic has also created opportunities for entrepreneurs to launch new businesses. For example, some businesses are being launched online to provide products and services to people staying at home.
Entrepreneurs often don’t know that many expenses incurred by start-ups can’t be currently deducted. You should be aware that the way you handle some of your initial expenses can make a large difference in your tax bill.
How expenses must be handled
If you’re starting or planning a new enterprise, keep these key points in mind:
- Start-up costs include those incurred or paid while creating an active trade or business — or investigating the creation or acquisition of one.
- Under the Internal Revenue Code, taxpayers can elect to deduct up to $5,000 of business start-up and $5,000 of organizational costs in the year the business begins. As you know, $5,000 doesn’t get you very far today! And the $5,000 deduction is reduced dollar-for-dollar by the amount by which your total start-up or organizational costs exceed $50,000. Any remaining costs must be amortized over 180 months on a straight-line basis.
- No deductions or amortization deductions are allowed until the year when “active conduct” of your new business begins. Generally, that means the year when the business has all the pieces in place to begin earning revenue. To determine if a taxpayer meets this test, the IRS and courts generally ask questions such as: Did the taxpayer undertake the activity intending to earn a profit? Was the taxpayer regularly and actively involved? Did the activity actually begin?
Expenses that qualify
In general, start-up expenses include all amounts you spend to:
- Investigate the creation or acquisition of a business,
- Create a business, or
- Engage in a for-profit activity in anticipation of that activity becoming an active business.
To be eligible for the election, an expense also must be one that would be deductible if it were incurred after a business began. One example is money you spend analyzing potential markets for a new product or service.
To qualify as an “organization expense,” the expenditure must be related to creating a corporation or partnership. Some examples of organization expenses are legal and accounting fees for services related to organizing a new business and filing fees paid to the state of incorporation.
Thinking ahead
If you have start-up expenses that you’d like to deduct this year, you need to decide whether to take the elections described above. Recordkeeping is critical. Contact us about your start-up plans. We can help with the tax and other aspects of your new business.
© 2020
If you’re selling your home, don’t forget about taxes

Traditionally, spring and summer are popular times for selling a home. Unfortunately, the COVID-19 crisis has resulted in a slowdown in sales. The National Association of Realtors (NAR) reports that existing home sales in April decreased year-over-year, 17.2% from a year ago. One bit of good news is that home prices are up. The median existing-home price in April was $286,800, up 7.4% from April 2019, according to the NAR.
If you’re planning to sell your home this year, it’s a good time to review the tax considerations.
Some gain is excluded
If you’re selling your principal residence, and you meet certain requirements, you can exclude up to $250,000 ($500,000 for joint filers) of gain. Gain that qualifies for the exclusion is also excluded from the 3.8% net investment income tax.
To be eligible for the exclusion, you must meet these tests:
- The ownership test. You must have owned the property for at least two years during the five-year period ending on the sale date.
- The use test. You must have used the property as a principal residence for at least two years during the same five-year period. (Periods of ownership and use don’t need to overlap.)
In addition, you can’t use the exclusion more than once every two years.
Larger gains
What if you have more than $250,000/$500,000 of profit when selling your home? Any gain that doesn’t qualify for the exclusion generally will be taxed at your long-term capital gains rate, provided you owned the home for at least a year. If you didn’t, the gain will be considered short term and subject to your ordinary-income rate, which could be more than double your long-term rate.
Here are two other tax considerations when selling a home:
- Keep track of your basis. To support an accurate tax basis, be sure to maintain complete records, including information on your original cost and subsequent improvements, reduced by any casualty losses and depreciation claimed based on business use.
- Be aware that you can’t deduct a loss. If you sell your principal residence at a loss, it generally isn’t deductible. But if a portion of your home is rented out or used exclusively for your business, the loss attributable to that part may be deductible.
If you’re selling a second home (for example, a beach house), it won’t be eligible for the gain exclusion. But if it qualifies as a rental property, it can be considered a business asset, and you may be able to defer tax on any gains through an installment sale or a Section 1031 like-kind exchange. In addition, you may be able to deduct a loss.
For many people, their homes are their most valuable asset. So before selling yours, make sure you understand the tax implications. We can help you plan ahead to minimize taxes and answer any questions you have about your home sale.
© 2020
Good records are the key to tax deductions and trouble-free IRS audits

If you operate a small business, or you’re starting a new one, you probably know you need to keep records of your income and expenses. In particular, you should carefully record your expenses in order to claim the full amount of the tax deductions to which you’re entitled. And you want to make sure you can defend the amounts reported on your tax returns if you’re ever audited by the IRS or state tax agencies.
Certain types of expenses, such as automobile, travel, meals and office-at-home expenses, require special attention because they’re subject to special recordkeeping requirements or limitations on deductibility.
It’s interesting to note that there’s not one way to keep business records. In its publication “Starting a Business and Keeping Records,” the IRS states: “Except in a few cases, the law does not require any specific kind of records. You can choose any recordkeeping system suited to your business that clearly shows your income and expenses.”
That being said, many taxpayers don’t make the grade when it comes to recordkeeping. Here are three court cases to illustrate some of the issues.
Case 1: Without records, the IRS can reconstruct your income
If a taxpayer is audited and doesn’t have good records, the IRS can perform a “bank-deposits analysis” to reconstruct income. It assumes that all money deposited in accounts during a given period is taxable income. That’s what happened in the case of the business owner of a coin shop and precious metals business. The owner didn’t agree with the amount of income the IRS attributed to him after it conducted a bank-deposits analysis.
But the U.S. Tax Court noted that if the taxpayer kept adequate records, “he could have avoided the bank-deposits analysis altogether.” Because he didn’t, the court found the bank analysis was appropriate and the owner underreported his business income for the year. (TC Memo 2020-4)
Case 2: Expenses must be business related
In another case, an independent insurance agent’s claims for a variety of business deductions were largely denied. The Tax Court found that he had documentation in the form of cancelled checks and credit card statements that showed expenses were paid. But there was no proof of a business purpose.
For example, he made utility payments for natural gas, electricity, water and sewer, but the records didn’t show whether the services were for his business or his home. (TC Memo 2020-25)
Case number 3: No records could mean no deductions
In this case, married taxpayers were partners in a travel agency and owners of a marketing company. The IRS denied their deductions involving auto expenses, gifts, meals and travel because of insufficient documentation. The couple produced no evidence about the business purpose of gifts they had given. In addition, their credit card statements and other information didn’t detail the time, place, and business relationship for meal expenses or indicate that travel was conducted for business purposes.
“The disallowed deductions in this case are directly attributable to (the taxpayer’s) failure to maintain adequate records,“ the court stated. (TC Memo 2020-7)
We can help
Contact us if you need assistance retaining adequate business records. Taking a meticulous, proactive approach to how you keep records can protect your deductions and help make an audit much less painful.
© 2020
Seniors: Can you deduct Medicare premiums?
|
Rioting damage at your business? You may be able to claim casualty loss deductions

|
A nonworking spouse can still have an IRA

It’s often difficult for married couples to save as much as they need for retirement when one spouse doesn’t work outside the home — perhaps so that spouse can take care of children or elderly parents. In general, an IRA contribution is allowed only if a taxpayer has compensation. However, an exception involves a “spousal” IRA. It allows a contribution to be made for a nonworking spouse.
Under the spousal IRA rules, the amount that a married couple can contribute to an IRA for a nonworking spouse in 2020 is $6,000, which is the same limit that applies for the working spouse.
Two main benefits
As you may be aware, IRAs offer two types of benefits for taxpayers who make contributions to them.
- Contributions of up to $6,000 a year to an IRA may be tax deductible.
- The earnings on funds within the IRA are not taxed until withdrawn. (Alternatively, you may make contributions to a Roth IRA. There’s no deduction for Roth IRA contributions, but, if certain requirements are met, distributions are tax-free.)
As long as the couple together has at least $12,000 of earned income, $6,000 can be contributed to an IRA for each, for a total of $12,000. (The contributions for both spouses can be made to either a regular IRA or a Roth IRA, or split between them, as long as the combined contributions don’t exceed the $12,000 limit.)
Catching up
In addition, individuals who are age 50 or older can make “catch-up” contributions to an IRA or Roth IRA in the amount of $1,000. Therefore, in 2020, for a taxpayer and his or her spouse, both of whom will have reached age 50 by the end of the year, the combined limit of the deductible contributions to an IRA for each spouse is $7,000, for a combined deductible limit of $14,000.
There’s one catch, however. If, in 2020, the working spouse is an active participant in either of several types of retirement plans, a deductible contribution of up to $6,000 (or $7,000 for a spouse who will be 50 by the end of the year) can be made to the IRA of the non-participant spouse only if the couple’s AGI doesn’t exceed $104,000. This limit is phased out for AGI between $196,000 and $206,000.
Contact us if you’d like more information about IRAs or you’d like to discuss retirement planning.
© 2020
Business meal deductions: The current rules amid proposed changes

Restaurants and entertainment venues have been hard hit by the novel coronavirus (COVID-19) pandemic. One of the tax breaks that President Trump has proposed to help them is an increase in the amount that can be deducted for business meals and entertainment.
It’s unclear whether Congress would go along with enhanced business meal and entertainment deductions. But in the meantime, let’s review the current rules.
Before the pandemic hit, many businesses spent money “wining and dining” current or potential customers, vendors and employees. The rules for deducting these expenses changed under the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA), but you can still claim some valuable write-offs. And keep in mind that deductions are available for business meal takeout and delivery.
One of the biggest changes is that you can no longer deduct most business-related entertainment expenses. Beginning in 2018, the TCJA disallows deductions for entertainment expenses, including those for sports events, theater productions, golf outings and fishing trips.
50% meal deductions
Currently, you can deduct 50% of the cost of food and beverages for meals conducted with business associates. However, you need to follow three basic rules in order to prove that your expenses are business related:
- The expenses must be “ordinary and necessary” in carrying on your business. This means your food and beverage costs are customary and appropriate. They shouldn’t be lavish or extravagant.
- The expenses must be directly related or associated with your business. This means that you expect to receive a concrete business benefit from them. The principal purpose for the meal must be business. You can’t go out with a group of friends for the evening, discuss business with one of them for a few minutes, and then write off the check.
- You must be able to substantiate the expenses. There are requirements for proving that meal and beverage expenses qualify for a deduction. You must be able to establish the amount spent, the date and place where the meals took place, the business purpose and the business relationship of the people involved.
It’s a good idea to set up detailed recordkeeping procedures to keep track of business meal costs. That way, you can prove them and the business connection in the event of an IRS audit.
Other considerations
What if you spend money on food and beverages at an entertainment event? The IRS has clarified that taxpayers can still deduct 50% of food and drink expenses incurred at entertainment events, but only if business was conducted during the event or shortly before or after. The food-and-drink expenses should also be “stated separately from the cost of the entertainment on one or more bills, invoices or receipts,” according to the guidance.
Another related tax law change involves meals provided to employees on the business premises. Before the TCJA, these meals provided to an employee for the convenience of the employer were 100% deductible by the employer. Beginning in 2018, meals provided for the convenience of an employer in an on-premises cafeteria or elsewhere on the business property are only 50% deductible. After 2025, these meals won’t be deductible at all.
Plan ahead
As you can see, the treatment of meal and entertainment expenses became more complicated after the TCJA. It’s possible the deductions could increase substantially under a new stimulus law, if Congress passes one. We’ll keep you updated. In the meantime, we can answer any questions you may have concerning business meal and entertainment deductions.
© 2020
IRS releases 2021 amounts for Health Savings Accounts

The IRS recently released the 2021 inflation-adjusted amounts for Health Savings Accounts (HSAs).
HSA basics
An HSA is a trust created or organized exclusively for the purpose of paying the “qualified medical expenses” of an “account beneficiary.” An HSA can only be established for the benefit of an “eligible individual” who is covered under a “high deductible health plan.” In addition, a participant can’t be enrolled in Medicare or have other health coverage (exceptions include dental, vision, long-term care, accident and specific disease insurance).
In general, a high deductible health plan (HDHP) is a plan that has an annual deductible that isn’t less than $1,000 for self-only coverage and $2,000 for family coverage. In addition, the sum of the annual deductible and other annual out-of-pocket expenses required to be paid under the plan for covered benefits (but not for premiums) cannot exceed $5,000 for self-only coverage, and $10,000 for family coverage.
Within specified dollar limits, an above-the-line tax deduction is allowed for an individual's contribution to an HSA. This annual contribution limitation and the annual deductible and out-of-pocket expenses under the tax code are adjusted annually for inflation.
Inflation adjustments for 2021 contributions
In Revenue Procedure 2020-32, the IRS released the 2021 inflation-adjusted figures for contributions to HSAs, which are as follows:
Annual contribution limitation. For calendar year 2021, the annual contribution limitation for an individual with self-only coverage under a HDHP is $3,600. For an individual with family coverage, the amount is $7,200. This is up from $3,550 and $7,100, respectively, for 2020.
High deductible health plan defined. For calendar year 2021, an HDHP is a health plan with an annual deductible that isn’t less than $1,400 for self-only coverage or $2,800 for family coverage (these amounts are unchanged from 2020). In addition, annual out-of-pocket expenses (deductibles, co-payments, and other amounts, but not premiums) can’t exceed $7,000 for self-only coverage or $14,000 for family coverage (up from $6,900 and $13,800, respectively, for 2020).
A variety of benefits
There are many advantages to HSAs. Contributions to the accounts are made on a pre-tax basis. The money can accumulate year after year tax free and be withdrawn tax free to pay for a variety of medical expenses such as doctor visits, prescriptions, chiropractic care and premiums for long-term-care insurance. In addition, an HSA is "portable." It stays with an account holder if he or she changes employers or leaves the work force. For more information about HSAs, contact your employee benefits and tax advisor.
© 2020
Student loan interest: Can you deduct it on your tax return?

The economic impact of the novel coronavirus (COVID-19) is unprecedented and many taxpayers with student loans have been hard hit.
The Coronavirus Aid, Relief and Economic Security (CARES) Act contains some assistance to borrowers with federal student loans. Notably, federal loans were automatically placed in an administrative forbearance, which allows borrowers to temporarily stop making monthly payments. This payment suspension is scheduled to last until September 30, 2020.
Tax deduction rules
Despite the suspension, borrowers can still make payments if they choose. And borrowers in good standing made payments earlier in the year and will likely make them later in 2020. So can you deduct the student loan interest on your tax return?
The answer is yes, depending on your income and subject to certain limits. The maximum amount of student loan interest you can deduct each year is $2,500. The deduction is phased out if your adjusted gross income (AGI) exceeds certain levels.
For 2020, the deduction is phased out for taxpayers who are married filing jointly with AGI between $140,000 and $170,000 ($70,000 and $85,000 for single filers). The deduction is unavailable for taxpayers with AGI of $170,000 ($85,000 for single filers) or more. Married taxpayers must file jointly to claim the deduction.
Other requirements
The interest must be for a “qualified education loan,” which means debt incurred to pay tuition, room and board, and related expenses to attend a post-high school educational institution. Certain vocational schools and post-graduate programs also may qualify.
The interest must be on funds borrowed to cover qualified education costs of the taxpayer, his or her spouse or a dependent. The student must be a degree candidate carrying at least half the normal full-time workload. Also, the education expenses must be paid or incurred within a reasonable time before or after the loan is taken out.
It doesn’t matter when the loan was taken out or whether interest payments made in earlier years on the loan were deductible or not. And no deduction is allowed to a taxpayer who can be claimed as a dependent on another taxpayer’s return.
The deduction is taken “above the line.” In other words, it’s subtracted from gross income to determine AGI. Thus, it’s available even to taxpayers who don’t itemize deductions.
Document expenses
Taxpayers should keep records to verify eligible expenses. Documenting tuition isn’t likely to pose a problem. However, take care to document other qualifying expenditures for items such as books, equipment, fees, and transportation. Documenting room and board expenses should be simple if a student lives in a dormitory. Student who live off campus should maintain records of room and board expenses, especially when there are complicating factors such as roommates.
Contact us if you have questions about deducting student loan interest or for information on other tax breaks related to paying for college.
© 2020
Fortunate enough to get a PPP loan? Forgiven expenses aren’t deductible

The IRS has issued guidance clarifying that certain deductions aren’t allowed if a business has received a Paycheck Protection Program (PPP) loan. Specifically, an expense isn’t deductible if both:
- The payment of the expense results in forgiveness of a loan made under the PPP, and ;
- The income associated with the forgiveness is excluded from gross income under the Coronavirus Aid, Relief, and Economic Security (CARES) Act.
PPP basics
The CARES Act allows a recipient of a PPP loan to use the proceeds to pay payroll costs, certain employee healthcare benefits, mortgage interest, rent, utilities and interest on other existing debt obligations.
A recipient of a covered loan can receive forgiveness of the loan in an amount equal to the sum of payments made for the following expenses during the 8-week “covered period” beginning on the loan’s origination date: 1) payroll costs, 2) interest on any covered mortgage obligation, 3) payment on any covered rent, and 4) covered utility payments.
The law provides that any forgiven loan amount “shall be excluded from gross income.”
Deductible expenses
So the question arises: If you pay for the above expenses with PPP funds, can you then deduct the expenses on your tax return?
The tax code generally provides for a deduction for all ordinary and necessary expenses paid or incurred during the taxable year in carrying on a trade or business. Covered rent obligations, covered utility payments, and payroll costs consisting of wages and benefits paid to employees comprise typical trade or business expenses for which a deduction generally is appropriate. The tax code also provides a deduction for certain interest paid or accrued during the taxable year on indebtedness, including interest paid or incurred on a mortgage obligation of a trade or business.
No double tax benefit
In IRS Notice 2020-32, theIRS clarifies that no deduction is allowed for an expense that is otherwise deductible if payment of the expense results in forgiveness of a covered loan pursuant to the CARES Act and the income associated with the forgiveness is excluded from gross income under the law. The Notice states that “this treatment prevents a double tax benefit.”
More possibly to come
Two members of Congress say they’re opposed to the IRS stand on this issue. Senate Finance Committee Chair Chuck Grassley (R-IA) and his counterpart in the House, Ways and Means Committee Chair Richard E. Neal (D-MA), oppose the tax treatment. Neal said it doesn’t follow congressional intent and that he’ll seek legislation to make certain expenses deductible. Stay tuned.
© 2020
Did you get an Economic Impact Payment that was less than you expected?

Nearly everyone has heard about the Economic Impact Payments (EIPs) that the federal government is sending to help mitigate the effects of the coronavirus (COVID-19) pandemic. The IRS reports that in the first four weeks of the program, 130 million individuals received payments worth more than $200 billion.
However, some people are still waiting for a payment. And others received an EIP but it was less than what they were expecting. Here are some answers why this might have happened.
Basic amounts
If you’re under a certain adjusted gross income (AGI) threshold, you’re generally eligible for the full $1,200 ($2,400 for married couples filing jointly). In addition, if you have a “qualifying child,” you’re eligible for an additional $500.
Here are some of the reasons why you may receive less:
Your child isn’t eligible.Only children eligible for the Child Tax Credit qualify for the additional $500 per child. That means you must generally be related to the child, live with them more than half the year and provide at least half of their support. A qualifying child must be a U.S. citizen, permanent resident or other qualifying resident alien; be under the age of 17 at the end of the year for the tax return on which the IRS bases the payment; and have a Social Security number or Adoption Taxpayer Identification Number.
Note: A dependent college student doesn’t qualify for an EIP, and even if their parents may claim him or her as a dependent, the student normally won’t qualify for the additional $500.
You make too much money.You’re eligible for a full EIP if your AGI is up to: $75,000 for individuals, $112,500 for head of household filers and $150,000 for married couples filing jointly. For filers with income above those amounts, the payment amount is reduced by $5 for each $100 above the $75,000/$112,500/$150,000 thresholds.
You’re eligible for a reduced payment if your AGI is between: $75,000 and $99,000 for an individual; $112,500 and $136,500 for a head of household; and $150,000 and $198,000 for married couples filing jointly. Filers with income exceeding those amounts with no children aren’t eligible and won’t receive payments.
You have some debts.The EIP is offset by past-due child support. And it may be reduced by garnishments from creditors. Federal tax refunds, including EIPs, aren’t protected from garnishment by creditors under federal law once the proceeds are deposited into a bank account.
If you receive an incorrect amount
These are only a few of the reasons why an EIP might be less than you expected. If you receive an incorrect amount and you meet the criteria to receive more, you may qualify to receive an additional amount early next year when you file your 2020 federal tax return. We can evaluate your situation when we prepare your return. And if you’re still waiting for a payment, be aware that the IRS is still mailing out paper EIPs and announced that they’ll continue to go out over the next few months.
© 2020
There’s still time to make a deductible IRA contribution for 2019

Do you want to save more for retirement on a tax-favored basis? If so, and if you qualify, you can make a deductible traditional IRA contribution for the 2019 tax year between now and the extended tax filing deadline and claim the write-off on your 2019 return. Or you can contribute to a Roth IRA and avoid paying taxes on future withdrawals.
You can potentially make a contribution of up to $6,000 (or $7,000 if you were age 50 or older as of December 31, 2019). If you’re married, your spouse can potentially do the same, thereby doubling your tax benefits.
The deadline for 2019 traditional and Roth contributions for most taxpayers would have been April 15, 2020. However, because of the novel coronavirus (COVID-19) pandemic, the IRS extended the deadline to file 2019 tax returns and make 2019 IRA contributions until July 15, 2020.
Of course, there are some ground rules. You must have enough 2019 earned income (from jobs, self-employment, etc.) to equal or exceed your IRA contributions for the tax year. If you’re married, either spouse can provide the necessary earned income.
Also, deductible IRA contributions are reduced or eliminated if last year’s modified adjusted gross income (MAGI) is too high.
Two contribution types
If you haven’t already maxed out your 2019 IRA contribution limit, consider making one of these three types of contributions by the deadline:
1. Deductible traditional. With traditional IRAs, account growth is tax-deferred and distributions are subject to income tax. If you and your spouse don’t participate in an employer-sponsored plan such as a 401(k), the contribution is fully deductible on your 2019 tax return. If you or your spouse do participate in an employer-sponsored plan, your deduction is subject to the following MAGI phaseout:
- For married taxpayers filing jointly, the phaseout range is specific to each spouse based on whether he or she is a participant in an employer-sponsored plan:
- For a spouse who participated in 2019: $103,000–$123,000.
- For a spouse who didn’t participate in 2019: $193,000-$203,000.
- For single and head-of-household taxpayers participating in an employer-sponsored plan: $64,000–$74,000.
Taxpayers with MAGIs within the applicable range can deduct a partial contribution. But those with MAGIs exceeding the applicable range can’t deduct any IRA contribution.
2. Roth. Roth IRA contributions aren’t deductible, but qualified distributions — including growth — are tax-free, if you satisfy certain requirements.
Your ability to contribute, however, is subject to a MAGI-based phaseout:
- For married taxpayers filing jointly: $193,000–$203,000.
- For single and head-of-household taxpayers: $122,000–$137,000.
You can make a partial contribution if your 2019 MAGI is within the applicable range, but no contribution if it exceeds the top of the range.
3. Nondeductible traditional.
If your income is too high for you to fully benefit from a deductible traditional or a Roth contribution, you may benefit from a nondeductible contribution to a traditional IRA. The account can still grow tax-deferred, and when you take qualified distributions, you’ll only be taxed on the growth.
Act soon
Because of the extended deadline, you still have time to make traditional and Roth IRA contributions for 2019 (and you can also contribute for 2020). This is a powerful way to save for retirement on a tax-advantaged basis. Contact us to learn more.
© 2020
Do you have tax questions related to COVID-19? Here are some answers

The coronavirus (COVID-19) pandemic has affected many Americans’ finances. Here are some answers to questions you may have right now.
My employer closed the office and I’m working from home. Can I deduct any of the related expenses?
Unfortunately, no. If you’re an employee who telecommutes, there are strict rules that govern whether you can deduct home office expenses. For 2018–2025 employee home office expenses aren’t deductible. (Starting in 2026, an employee may deduct home office expenses, within limits, if the office is for the convenience of his or her employer and certain requirements are met.)
Be aware that these are the rules for employees. Business owners who work from home may qualify for home office deductions.
My son was laid off from his job and is receiving unemployment benefits. Are they taxable?
Yes. Unemployment compensation is taxable for federal tax purposes. This includes your son’s state unemployment benefits plus the temporary $600 per week from the federal government. (Depending on the state he lives in, his benefits may be taxed for state tax purposes as well.)
Your son can have tax withheld from unemployment benefits or make estimated tax payments to the IRS.
The value of my stock portfolio is currently down. If I sell a losing stock now, can I deduct the loss on my 2020 tax return?
It depends. Let’s say you sell a losing stock this year but earlier this year, you sold stock shares at a gain. You have both a capital loss and a capital gain. Your capital gains and losses for the year must be netted against one another in a specific order, based on whether they’re short-term (held one year or less) or long-term (held for more than one year).
If, after the netting, you have short-term or long-term losses (or both), you can use them to offset up to $3,000 ordinary income ($1,500 for married taxpayers filing separately). Any loss in excess of this limit is carried forward to later years, until all of it is either offset against capital gains or deducted against ordinary income in those years, subject to the $3,000 limit.
I know the tax filing deadline has been extended until July 15 this year. Does that mean I have more time to contribute to my IRA?
Yes. You have until July 15 to contribute to an IRA for 2019. If you’re eligible, you can contribute up to $6,000 to an IRA, plus an extra $1,000 “catch-up” amount if you were age 50 or older on December 31, 2019.
What about making estimated payments for 2020?
The 2020 estimated tax payment deadlines for the first quarter (due April 15) and the second quarter (due June 15) have been extended until July 15, 2020.
Need help?
These are only some of the tax-related questions you may have related to COVID-19. Contact us if you have other questions or need more information about the topics discussed above.
© 2020
The CARES Act liberalizes net operating losses

The Coronavirus Aid, Relief, and Economic Security (CARES) Act eliminates some of the tax-revenue-generating provisions included in a previous tax law. Here’s a look at how the rules for claiming certain tax losses have been modified to provide businesses with relief from the novel coronavirus (COVID-19) crisis.
NOL deductions
Basically, you may be able to benefit by carrying a net operating loss (NOL) into a different year — a year in which you have taxable income — and taking a deduction for it against that year’s income. The CARES Act includes favorable changes to the rules for deducting NOLs. First, it permanently eases the taxable income limitation on deductions.
Under an unfavorable provision included in the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA), an NOL arising in a tax year beginning in 2018 and later and carried over to a later tax year couldn’t offset more than 80% of the taxable income for the carryover year (the later tax year), calculated before the NOL deduction. As explained below, under the TCJA, most NOLs arising in tax years ending after 2017 also couldn’t be carried back to earlier years and used to offset taxable income in those earlier years. These unfavorable changes to the NOL deduction rules were permanent — until now.
For tax years beginning before 2021, the CARES Act removes the TCJA taxable income limitation on deductions for prior-year NOLs carried over into those years. So NOL carryovers into tax years beginning before 2021 can be used to fully offset taxable income for those years. For tax years beginning after 2020, the CARES Act allows NOL deductions equal to the sum of:
- 100% of NOL carryovers from pre-2018 tax years, plus
- The lesser of 100% of NOL carryovers from post-2017 tax years, or 80% of remaining taxable income (if any) after deducting NOL carryovers from pre-2018 tax years.
As you can see, this is a complex rule. But it’s more favorable than what the TCJA allowed and the change is permanent.
Carrybacks allowed for certain losses
Under another unfavorable TCJA provision, NOLs arising in tax years ending after 2017 generally couldn’t be carried back to earlier years and used to offset taxable income in those years. Instead, NOLs arising in tax years ending after 2017 could only be carried forward to later years. But they could be carried forward for an unlimited number of years. (There were exceptions to the general no-carryback rule for losses by farmers and property/casualty insurance companies).
Under the CARES Act, NOLs that arise in tax years beginning in 2018 through 2020 can be carried back for five years.
Important: If it’s beneficial, you can elect to waive the carryback privilege for an NOL and, instead, carry the NOL forward to future tax years. In addition, barring a further tax-law change, the no-carryback rule will come back for NOLs that arise in tax years beginning after 2020.
Past year opportunities
These favorable CARES Act changes may affect prior tax years for which you’ve already filed tax returns. To benefit from the changes, you may need to file an amended tax return. Contact us to learn more.
© 2020
IRA account value down? It might be a good time for a Roth conversion

|
Hiring independent contractors? Make sure they’re properly classified

s a result of the coronavirus (COVID-19) crisis, your business may be using independent contractors to keep costs low. But you should be careful that these workers are properly classified for federal tax purposes. If the IRS reclassifies them as employees, it can be an expensive mistake.
The question of whether a worker is an independent contractor or an employee for federal income and employment tax purposes is a complex one. If a worker is an employee, your company must withhold federal income and payroll taxes, pay the employer’s share of FICA taxes on the wages, plus FUTA tax. Often, a business must also provide the worker with the fringe benefits that it makes available to other employees. And there may be state tax obligations as well.
These obligations don’t apply if a worker is an independent contractor. In that case, the business simply sends the contractor a Form 1099-MISC for the year showing the amount paid (if the amount is $600 or more).
No uniform definition
Who is an “employee?” Unfortunately, there’s no uniform definition of the term.
The IRS and courts have generally ruled that individuals are employees if the organization they work for has the right to control and direct them in the jobs they’re performing. Otherwise, the individuals are generally independent contractors. But other factors are also taken into account.
Some employers that have misclassified workers as independent contractors may get some relief from employment tax liabilities under Section 530. In general, this protection applies only if an employer:
- Filed all federal returns consistent with its treatment of a worker as a contractor,
- Treated all similarly situated workers as contractors, and
- Had a “reasonable basis” for not treating the worker as an employee. For example, a “reasonable basis” exists if a significant segment of the employer’s industry traditionally treats similar workers as contractors.
Note: Section 530 doesn’t apply to certain types of technical services workers. And some categories of individuals are subject to special rules because of their occupations or identities.
Asking for a determination
Under certain circumstances, you may want to ask the IRS (on Form SS-8) to rule on whether a worker is an independent contractor or employee. However, be aware that the IRS has a history of classifying workers as employees rather than independent contractors.
Businesses should consult with us before filing Form SS-8 because it may alert the IRS that your business has worker classification issues — and inadvertently trigger an employment tax audit.
It may be better to properly treat a worker as an independent contractor so that the relationship complies with the tax rules.
Be aware that workers who want an official determination of their status can also file Form SS-8. Disgruntled independent contractors may do so because they feel entitled to employee benefits and want to eliminate self-employment tax liabilities.
If a worker files Form SS-8, the IRS will send a letter to the business. It identifies the worker and includes a blank Form SS-8. The business is asked to complete and return the form to the IRS, which will render a classification decision.
Contact us if you receive such a letter or if you’d like to discuss how these complex rules apply to your business. We can help ensure that none of your workers are misclassified.
© 2020
Answers to questions you may have about Economic Impact Payments

Millions of eligible Americans have already received their Economic Impact Payments (EIPs) via direct deposit or paper checks, according to the IRS. Others are still waiting. The payments are part of the Coronavirus Aid, Relief, and Economic Security (CARES) Act. Here are some answers to questions you may have about EIPs.
Who’s eligible to get an EIP?
Eligible taxpayers who filed their 2018 or 2019 returns and chose direct deposit of their refunds automatically receive an Economic Impact Payment. You must be a U.S. citizen or U.S. resident alien and you can’t be claimed as a dependent on someone else’s tax return. In general, you must also have a valid Social Security number and have adjusted gross income (AGI) under a certain threshold.
The IRS also says that automatic payments will go to people receiving Social Security retirement or disability benefits and Railroad Retirement benefits.
How much are the payments?
EIPs can be up to $1,200 for individuals, or $2,400 for married couples, plus $500 for each qualifying child.
How much income must I have to receive a payment?
You don’t need to have any income to receive a payment. But for higher income people, the payments phase out. The EIP is reduced by 5% of the amount that your AGI exceeds $75,000 ($112,500 for heads of household or $150,000 for married joint filers), until it’s $0.
The payment for eligible individuals with no qualifying children is reduced to $0 once AGI reaches:
$198,000 for married joint filers,
$136,500 for heads of household, and
$99,000 for all others
Each of these threshold amounts increases by $10,000 for each additional qualifying child. For example, because families with one qualifying child receive an additional $500 Payment, their $1,700 Payment ($2,900 for married joint filers) is reduced to $0 once adjusted gross income reaches:
$208,000 for married joint filers,
$146,500 for heads of household,
$109,000 for all others
How will I know if money has been deposited into my bank account?
The IRS stated that it will send letters to EIP recipients about the payment within 15 days after they’re made. A letter will be sent to a recipient’s last known address and will provide information on how the payment was made and how to report any failure to receive it.
Is there a way to check on the status of a payment?
The IRS has introduced a new “Get My Payment” web-based tool that will: show taxpayers either their EIP amount and the scheduled delivery date by direct deposit or paper check, or that a payment hasn’t been scheduled. It also allows taxpayers who didn’t use direct deposit on their last-filed return to provide bank account information. In order to use the tool, you must enter information such as your Social Security number and birthdate. You can access it here: https://bit.ly/2ykLSwa
I tried the tool and I got the message “payment status not available.” Why?
Many people report that they’re getting this message. The IRS states there are many reasons why you may see this. For example, you’re not eligible for a payment or you’re required to file a tax return and haven’t filed yet. In some cases, people are eligible but are still getting this message. Hopefully, the IRS will have it running seamlessly soon.
© 2020
COVID-19: IRS announces more relief and details
|
Relief from not making employment tax deposits due to COVID-19 tax credits

The IRS has issued guidance providing relief from failure to make employment tax deposits for employers that are entitled to the refundable tax credits provided under two laws passed in response to the coronavirus (COVID-19) pandemic. The two laws are the Families First Coronavirus Response Act, which was signed on March 18, 2020, and the Coronavirus Aid, Relief, and Economic Security Act (CARES) Act, which was signed on March 27, 2020.
Employment tax penalty basics
The tax code imposes a penalty for any failure to deposit amounts as required on the date prescribed, unless such failure is due to reasonable cause rather than willful neglect.
An employer’s failure to deposit certain federal employment taxes, including deposits of withheld income taxes and taxes under the Federal Insurance Contributions Act (FICA) is generally subject to a penalty.
COVID-19 relief credits
Employers paying qualified sick leave wages and qualified family leave wages required by the Families First Act, as well as qualified health plan expenses allocable to qualified leave wages, are eligible for refundable tax credits under the Families First Act.
Specifically, provisions of the Families First Act provide a refundable tax credit against an employer’s share of the Social Security portion of FICA tax for each calendar quarter, in an amount equal to 100% of qualified leave wages paid by the employer (plus qualified health plan expenses with respect to that calendar quarter).
Additionally, under the CARES Act, certain employers are also allowed a refundable tax credit under the CARES Act of up to 50% of the qualified wages, including allocable qualified health expenses if they are experiencing:
- A full or partial business suspension due to orders from governmental authorities due to COVID-19, or
- A specified decline in business.
This credit is limited to $10,000 per employee over all calendar quarters combined.
An employer paying qualified leave wages or qualified retention wages can seek an advance payment of the related tax credits by filing Form 7200, Advance Payment of Employer Credits Due to COVID-19.
Available relief
The Families First Act and the CARES Act waive the penalty for failure to deposit the employer share of Social Security tax in anticipation of the allowance of the refundable tax credits allowed under the two laws.
IRS Notice 2020-22 provides that an employer won’t be subject to a penalty for failing to deposit employment taxes related to qualified leave wages or qualified retention wages in a calendar quarter if certain requirements are met. Contact us for more information about whether you can take advantage of this relief.
More breaking news
Be aware the IRS also just extended more federal tax deadlines. The extension, detailed in Notice 2020-23, involves a variety of tax form filings and payment obligations due between April 1 and July 15. It includes estimated tax payments due June 15 and the deadline to claim refunds from 2016. The extended deadlines cover individuals, estates, corporations and others. In addition, the guidance suspends associated interest, additions to tax, and penalties for late filing or late payments until July 15, 2020. Previously, the IRS postponed the due dates for certain federal income tax payments. The new guidance expands on the filing and payment relief. Contact us if you have questions.
© 2020
CARES ACT changes retirement plan and charitable contribution rules

As we all try to keep ourselves, our loved ones, and our communities safe from the coronavirus (COVID-19) pandemic, you may be wondering about some of the recent tax changes that were part of a tax law passed on March 27.
The Coronavirus Aid, Relief, and Economic Security (CARES) Act contains a variety of relief, notably the “economic impact payments” that will be made to people under a certain income threshold. But the law also makes some changes to retirement plan rules and provides a new tax break for some people who contribute to charity.
Waiver of 10% early distribution penalty
IRAs and employer sponsored retirement plans are established to be long-term retirement planning accounts. As such, the IRS imposes a penalty tax of an additional 10% if funds are distributed before reaching age 59½. (However, there are some exceptions to this rule.)
Under the CARES Act, the additional 10% tax on early distributions from IRAs and defined contribution plans (such as 401(k) plans) is waived for distributions made between January 1 and December 31, 2020 by a person who (or whose family) is infected with COVID-19 or is economically harmed by it. Penalty-free distributions are limited to $100,000, and may, subject to guidelines, be re-contributed to the plan or IRA. Income arising from the distributions is spread out over three years unless the employee elects to turn down the spread-out.
Employers may amend defined contribution plans to provide for these distributions. Additionally, defined contribution plans are permitted additional flexibility in the amount and repayment terms of loans to employees who are qualified individuals.
Waiver of required distribution rules
Depending on when you were born, you generally must begin taking annual required minimum distributions (RMDs) from tax-favored retirement accounts — including traditional IRAs, SEP accounts and 401(k)s — when you reach age 70½ or 72. These distributions also are subject to federal and state income taxes. (However, you don’t need to take RMDs from Roth IRAs.)
Under the CARES Act, RMDs that otherwise would have to be made in 2020 from defined contribution plans and IRAs are waived. This includes distributions that would have been required by April 1, 2020, due to the account owner’s having turned age 70½ in 2019.
New charitable deduction tax breaks
The CARES Act makes significant liberalizations to the rules governing charitable deductions including:
- Individuals can claim a $300 “above-the-line” deduction for cash contributions made, generally, to public charities in 2020. This rule means that taxpayers claiming the standard deduction and not itemizing deductions can claim a limited charitable deduction.
- The limit on charitable deductions for individuals that is generally 60% of modified adjusted gross income (the contribution base) doesn’t apply to cash contributions made, generally, to public charities in 2020. Instead, an individual’s eligible contributions, reduced by other contributions, can be as much as 100% of the contribution base. No connection between the contributions and COVID-19 is required.
Far beyond
The CARES Act goes far beyond what is described here. The new law contains many different types of tax and financial relief meant to help individuals and businesses cope with the fallout.
© 2020
Answers to questions about the CARES Act employee retention tax credit

The recently enacted Coronavirus Aid, Relief, and Economic Security (CARES) Act provides a refundable payroll tax credit for 50% of wages paid by eligible employers to certain employees during the COVID-19 pandemic. The employee retention credit is available to employers, including nonprofit organizations, with operations that have been fully or partially suspended as a result of a government order limiting commerce, travel or group meetings.
The credit is also provided to employers who have experienced a greater than 50% reduction in quarterly receipts, measured on a year-over-year basis.
IRS issues FAQs
The IRS has now released FAQs about the credit. Here are some highlights.
How is the credit calculated? The credit is 50% of qualifying wages paid up to $10,000 in total. So the maximum credit for an eligible employer for qualified wages paid to any employee is $5,000.
Wages paid after March 12, 2020, and before Jan. 1, 2021, are eligible for the credit. Therefore, an employer may be able to claim it for qualified wages paid as early as March 13, 2020. Wages aren’t limited to cash payments, but also include part of the cost of employer-provided health care.
When is the operation of a business “partially suspended” for the purposes of the credit?The operation of a business is partially suspended if a government authority imposes restrictions by limiting commerce, travel or group meetings due to COVID-19 so that the business still continues but operates below its normal capacity.
Example: A state governor issues an executive order closing all restaurants and similar establishments to reduce the spread of COVID-19. However, the order allows establishments to provide food or beverages through carry-out, drive-through or delivery. This results in a partial suspension of businesses that provided sit-down service or other on-site eating facilities for customers prior to the executive order.
Is an employer required to pay qualified wages to its employees? No. The CARES Act doesn’t require employers to pay qualified wages.
Is a government employer or self-employed person eligible?No.Government employers aren’t eligible for the employee retention credit. Self-employed individuals also aren’t eligible for the credit for self-employment services or earnings.
Can an employer receive both the tax credits for the qualified leave wages under the Families First Coronavirus Response Act (FFCRA) and the employee retention credit under the CARES Act? Yes, but not for the same wages. The amount of qualified wages for which an employer can claim the employee retention credit doesn’t include the amount of qualified sick and family leave wages for which the employer received tax credits under the FFCRA.
Can an eligible employer receive both the employee retention credit and a loan under the Paycheck Protection Program? No. An employer can’t receive the employee retention credit if it receives a Small Business Interruption Loan under the Paycheck Protection Program, which is authorized under the CARES Act. So an employer that receives a Paycheck Protection loan shouldn’t claim the employee retention credit.
For more information
Here’s a link to more questions: https://bit.ly/2R8syZx . Contact us if you need assistance with tax or financial issues due to COVID-19.
© 2020
Cash payments and tax relief for individuals in new law
|
The new COVID-19 law provides businesses with more relief
|
Individuals get coronavirus (COVID-19) tax and other relief

Taxpayers now have more time to file their tax returns and pay any tax owed because of the coronavirus (COVID-19) pandemic. The Treasury Department and IRS announced that the federal income tax filing due date is automatically extended from April 15, 2020, to July 15, 2020.
Taxpayers can also defer making federal income tax payments, which are due on April 15, 2020, until July 15, 2020, without penalties and interest, regardless of the amount they owe. This deferment applies to all taxpayers, including individuals, trusts and estates, corporations and other non-corporate tax filers as well as those who pay self-employment tax. They can also defer their initial quarterly estimated federal income tax payments for the 2020 tax year (including any self-employment tax) from the normal April 15 deadline until July 15.
No forms to file
Taxpayers don’t need to file any additional forms to qualify for the automatic federal tax filing and payment relief to July 15. However, individual taxpayers who need additional time to file beyond the July 15 deadline, can request a filing extension by filing Form 4868. Businesses who need additional time must file Form 7004. Contact us if you need assistance filing these forms.
If you expect a refund
Of course, not everybody will owe the IRS when they file their 2019 tax returns. If you’re due a refund, you should file as soon as possible. The IRS has stated that despite the COVID-19 outbreak, most tax refunds are still being issued within 21 days.
New law passes, another on the way
On March 18, 2020, President Trump signed the “Families First Coronavirus Response Act,” which provides a wide variety of relief related to COVID-19. It includes free testing, waivers and modifications of Federal nutrition programs, employment-related protections and benefits, health programs and insurance coverage requirements, and related employer tax credits and tax exemptions.
If you’re an employee, you may be eligible for paid sick leave for COVID-19 related reasons. Here are the specifics, according to the IRS:
- An employee who is unable to work because of a need to care for an individual subject to quarantine, to care for a child whose school is closed or whose child care provider is unavailable, and/or the employee is experiencing substantially similar conditions as specified by the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services can receive two weeks (up to 80 hours) of paid sick leave at 2/3 the employee’s pay.
- An employee who is unable to work due to a need to care for a child whose school is closed, or child care provider is unavailable for reasons related to COVID-19, may in some instances receive up to an additional ten weeks of expanded paid family and medical leave at 2/3 the employee’s pay.
As of this writing, Congress was working on passing another bill that would provide additional relief, including checks that would be sent to Americans under certain income thresholds. We will keep you updated about any developments. In the meantime, please contact us with any questions or concerns about your tax or financial situation.
© 2020
Coronavirus (COVID-19): Tax relief for small businesses

Businesses across the country are being affected by the coronavirus (COVID-19). Fortunately, Congress recently passed a law that provides at least some relief. In a separate development, the IRS has issued guidance allowing taxpayers to defer any amount of federal income tax payments due on April 15, 2020, until July 15, 2020, without penalties or interest.
New law
On March 18, the Senate passed the House's coronavirus bill, the Families First Coronavirus Response Act. President Trump signed the bill that day. It includes:
- Paid leave benefits to employees,
- Tax credits for employers and self-employed taxpayers, and
- FICA tax relief for employers.
FICA tax relief for employers.
In Notice 2020-18, the IRS provides relief for taxpayers with a federal income tax payment due April 15, 2020. The due date for making federal income tax payments usually due April 15, 2020 is postponed to July 15, 2020.
Important:The IRS announced that the 2019 income tax filing deadline will be moved to July 15, 2020 from April 15, 2020, because of COVID-19.
Treasury Department Secretary Steven Mnuchin announced on Twitter, “we are moving Tax Day from April 15 to July 15. All taxpayers and businesses will have this additional time to file and make payments without interest or penalties.”
Previously, the U.S. Treasury Department and the IRS had announced that taxpayers could defer making income tax payments for 2019 and estimated income tax payments for 2020 due April 15 (up to certain amounts) until July 15, 2020. Later, the federal government stated that you also don’t have to file a return by April 15.
Of course, if you’re due a tax refund, you probably want to file as soon as possible so you can receive the refund money. And you can still get an automatic filing extension, to October 15, by filing IRS Form 4868. Contact us with any questions you have about filing your return.
Any amount can be deferred
In Notice 2020-18, the IRS stated: “There is no limitation on the amount of the payment that may be postponed.” (Previously, the IRS had announced dollar limits on the tax deferrals but then made a new announcement on March 21 that taxpayers can postpone payments “regardless of the amount owed.”)
In Notice 2020-18, the due date is postponed only for federal income tax payments for 2019 normally due on April 15, 2020 and federal estimated income tax payments (including estimated payments on self-employment income) due on April 15, 2020 for the 2020 tax year.
As of this writing, the IRS hasn’t provided a payment extension for the payment or deposit of other types of federal tax (including payroll taxes and excise taxes).
Contact us
This only outlines the basics of the federal tax relief available at the time this was written. New details are coming out daily. Be aware that many states have also announced tax relief related to COVID-19. And Congress is working on more legislation that will provide additional relief, including sending checks to people under a certain income threshold and providing relief to various industries and small businesses.
We’ll keep you updated. In the meantime, contact us with any questions you have about your situation.
© 2020
Why you should keep life insurance out of your estate

If you have a life insurance policy, you probably want to make sure that the life insurance benefits your family will receive after your death won’t be included in your estate. That way, the benefits won’t be subject to the federal estate tax.
Under the estate tax rules, life insurance will be included in your taxable estate if either:
- Your estate is the beneficiary of the insurance proceeds, or
- You possessed certain economic ownership rights (called “incidents of ownership”) in the policy at your death (or within three years of your death).
The first situation is easy to avoid. You can just make sure your estate isn’t designated as beneficiary of the policy.
The second situation is more complicated. It’s clear that if you’re the owner of the policy, the proceeds will be included in your estate regardless of the beneficiary. However, simply having someone else possess legal title to the policy won’t prevent this result if you keep so-called “incidents of ownership” in the policy. If held by you, the rights that will cause the proceeds to be taxed in your estate include:
- The right to change beneficiaries,
- The right to assign the policy (or revoke an assignment),
- The right to borrow against the policy’s cash surrender value,
- The right to pledge the policy as security for a loan, and
- The right to surrender or cancel the policy.
Keep in mind that merely having any of the above powers will cause the proceeds to be taxed in your estate even if you never exercise the power.
Buy-sell agreements
If life insurance is obtained to fund a buy-sell agreement for a business interest under a “cross-purchase” arrangement, it won’t be taxed in your estate (unless the estate is named as beneficiary). For example, say Andrew and Bob are partners who agree that the partnership interest of the first of them to die will be bought by the surviving partner. To fund these obligations, Andrew buys a life insurance policy on Bob’s life. Andrew pays all the premiums, retains all incidents of ownership, and names himself as beneficiary. Bob does the same regarding Andrew. When the first partner dies, the insurance proceeds aren’t taxed in the first partner’s estate.
Life insurance trusts
An irrevocable life insurance trust (ILIT) is an effective vehicle that can be set up to keep life insurance proceeds from being taxed in the insured’s estate. Typically, the policy is transferred to the trust along with assets that can be used to pay future premiums. Alternatively, the trust buys the insurance with funds contributed by the insured person. So long as the trust agreement gives the insured person none of the ownership rights described above, the proceeds won’t be included in his or her estate.
The three-year rule
If you’re considering setting up a life insurance trust with a policy you own now or you just want to assign away your ownership rights in a policy, contact us to help you make these moves. Unless you live for at least three years after these steps are taken, the proceeds will be taxed in your estate. For policies in which you never held incidents of ownership, the three-year rule doesn’t apply. Don’t hesitate to contact us with any questions about your situation.
© 2020
Small business owners still have time to set up a SEP plan for last year

Do you own a business but haven’t gotten around to setting up a tax-advantaged retirement plan? Fortunately, it’s not too late to establish one and reduce your 2019 tax bill. A Simplified Employee Pension (SEP) can still be set up for 2019, and you can make contributions to it that you can deduct on your 2019 income tax return. Even better, SEPs keep administrative costs low.
Deadlines for contributions
A SEP can be set up as late as the due date (including extensions) of your income tax return for the tax year for which the SEP first applies. That means you can establish a SEP for 2019 in 2020 as long as you do it before your 2019 return filing deadline. You have until the same deadline to make 2019 contributions and still claim a potentially substantial deduction on your 2019 return.
Generally, most other types of retirement plans would have to have been established by December 31, 2019, in order for 2019 contributions to be made (though many of these plans do allow 2019 contributions to be made in 2020).
Contributions are optional
With a SEP, you can decide how much to contribute each year. You aren’t required to make any certain minimum contributions annually.
However, if your business has employees other than you:
- Contributions must be made for all eligible employees using the same percentage of compensation as for yourself, and
- Employee accounts must be immediately 100% vested.
The contributions go into SEP-IRAs established for each eligible employee. As the employer, you’ll get a current income tax deduction for contributions you make on behalf of your employees. Your employees won’t be taxed when the contributions are made, but at a later date when distributions are made — usually in retirement.
For 2019, the maximum contribution that can be made to a SEP-IRA is 25% of compensation (or 20% of self-employed income net of the self-employment tax deduction), subject to a contribution cap of $56,000. (The 2020 cap is $57,000.)
How to proceed
To set up a SEP, you complete and sign the simple Form 5305-SEP (“Simplified Employee Pension — Individual Retirement Accounts Contribution Agreement”). You don’t need to file Form 5305-SEP with the IRS, but you should keep it as part of your permanent tax records. A copy of Form 5305-SEP must be given to each employee covered by the SEP, along with a disclosure statement.
Although there are rules and limits that apply to SEPs beyond what we’ve discussed here, SEPs generally are much simpler to administer than other retirement plans. Contact us with any questions you have about SEPs and to discuss whether it makes sense for you to set one up for 2019 (or 2020).
© 2020
Home is where the tax breaks might be

If you own a home, the interest you pay on your home mortgage may provide a tax break. However, many people believe that any interest paid on their home mortgage loans and home equity loans is deductible. Unfortunately, that’s not true.
First, keep in mind that you must itemize deductions in order to take advantage of the mortgage interest deduction.
Deduction and limits for “acquisition debt”
A personal interest deduction generally isn’t allowed, but one kind of interest that is deductible is interest on mortgage “acquisition debt.” This means debt that’s: 1) secured by your principal home and/or a second home, and 2) incurred in acquiring, constructing or substantially improving the home. You can deduct interest on acquisition debt on up to two qualified residences: your primary home and one vacation home or similar property.
The deduction for acquisition debt comes with a stipulation. From 2018 through 2025, you can’t deduct the interest for acquisition debt greater than $750,000 ($375,000 for married filing separately taxpayers). So if you buy a $2 million house with a $1.5 million mortgage, only the interest you pay on the first $750,000 in debt is deductible. The rest is nondeductible personal interest.
Higher limit before 2018 and after 2025
Beginning in 2026, you’ll be able to deduct the interest for acquisition debt up to $1 million ($500,000 for married filing separately). This was the limit that applied before 2018.
The higher $1 million limit applies to acquisition debt incurred before Dec. 15, 2017, and to debt arising from the refinancing of pre-Dec. 15, 2017 acquisition debt, to the extent the debt resulting from the refinancing doesn’t exceed the original debt amount. Thus, taxpayers can refinance up to $1 million of pre-Dec. 15, 2017 acquisition debt, and that refinanced debt amount won’t be subject to the $750,000 limitation.
The limit on home mortgage debt for which interest is deductible includes both your primary residence and your second home, combined. Some taxpayers believe they can deduct the interest on $750,000 for each mortgage. But if you have a $700,000 mortgage on your primary home and a $500,000 mortgage on your vacation place, the interest on $450,000 of the total debt will be nondeductible personal interest.
“Home equity loan” interest
“Home equity debt,” as specially defined for purposes of the mortgage interest deduction, means debt that: is secured by the taxpayer’s home, and isn’t “acquisition indebtedness” (meaning it wasn’t incurred to acquire, construct or substantially improve the home). From 2018 through 2025, there’s no deduction for home equity debt interest. Note that interest may be deductible on a “home equity loan,” or a “home equity line of credit,” if that loan fits the tax law’s definition of “acquisition debt” because the proceeds are used to substantially improve or construct the home.
Home equity interest after 2025
Beginning with 2026, home equity debt up to certain limits will be deductible (as it was before 2018). The interest on a home equity loan will generally be deductible regardless of how you use the loan proceeds.
Thus, taxpayers considering taking out a home equity loan— one that’s not incurred to acquire, construct or substantially improve the home — should be aware that interest on the loan won’t be deductible. Further, taxpayers with outstanding home equity debt (again, meaning debt that’s not incurred to acquire, construct or substantially improve the home) will currently lose the interest deduction for interest on that debt.
Contact us with questions or if you would like more information about the mortgage interest deduction.
© 2020
Work Opportunity Tax Credit extended through 2020

If you’re a business owner, be aware that a recent tax law extended a credit for hiring individuals from one or more targeted groups. Employers can qualify for a valuable tax credit known as the Work Opportunity Tax Credit (WOTC).
The WOTC was set to expire on December 31, 2019. But a new law passed late last year extends it through December 31, 2020.
Generally, an employer is eligible for the credit for qualified wages paid to qualified members of these targeted groups: 1) members of families receiving assistance under the Temporary Assistance for Needy Families program, 2) veterans, 3) ex-felons, 4) designated community residents, 5) vocational rehabilitation referrals, 6) summer youth employees, 7) members of families in the Supplemental Nutritional Assistance Program, 8) qualified Supplemental Security Income recipients, 9) long-term family assistance recipients and 10) long-term unemployed individuals.
Several requirements
For each employee, there’s a minimum requirement that the employee has completed at least 120 hours of service for the employer. The credit isn’t available for certain employees who are related to the employer or work more than 50% of the time outside of a trade or business of the employer (for example, a maid working in the employer’s home). Additionally, the credit generally isn’t available for employees who’ve previously worked for the employer.
There are different rules and credit amounts for certain employees. The maximum credit available for the first-year wages is $2,400 for each employee, $4,000 for long-term family assistance recipients, and $4,800, $5,600 or $9,600 for certain veterans. Additionally, for long-term family assistance recipients, there’s a 50% credit for up to $10,000 of second-year wages, resulting in a total maximum credit, over two years, of $9,000.
For summer youth employees, the wages must be paid for services performed during any 90-day period between May 1 and September 15. The maximum WOTC credit available for summer youth employees is $1,200 per employee.
Here are a few other rules:
- No deduction is allowed for the portion of wages equal to the amount of the WOTC determined for the tax year;
- Other employment-related credits are generally reduced with respect to an employee for whom a WOTC is allowed; and
- The credit is subject to the overall limits on the amount of business credits that can be taken in any tax year, but a 1-year carryback and 20-year carryforward of unused business credits is allowed.
Make sure you qualify
Because of these rules, there may be circumstances when the employer might elect not to have the WOTC apply. There are some additional rules that, in limited circumstances, prohibit the credit or require an allocation of it. Contact us with questions or for more information about your situation.
© 2020
Tax credits may help with the high cost of raising children

If you’re a parent, or if you’re planning on having children, you know that it’s expensive to pay for their food, clothes, activities and education. Fortunately, there’s a tax credit available for taxpayers with children under the age of 17, as well as a dependent credit for older children.
Recent tax law changes
Changes made by the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA) make the child tax credit more valuable and allow more taxpayers to be able to benefit from it. These changes apply through 2025.
Prior law: Before the TCJA kicked in for the 2018 tax year, the child tax credit was $1,000 per qualifying child. But it was reduced for married couples filing jointly by $50 for every $1,000 (or part of $1,000) by which their adjusted gross income (AGI) exceeded $110,000 ($75,000 for unmarried taxpayers). To the extent the $1,000-per-child credit exceeded a taxpayer’s tax liability, it resulted in a refund up to 15% of earned income (wages or net self-employment income) above $3,000. For taxpayers with three or more qualifying children, the excess of the taxpayer’s Social Security taxes for the year over the taxpayer’s earned income credit for the year was refundable. In all cases, the refund was limited to $1,000 per qualifying child.
Current law. Starting with the 2018 tax year, the TCJA doubled the child tax credit to $2,000 per qualifying child under 17. It also allows a $500 credit (per dependent) for any of your dependents who aren’t qualifying children under 17. There’s no age limit for the $500 credit, but tax tests for dependency must be met. Under the TCJA, the refundable portion of the credit is increased to a maximum of $1,400 per qualifying child. In addition, the earned threshold is decreased to $2,500 (from $3,000 under prior law), which has the potential to result in a larger refund. The $500 credit for dependents other than qualifying children is nonrefundable.
More parents are eligible
The TCJA also substantially increased the “phase-out” thresholds for the credit. Starting with the 2018 tax year, the total credit amount allowed to a married couple filing jointly is reduced by $50 for every $1,000 (or part of a $1,000) by which their AGI exceeds $400,000 (up from the prior threshold of $110,000). The threshold is $200,000 for other taxpayers. So, if you were previously prohibited from taking the credit because your AGI was too high, you may now be eligible to claim the credit.
In order to claim the credit for a qualifying child, you must include the child’s Social Security number (SSN) on your tax return. Under prior law, you could also use an individual taxpayer identification number (ITIN) or adoption taxpayer identification number (ATIN). If a qualifying child doesn’t have an SSN, you won’t be able to claim the $1,400 credit, but you can claim the $500 credit for that child using an ITIN or an ATIN. The SSN requirement doesn’t apply for non-qualifying-child dependents, but you must provide an ITIN or ATIN for each dependent for whom you’re claiming a $500 credit.
The changes made by the TCJA generally make these credits more valuable and more widely available to many parents.
If you have children and would like to determine if these tax credits can benefit you, please contact us or ask about them when we prepare your tax return.
© 2020
Do you run your business from home? You might be eligible for home office deductions

If you’re self-employed and work out of an office in your home, you may be entitled to home office deductions. However, you must satisfy strict rules.
If you qualify, you can deduct the “direct expenses” of the home office. This includes the costs of painting or repairing the home office and depreciation deductions for furniture and fixtures used there. You can also deduct the “indirect” expenses of maintaining the office. This includes the allocable share of utility costs, depreciation and insurance for your home, as well as the allocable share of mortgage interest, real estate taxes and casualty losses.
In addition, if your home office is your “principal place of business,” the costs of traveling between your home office and other work locations are deductible transportation expenses, rather than nondeductible commuting costs. And, generally, you can deduct the cost (reduced by the percentage of non-business use) of computers and related equipment that you use in your home office, in the year that they’re placed into service.
Deduction tests
You can deduct your expenses if you meet any of these three tests:
Principal place of business. You’re entitled to deductions if you use your home office, exclusively and regularly, as your principal place of business. Your home office is your principal place of business if it satisfies one of two tests. You satisfy the “management or administrative activities test” if you use your home office for administrative or management activities of your business, and you meet certain other requirements. You meet the “relative importance test” if your home office is the most important place where you conduct business, compared with all the other locations where you conduct that business.
Meeting place. You’re entitled to home office deductions if you use your home office, exclusively and regularly, to meet or deal with patients, clients, or customers. The patients, clients or customers must physically come to the office.
Separate structure. You’re entitled to home office deductions for a home office, used exclusively and regularly for business, that’s located in a separate unattached structure on the same property as your home. For example, this could be in an unattached garage, artist’s studio or workshop.
You may also be able to deduct the expenses of certain storage space for storing inventory or product samples. If you’re in the business of selling products at retail or wholesale, and if your home is your sole fixed business location, you can deduct home expenses allocable to space that you use to store inventory or product samples.
Deduction limitations
The amount of your home office deductions is subject to limitations based on the income attributable to your use of the office, your residence-based deductions that aren’t dependent on use of your home for business (such as mortgage interest and real estate taxes), and your business deductions that aren’t attributable to your use of the home office. But any home office expenses that can’t be deducted because of these limitations can be carried over and deducted in later years.
Selling the home
Be aware that if you sell — at a profit — a home that contains (or contained) a home office, there may be tax implications. We can explain them to you.
Pin down the best tax treatment
Proper planning can be the key to claiming the maximum deduction for your home office expenses. Contact us if you’d like to discuss your situation.
© 2020
How business owners may be able to reduce tax by using an S corporation

Do you conduct your business as a sole proprietorship or as a wholly owned limited liability company (LLC)? If so, you’re subject to both income tax and self-employment tax. There may be a way to cut your tax bill by using an S corporation.
Self-employment tax basics
The self-employment tax is imposed on 92.35% of self-employment income at a 12.4% rate for Social Security up to a certain maximum ($137,700 for 2020) and at a 2.9% rate for Medicare. No maximum tax limit applies to the Medicare tax. An additional 0.9% Medicare tax is imposed on income exceeding $250,000 for married couples ($125,000 for married persons filing separately) and $200,000 in all other cases.
Similarly, if you conduct your business as a partnership in which you’re a general partner, in addition to income tax you are subject to the self-employment tax on your distributive share of the partnership’s income. On the other hand, if you conduct your business as an S corporation, you’ll be subject to income tax, but not self-employment tax, on your share of the S corporation’s income.
An S corporation isn’t subject to tax at the corporate level. Instead, the corporation’s items of income, gain, loss and deduction are passed through to the shareholders. However, the income passed through to the shareholder isn’t treated as self-employment income. Thus, by using an S corporation, you may be able to avoid self-employment income tax.
Salary must be reasonable
However, be aware that the IRS requires that the S corporation pay you reasonable compensation for your services to the business. The compensation is treated as wages subject to employment tax (split evenly between the corporation and the employee), which is equivalent to the self-employment tax. If the S corporation doesn’t pay you reasonable compensation for your services, the IRS may treat a portion of the S corporation’s distributions to you as wages and impose Social Security taxes on the amount it considers wages.
There’s no simple formula regarding what is considered reasonable compensation. Presumably, reasonable compensation is the amount that unrelated employers would pay for comparable services under similar circumstances. There are many factors that should be taken into account in making this determination.
Converting from a C to an S corp
There can be complications if you convert a C corporation to an S corporation. A “built-in gains tax” may apply when appreciated assets held by the C corporation at the time of the conversion are subsequently disposed of. However, there may be ways to minimize its impact.
As explained above, an S corporation isn’t normally subject to tax, but when a C corporation converts to S corporation status, the tax law imposes a tax at the highest corporate rate (21%) on the net built-in gains of the corporation. The idea is to prevent the use of an S election to escape tax at the corporate level on the appreciation that occurred while the corporation was a C corporation. This tax is imposed when the built-in gains are recognized (in other words, when the appreciated assets are sold or otherwise disposed of) during the five-year period after the S election takes effect (referred to as the “recognition period”).
Consider all issues
Contact us if you’d like to discuss the factors involved in conducting your business as an S corporation, including the built-in gains tax and how much the business should pay you as compensation.
© 2020
Reasons why married couples might want to file separate tax returns

Married couples often wonder whether they should file joint or separate tax returns. The answer depends on your individual tax situation.
It generally depends on which filing status results in the lowest tax. But keep in mind that, if you and your spouse file a joint return, each of you is “jointly and severally” liable for the tax on your combined income. And you’re both equally liable for any additional tax the IRS assesses, plus interest and most penalties. This means that the IRS can come after either of you to collect the full amount.
>Although there are provisions in the law that offer relief, they have limitations. Therefore, even if a joint return results in less tax, you may want to file separately if you want to only be responsible for your own tax.
In most cases, filing jointly offers the most tax savings, especially when the spouses have different income levels. Combining two incomes can bring some of it out of a higher tax bracket. For example, if one spouse has $75,000 of taxable income and the other has just $15,000, filing jointly instead of separately can save $2,512.50 for 2020.
Filing separately doesn’t mean you go back to using the “single” rates that applied before you were married. Instead, each spouse must use “married filing separately” rates. They’re less favorable than the single rates.
However, there are cases when people save tax by filing separately. For example:
One spouse has significant medical expenses. For 2019 and 2020, medical expenses are deductible only to the extent they exceed 7.5% of adjusted gross income (AGI). If a medical expense deduction is claimed on a spouse’s separate return, that spouse’s lower separate AGI, as compared to the higher joint AGI, can result in larger total deductions.
Some tax breaks are only available on a joint return. The child and dependent care credit, adoption expense credit, American Opportunity tax credit and Lifetime Learning credit are only available to married couples on joint returns. And you can’t take the credit for the elderly or the disabled if you file separately unless you and your spouse lived apart for the entire year. You also may not be able to deduct IRA contributions if you or your spouse were covered by an employer retirement plan and you file separate returns. You also can’t exclude adoption assistance payments or interest income from series EE or Series I savings bonds used for higher education expenses.
Social Security benefits may be taxed more. Benefits are tax-free if your “provisional income” (AGI with certain modifications plus half of your Social Security benefits) doesn’t exceed a “base amount.” The base amount is $32,000 on a joint return, but zero on separate return (or $25,000 if the spouses didn’t live together for the whole year).
No hard and fast rules
The decision you make on your federal tax return may affect your state or local income tax bill, so the total tax impact should be compared. There’s often no simple answer to whether a couple should file separate returns. A number of factors must be examined. We can look at your tax bill jointly and separately. Contact us to prepare your return or if you have any questions.
© 2020
The tax aspects of selling mutual fund shares

Perhaps you’re an investor in mutual funds or you’re interested in putting some money into them. You’re not alone. The Investment Company Institute estimates that 56.2 million households owned mutual funds in mid-2017. But despite their popularity, the tax rules involved in selling mutual fund shares can be complex.
Tax basics
If you sell appreciated mutual fund shares that you’ve owned for more than one year, the resulting profit will be a long-term capital gain. As such, the maximum federal income tax rate will be 20%, and you may also owe the 3.8% net investment income tax.
When a mutual fund investor sells shares, gain or loss is measured by the difference between the amount realized from the sale and the investor’s basis in the shares. One difficulty is that certain mutual fund transactions are treated as sales even though they might not be thought of as such. Another problem may arise in determining your basis for shares sold.
What’s considered a sale
It’s obvious that a sale occurs when an investor redeems all shares in a mutual fund and receives the proceeds. Similarly, a sale occurs if an investor directs the fund to redeem the number of shares necessary for a specific dollar payout.
It’s less obvious that a sale occurs if you’re swapping funds within a fund family. For example, you surrender shares of an Income Fund for an equal value of shares of the same company’s Growth Fund. No money changes hands but this is considered a sale of the Income Fund shares.
Another example: Many mutual funds provide check-writing privileges to their investors. However, each time you write a check on your fund account, you’re making a sale of shares.
Determining the basis of shares
If an investor sells all shares in a mutual fund in a single transaction, determining basis is relatively easy. Simply add the basis of all the shares (the amount of actual cash investments) including commissions or sales charges. Then add distributions by the fund that were reinvested to acquire additional shares and subtract any distributions that represent a return of capital.
The calculation is more complex if you dispose of only part of your interest in the fund and the shares were acquired at different times for different prices. You can use one of several methods to identify the shares sold and determine your basis.
- First-in first-out. The basis of the earliest acquired shares is used as the basis for the shares sold. If the share price has been increasing over your ownership period, the older shares are likely to have a lower basis and result in more gain.>
- Specific identification. At the time of sale, you specify the shares to sell. For example, “sell 100 of the 200 shares I purchased on June 1, 2015.” You must receive written confirmation of your request from the fund. This method may be used to lower the resulting tax bill by directing the sale of the shares with the highest basis.
- Average basis. The IRS permits you to use the average basis for shares that were acquired at various times and that were left on deposit with the fund or a custodian agent.
As you can see, mutual fund investing can result in complex tax situations. Contact us if you have questions. We can explain in greater detail how the rules apply to you.
© 2020
Do you want to go into business for yourself?

Many people who launch small businesses start out as sole proprietors. Here are nine tax rules and considerations involved in operating as that entity.
1. You may qualify for the pass-through deduction. To the extent your business generates qualified business income, you are eligible to claim the 20% pass-through deduction, subject to limitations. The deduction is taken “below the line,” meaning it reduces taxable income, rather than being taken “above the line” against your gross income. However, you can take the deduction even if you don’t itemize deductions and instead claim the standard deduction.
2. Report income and expenses on Schedule C of Form 1040. The net income will be taxable to you regardless of whether you withdraw cash from the business. Your business expenses are deductible against gross income and not as itemized deductions. If you have losses, they will generally be deductible against your other income, subject to special rules related to hobby losses, passive activity losses and losses in activities in which you weren’t “at risk.”
3. Pay self-employment taxes. For 2020, you pay self-employment tax (Social Security and Medicare) at a 15.3% rate on your net earnings from self-employment of up to $137,700, and Medicare tax only at a 2.9% rate on the excess. An additional 0.9% Medicare tax (for a total of 3.8%) is imposed on self-employment income in excess of $250,000 for joint returns; $125,000 for married taxpayers filing separate returns; and $200,000 in all other cases. Self-employment tax is imposed in addition to income tax, but you can deduct half of your self-employment tax as an adjustment to income.
4. Make quarterly estimated tax payments. For 2019, these are due April 15, June 15, September 15 and January 15, 2021.
5. You may be able to deduct home office expenses. If you work from a home office, perform management or administrative tasks there, or store product samples or inventory at home, you may be entitled to deduct an allocable portion of some costs of maintaining your home. And if you have a home office, you may be able to deduct expenses of traveling from there to another work location.
6. You can deduct 100% of your health insurance costs as a business expense. This means your deduction for medical care insurance won’t be subject to the rule that limits medical expense deductions.
7. Keep complete records of your income and expenses. Specifically, you should carefully record your expenses in order to claim all the tax breaks to which you’re entitled. Certain expenses, such as automobile, travel, meals, and office-at-home expenses, require special attention because they’re subject to special recordkeeping rules or deductibility limits.
8. If you hire employees, you need to get a taxpayer identification number and withhold and pay employment taxes.
9. Consider establishing a qualified retirement plan. The advantage is that amounts contributed to the plan are deductible at the time of the contribution and aren’t taken into income until they’re are withdrawn. Because many qualified plans can be complex, you might consider a SEP plan, which requires less paperwork. A SIMPLE plan is also available to sole proprietors that offers tax advantages with fewer restrictions and administrative requirements. If you don’t establish a retirement plan, you may still be able to contribute to an IRA.
Seek assistance
If you want additional information regarding the tax aspects of your new business, or if you have questions about reporting or recordkeeping requirements, please contact us.
© 2020
There still might be time to cut your tax bill with IRAs
|
Do your employees receive tips? You may be eligible for a tax credit

Are you an employer who owns a business where tipping is customary for providing food and beverages? You may qualify for a tax credit involving the Social Security and Medicare (FICA) taxes that you pay on your employees’ tip income.
How the credit works
The FICA credit applies with respect to tips that your employees receive from customers in connection with the provision of food or beverages, regardless of whether the food or beverages are for consumption on or off the premises. Although these tips are paid by customers, they’re treated for FICA tax purposes as if you paid them to your employees. Your employees are required to report their tips to you. You must withhold and remit the employee’s share of FICA taxes, and you must also pay the employer’s share of those taxes.
You claim the credit as part of the general business credit. It’s equal to the employer’s share of FICA taxes paid on tip income in excess of what’s needed to bring your employee’s wages up to $5.15 per hour. In other words, no credit is available to the extent the tip income just brings the employee up to the $5.15 per hour level, calculated monthly. If you pay each employee at least $5.15 an hour (excluding tips), you don’t have to be concerned with this calculation.
Note: A 2007 tax law froze the per-hour amount at $5.15, which was the amount of the federal minimum wage at that time. The minimum wage is now $7.25 per hour but the amount for credit computation purposes remains $5.15.
How it works
Example: A waiter works at your restaurant. He’s paid $2 an hour plus tips. During the month, he works 160 hours for $320 and receives $2,000 in cash tips which he reports to you.
The waiter’s $2 an hour rate is below the $5.15 rate by $3.15 an hour. Thus, for the 160 hours worked, he or she is below the $5.15 rate by $504 (160 times $3.15). For the waiter, therefore, the first $504 of tip income just brings him up to the minimum rate. The rest of the tip income is $1,496 ($2,000 minus $504). The waiter’s employer pays FICA taxes at the rate of 7.65% for him. Therefore, the employer’s credit is $114.44 for the month: $1,496 times 7.65%.
While the employer’s share of FICA taxes is generally deductible, the FICA taxes paid with respect to tip income used to determine the credit can’t be deducted, because that would amount to a double benefit. However, you can elect not to take the credit, in which case you can claim the deduction.
Get the credit you’re due
If your business pays FICA taxes on tip income paid to your employees, the tip tax credit may be valuable to you. Other rules may apply. Contact us if you have any questions.
Answers to your questions about 2020 individual tax limits

Right now, you may be more concerned about your 2019 tax bill than you are about your 2020 tax situation. That’s understandable because your 2019 individual tax return is due to be filed in less than three months.
However, it’s a good idea to familiarize yourself with tax-related amounts that may have changed for 2020. For example, the amount of money you can put into a 401(k) plan has increased and you may want to start making contributions as early in the year as possible because retirement plan contributions will lower your taxable income.
Note: Not all tax figures are adjusted for inflation and even if they are, they may be unchanged or change only slightly each year due to low inflation. In addition, some tax amounts can only change with new tax legislation.
So below are some Q&As about tax-related figures for this year.
How much can I contribute to an IRA for 2020?
If you’re eligible, you can contribute $6,000 a year into a traditional or Roth IRA, up to 100% of your earned income. If you’re age 50 or older, you can make another $1,000 “catch up” contribution. (These amounts are the same as they were for 2019.)
I have a 401(k) plan through my job. How much can I contribute to it?
For 2020, you can contribute up to $19,500 (up from $19,000) to a 401(k) or 403(b) plan. You can make an additional $6,500 catch-up contribution if you’re age 50 or older.
I sometimes hire a babysitter and a cleaning person. Do I have to withhold and pay FICA tax on the amounts I pay them?
In 2020, the threshold when a domestic employer must withhold and pay FICA for babysitters, house cleaners, etc. is $2,200 (up from $2,100 in 2019).
How much do I have to earn in 2020 before I can stop paying Social Security on my salary?
The Social Security tax wage base is $137,700 for this year (up from $132,900 last year). That means that you don’t owe Social Security tax on amounts earned above that. (You must pay Medicare tax on all amounts that you earn.)
I didn’t qualify to itemize deductions on my last tax return. Will I qualify for 2020?
The Tax Cuts and Jobs Act eliminated the tax benefit of itemizing deductions for many people by increasing the standard deduction and reducing or eliminating various deductions. For 2020, the standard deduction amount is $24,800 for married couples filing jointly (up from $24,400). For single filers, the amount is $12,400 (up from $12,200) and for heads of households, it’s $18,650 (up from $18,350). So if the amount of your itemized deductions (such as charitable gifts and mortgage interest) are less than the applicable standard deduction amount, you won’t itemize for 2020.
How much can I give to one person without triggering a gift tax return in 2020?
The annual gift exclusion for 2020 is $15,000 and is unchanged from last year. This amount is only adjusted in $1,000 increments, so it typically only increases every few years.
Your tax picture
These are only some of the tax figures that may apply to you. For more information about your tax picture, or if you have questions, don’t hesitate to contact us.
© 2020
Numerous tax limits affecting businesses have increased for 2020
|
Can you deduct charitable gifts on your tax return?
|
Cents-per-mile rate for business miles decreases slightly for 2020
|
Help protect your personal information by filing your 2019 tax return early
|
New rules will soon require employers to annually disclose retirement income to employees.

|
4 new law changes that may affect your retirement plan

If you save for retirement with an IRA or other plan, you’ll be interested to know that Congress recently passed a law that makes significant modifications to these accounts. The SECURE Act, which was signed into law on December 20, 2019, made these four changes.
Change #1: The maximum age for making traditional IRA contributions is repealed. Before 2020, traditional IRA contributions weren’t allowed once you reached age 70½. Starting in 2020, an individual of any age can make contributions to a traditional IRA, as long he or she has compensation, which generally means earned income from wages or self-employment.
Change #2: The required minimum distribution (RMD) age was raised from 70½ to 72. Before 2020, retirement plan participants and IRA owners were generally required to begin taking RMDs from their plans by April 1 of the year following the year they reached age 70½. The age 70½ requirement was first applied in the early 1960s and, until recently, hadn’t been adjusted to account for increased life expectancies.
For distributions required to be made after December 31, 2019, for individuals who attain age 70½ after that date, the age at which individuals must begin taking distributions from their retirement plans or IRAs is increased from 70½ to 72.
Change #3: “Stretch IRAs” were partially eliminated. If a plan participant or IRA owner died before 2020, their beneficiaries (spouses and non-spouses) were generally allowed to stretch out the tax-deferral advantages of the plan or IRA by taking distributions over the beneficiary’s life or life expectancy. This is sometimes called a “stretch IRA.”
However, for deaths of plan participants or IRA owners beginning in 2020 (later for some participants in collectively bargained plans and governmental plans), distributions to most non-spouse beneficiaries are generally required to be distributed within 10 years following a plan participant’s or IRA owner’s death. That means the “stretch” strategy is no longer allowed for those beneficiaries.
There are some exceptions to the 10-year rule. For example, it’s still allowed for: the surviving spouse of a plan participant or IRA owner; a child of a plan participant or IRA owner who hasn’t reached the age of majority; a chronically ill individual; and any other individual who isn’t more than 10 years younger than a plan participant or IRA owner. Those beneficiaries who qualify under this exception may generally still take their distributions over their life expectancies.
Change #4: Penalty-free withdrawals are now allowed for birth or adoption expenses. A distribution from a retirement plan must generally be included in income. And, unless an exception applies, a distribution before the age of 59½ is subject to a 10% early withdrawal penalty on the amount includible in income.
Starting in 2020, plan distributions (up to $5,000) that are used to pay for expenses related to the birth or adoption of a child are penalty-free. The $5,000 amount applies on an individual basis. Therefore, each spouse in a married couple may receive a penalty-free distribution up to $5,000 for a qualified birth or adoption.
Questions?
These are only some of the changes included in the new law. If you have questions about your situation, don’t hesitate to contact us.
© 2020
New law helps businesses make their employees’ retirement secure.

|
Your home office expenses may be tax deductible.

|
New law provides a variety of tax breaks to businesses and employers

While you were celebrating the holidays, you may not have noticed that Congress passed a law with a grab bag of provisions that provide tax relief to businesses and employers. The “Further Consolidated Appropriations Act, 2020” was signed into law on December 20, 2019. It makes many changes to the tax code, including an extension (generally through 2020) of more than 30 provisions that were set to expire or already expired.
Two other laws were passed as part of the law (The Taxpayer Certainty and Disaster Tax Relief Act of 2019 and the Setting Every Community Up for Retirement Enhancement Act).
Here are five highlights.
Long-term part-timers can participate in 401(k)s.
Under current law, employers generally can exclude part-time employees (those who work less than 1,000 hours per year) when providing a 401(k) plan to their employees. A qualified retirement plan can generally delay participation in the plan based on an employee attaining a certain age or completing a certain number of years of service but not beyond the later of completion of one year of service (that is, a 12-month period with at least 1,000 hours of service) or reaching age 21.
Qualified retirement plans are subject to various other requirements involving who can participate.
For plan years beginning after December 31, 2020, the new law requires a 401(k) plan to allow an employee to make elective deferrals if the employee has worked with the employer for at least 500 hours per year for at least three consecutive years and has met the age-21 requirement by the end of the three-consecutive-year period. There are a number of other rules involved that will determine whether a part-time employee qualifies to participate in a 401(k) plan.
The employer tax credit for paid family and medical leave is extended.
Tax law provides an employer credit for paid family and medical leave. It permits eligible employers to claim an elective general business credit based on eligible wages paid to qualifying employees with respect to family and medical leave. The credit is equal to 12.5% of eligible wages if the rate of payment is 50% of such wages and is increased by 0.25 percentage points (but not above 25%) for each percentage point that the rate of payment exceeds 50%. The maximum leave amount that can be taken into account for a qualifying employee is 12 weeks per year.
The credit was set to expire on December 31, 2019. The new law extends it through 2020.
The Work Opportunity Tax Credit (WOTC) is extended.
Under the WOTC, an elective general business credit is provided to employers hiring individuals who are members of one or more of 10 targeted groups. The new law extends this credit through 2020.
The medical device excise tax is repealed.
The Affordable Care Act (ACA) contained a provision that required that the sale of a taxable medical device by the manufacturer, producer or importer is subject to a tax equal to 2.3% of the price for which it is sold. This medical device excise tax originally applied to sales of taxable medical devices after December 31, 2012.
The new law repeals the excise tax for sales occurring after December 31, 2019.
The high-cost, employer-sponsored health coverage tax is repealed.
The ACA also added a nondeductible excise tax on insurers when the aggregate value of employer-sponsored health insurance coverage for an employee, former employee, surviving spouse or other primary insured individual exceeded a threshold amount. This tax is commonly referred to as the tax on “Cadillac” plans.
The new law repeals the Cadillac tax for tax years beginning after December 31, 2019.
Stay tuned
These are only some of the provisions of the new law. We will be covering them in the coming weeks. If you have questions about your situation, don’t hesitate to contact us.
© 2019
Congress gives a holiday gift in the form of favorable tax provisions.

|
Wayfair revisited — It’s time to review your sales tax obligations

In its 2018 decision in South Dakota v. Wayfair, the U.S. Supreme Court upheld South Dakota’s “economic nexus” statute, expanding the power of states to collect sales tax from remote sellers. Today, nearly every state with a sales tax has enacted a similar law, so if your company does business across state lines, it’s a good idea to reexamine your sales tax obligations.
What’s nexus?
A state is constitutionally prohibited from taxing business activities unless those activities have a substantial “nexus,” or connection, with the state. Before Wayfair, simply selling to customers in a state wasn’t enough to establish nexus. The business also had to have a physical presence in the state, such as offices, retail stores, manufacturing or distribution facilities, or sales reps.
In Wayfair, the Supreme Court ruled that a business could establish nexus through economic or virtual contacts with a state, even if it didn’t have a physical presence. The Court didn’t create a bright-line test for determining whether contacts are “substantial,” but found that the thresholds established by South Dakota’s law are sufficient: Out-of-state businesses must collect and remit South Dakota sales taxes if, in the current or previous calendar year, they have 1) more than $100,000 in gross sales of products or services delivered into the state, or 2) 200 or more separate transactions for the delivery of goods or services into the state.
Nexus steps
The vast majority of states now have economic nexus laws, although the specifics vary:Many states adopted the same sales and transaction thresholds accepted in Wayfair, but a number of states apply different thresholds. And some chose not to impose transaction thresholds, which many view as unfair to smaller sellers (an example of a threshold might be 200 sales of $5 each would create nexus).
If your business makes online, telephone or mail-order sales in states where it lacks a physical presence, it’s critical to find out whether those states have economic nexus laws and determine whether your activities are sufficient to trigger them. If you have nexus with a state, you’ll need to register with the state and collect state and applicable local taxes on your taxable sales there. Even if some or all of your sales are tax-exempt, you’ll need to secure exemption certifications for each jurisdiction where you do business. Alternatively, you might decide to reduce or eliminate your activities in a state if the benefits don’t justify the compliance costs.
Need help?
Note: If you make sales through a “marketplace facilitator,” such as Amazon or Ebay, be aware that an increasing number of states have passed laws that require such providers to collect taxes on sales they facilitate for vendors using their platforms.
If you need assistance in setting up processes to collect sales tax or you have questions about your responsibilities, contact us.
© 2019
Do you have a side gig? Make sure you understand your tax obligations.

|
Small Businesses: It may not be not too late to cut your 2019 taxes
|
Adopting a child? Bring home tax savings with your bundle of joy

|
2020 Q1 tax calendar: Key deadlines for businesses and other employers
Here are some of the key tax-related deadlines affecting businesses and other employers during the first quarter of 2020. Keep in mind that this list isn’t all-inclusive, so there may be additional deadlines that apply to you. Contact us to ensure you’re meeting all applicable deadlines and to learn more about the filing requirements.
January 31
- File 2019 Forms W-2, “Wage and Tax Statement,” with the Social Security Administration and provide copies to your employees.
- Provide copies of 2019 Forms 1099-MISC, “Miscellaneous Income,” to recipients of income from your business where required.
- File 2019 Forms 1099-MISC reporting nonemployee compensation payments in Box 7 with the IRS.
- File Form 940, “Employer’s Annual Federal Unemployment (FUTA) Tax Return,” for 2019. If your undeposited tax is $500 or less, you can either pay it with your return or deposit it. If it’s more than $500, you must deposit it. However, if you deposited the tax for the year in full and on time, you have until February 10 to file the return.
- File Form 941, “Employer’s Quarterly Federal Tax Return,” to report Medicare, Social Security and income taxes withheld in the fourth quarter of 2019. If your tax liability is less than $2,500, you can pay it in full with a timely filed return. If you deposited the tax for the quarter in full and on time, you have until February 10 to file the return. (Employers that have an estimated annual employment tax liability of $1,000 or less may be eligible to file Form 944, “Employer’s Annual Federal Tax Return.”)
- File Form 945, “Annual Return of Withheld Federal Income Tax,” for 2019 to report income tax withheld on all nonpayroll items, including backup withholding and withholding on accounts such as pensions, annuities and IRAs. If your tax liability is less than $2,500, you can pay it in full with a timely filed return. If you deposited the tax for the year in full and on time, you have until February 10 to file the return.
February 28
- File 2019 Forms 1099-MISC with the IRS if 1) they’re not required to be filed earlier and 2) you’re filing paper copies. (Otherwise, the filing deadline is March 31.)
March 16
- If a calendar-year partnership or S corporation, file or extend your 2019 tax return and pay any tax due. If the return isn’t extended, this is also the last day to make 2019 contributions to pension and profit-sharing plans.
© 2019
3 last-minute tips that may help trim your tax bill

If you’re starting to fret about your 2019 tax bill, there’s good news — you may still have time to reduce your liability. Three strategies are available that may help you cut your taxes before year-end, including:
1. Accelerate deductions/defer income. Certain tax deductions are claimed for the year of payment, such as the mortgage interest deduction. So, if you make your January 2020 payment this month, you can deduct the interest portion on your 2019 tax return (assuming you itemize).
Pushing income into the new year also will reduce your taxable income. If you’re expecting a bonus at work, for example, and you don’t want the income this year, ask if your employer can hold off on paying it until January. If you’re self-employed, you can delay your invoices until late in December to divert the revenue to 2020.
You shouldn’t pursue this approach if you expect to land in a higher tax bracket next year. Also, if you’re eligible for the qualified business income deduction for pass-through entities, you might reduce the amount of that deduction if you reduce your income.
2. Maximize your retirement contributions. What could be better than paying yourself instead of Uncle Sam? Federal tax law encourages individual taxpayers to make the maximum allowable contributions for the year to their retirement accounts, including traditional IRAs and SEP plans, 401(k)s and deferred annuities.
For 2019, you generally can contribute as much as $19,000 to 401(k)s and $6,000 for traditional IRAs. Self-employed individuals can contribute up to 25% of your net income (but no more than $56,000) to a SEP IRA.
3. Harvest your investment losses. Losing money on your investments has a bit of an upside — it gives you the opportunity to offset taxable gains.
If you sell underperforming investments before the end of the year, you can offset gains realized this year on a dollar-for-dollar basis. If you have more losses than gains, you generally can apply up to $3,000 of the excess to reduce your ordinary income. Any remaining losses are carried forward to future tax years.
We can help
The strategies described above are only a sampling of strategies that may be available. Contact us if you have questions about these or other methods for minimizing your tax liability for 2019.
© 2019
Holiday parties and gifts can help show your appreciation and provide tax breaks.

|
2 valuable year-end tax-saving tools for your business

|
Medical expenses: What it takes to qualify for a tax deduction

|
What is your taxpayer filing status?

|
The tax implications if your business engages in environmental cleanup.

|
Using your 401(k) plan to save this year and next
|
Small businesses: Get ready for your 1099-MISC reporting requirements
|
Small businesses: Stay clear of a severe payroll tax penalty
|
You may be ABLE to save for a disabled family member with a tax-advantaged account
|
IRA charitable donations are an alternative to taxable required distributions

Are you charitably minded and have a significant amount of money in an IRA? If you’re age 70½ or older, and don’t need the money from required minimum distributions, you may benefit by giving these amounts to charity.
IRA distribution basics
A popular way to transfer IRA assets to charity is through a tax provision that allows IRA owners who are 70½ or older to give up to $100,000 per year of their IRA distributions to charity. These distributions are called qualified charitable distributions, or QCDs. The money given to charity counts toward the donor’s required minimum distributions (RMDs), but doesn’t increase the donor’s adjusted gross income or generate a tax bill.
So while QCDs are exempt from federal income taxes, other traditional IRA distributions are taxable (either wholly or partially depending on whether you’ve made any nondeductible contributions over the years).
Unlike regular charitable donations, QCDs can’t be claimed as itemized deductions.
Keeping the donation out of your AGI may be important because doing so can:
- Help the donor qualify for other tax breaks (for example, a lower AGI can reduce the threshold for deducting medical expenses, which are only deductible to the extent they exceed 10% of AGI);
- Reduce taxes on your Social Security benefits; and
- Help you avoid a high-income surcharge for Medicare Part B and Part D premiums, (which kicks in if AGI hits certain levels).
In addition, keep in mind that charitable contributions don’t yield a tax benefit for those individuals who no longer itemize their deductions (because of the larger standard deduction under the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act). So those who are age 70½ or older and are receiving RMDs from IRAs may gain a tax advantage by making annual charitable contributions via a QCD from an IRA. This charitable contribution will reduce RMDs by a commensurate amount, and the amount of the reduction will be tax-free.
Annual limit
There’s a $100,000 limit on total QCDs for any one year. But if you and your spouse both have IRAs set up in your respective names, each of you is entitled to a separate $100,000 annual QCD limit, for a combined total of $200,000.
Plan ahead,
The QCD strategy can be a smart tax move for high-net-worth individuals over 70½ years old. If you’re interested in this opportunity, don’t wait until year end to act. Contact us for more information.
© 2019Thinking about converting from a C corporation to an S corporation?

|
Selling securities by year end? Avoid the wash sale rule

If you’re planning to sell assets at a loss to offset gains that have been realized during the year, it’s important to be aware of the “wash sale” rule.
How the rule works
Under this rule, if you sell stock or securities for a loss and buy substantially identical stock or securities back within the 30-day period before or after the sale date, the loss can’t be claimed for tax purposes. The rule is designed to prevent taxpayers from using the tax benefit of a loss without parting with ownership in any significant way. Note that the rule applies to a 30-day period before or after the sale date to prevent “buying the stock back” before it’s even sold. (If you participate in any dividend reinvestment plans, the wash sale rules may be inadvertently triggered when dividends are reinvested under the plan, if you’ve separately sold some of the same stock at a loss within the 30-day period.)
Keep in mind that the rule applies even if you repurchase the security in a tax-advantaged retirement account, such as a traditional or Roth IRA.
Although the loss can’t be claimed on a wash sale, the disallowed amount is added to the cost of the new stock. So, the disallowed amount can be claimed when the new stock is finally disposed of (other than in a wash sale).
Here’s an example
Let’s say you buy 500 shares of XYZ Inc. for $10,000 and sell them on November 5 for $3,000. On November 29, you buy 500 shares of XYZ again for $3,200. Since the shares were “bought back” within 30 days of the sale, the wash sale rule applies. Therefore, you can’t claim a $7,000 loss. Your basis in the new 500 shares is $10,200: the actual cost plus the $7,000 disallowed loss.
If only a portion of the stock sold is bought back, only that portion of the loss is disallowed. So, in the above example, if you’d only bought back 300 of the 500 shares (60%), you would be able to claim 40% of the loss on the sale ($2,800). The remaining $4,200 loss that is disallowed under the wash sale rule would be added to your cost of the 300 shares.
If you’ve cashed in some big gains in 2019, you may be looking for unrealized losses in your portfolio so you can sell those investments before year end. By doing so, you can offset your gains with your losses and reduce your 2019 tax liability. But don’t run afoul of the wash sale rule. Contact us if you have any questions.
© 2019Use a Coverdell ESA to help pay college, elementary and secondary school costs
There are several ways to save for your child’s or grandchild’s education, including with a Coverdell Education Savings Account (ESA). Although for federal tax purposes there’s no upfront deduction for contributions made to an ESA, the earnings on the contributions grow tax-free. In addition, no tax is due when the funds in the account are distributed, to the extent the amounts withdrawn don’t exceed the child’s qualified education expenses.
Qualified expenses include higher education tuition, fees, books and room, as well as elementary and secondary school expenses.
Contribution limits
The annual limit that can be contributed to a child’s ESA is $2,000 per year — from all contributors for all ESAs for the same child. The maximum dollar amount that any individual can contribute is phased out if the contributor’s adjusted gross income (with certain modifications) exceeds $95,000 ($190,000 for married joint filers).
However, this phaseout is easily avoided. A child can contribute to his or her own ESA, so a parent or other person whose contribution may be limited by the phaseout rule can give the money to an ESA as custodian for the child. Under those circumstances, the child is considered to be the contributor and, if the child’s adjusted gross income is below $95,000, the phaseout won’t apply.
Contributions that exceed $2,000 in total for a child for a year are subject to a 6% penalty tax until the excess (plus earnings) are withdrawn.
How long can you make ESA contributions? They can be made until a child reaches age 18 (but this age limit doesn’t apply to a beneficiary with special needs who requires additional time to complete his or her education). A beneficiary doesn’t have to be your own child.
Taking money out
Withdrawals from an ESA during a year that exceed the child’s qualified education expenses for that year are included in the child’s income (to the extent of the earnings portion of the distribution) and are also subject to an additional 10% tax.
Tax-free transfers or rollovers of account balances from an ESA benefiting one beneficiary to another account benefiting another person are allowed, if the new beneficiary hasn’t reached 30, and is a member of the family of the old beneficiary. (The age limit doesn’t apply to a beneficiary with special needs.)
If you’re interested in discussing a Coverdell ESA, or other education planning options, please contact us.
© 2019
Setting up a Health Savings Account for your small business
Given the escalating cost of employee health care benefits, your business may be interested in providing some of these benefits through an employer-sponsored Health Savings Account (HSA). For eligible individuals, HSAs offer a tax-advantaged way to set aside funds (or have their employers do so) to meet future medical needs. Here are the key tax benefits:
- Contributions that participants make to an HSA are deductible, within limits.
- Contributions that employers make aren’t taxed to participants.
- Earnings on the funds within an HSA aren’t taxed, so the money can accumulate year after year tax free.
- HSA distributions to cover qualified medical expenses aren’t taxed.
- Employers don’t have to pay payroll taxes on HSA contributions made by employees through payroll deductions.
Who is eligible?
To be eligible for an HSA, an individual must be covered by a “high deductible health plan.” For 2019, a “high deductible health plan” is one with an annual deductible of at least $1,350 for self-only coverage, or at least $2,700 for family coverage. For self-only coverage, the 2019 limit on deductible contributions is $3,500. For family coverage, the 2019 limit on deductible contributions is $7,000. Additionally, annual out-of-pocket expenses required to be paid (other than for premiums) for covered benefits cannot exceed $6,750 for self-only coverage or $13,500 for family coverage. An individual (and the individual’s covered spouse, as well) who has reached age 55 before the close of the tax year (and is an eligible HSA contributor) may make additional “catch-up” contributions for 2019 of up to $1,000.
Employer Contributions
If an employer contributes to the HSA of an eligible individual, the employer’s contribution is treated as employer-provided coverage for medical expenses under an accident or health plan and is excludable from an employee’s gross income up to the deduction limitation. There’s no “use-it-or-lose-it” provision, so funds can be built up for years. An employer that decides to make contributions on its employees’ behalf must generally make comparable contributions to the HSAs of all comparable participating employees for that calendar year. If the employer doesn’t make comparable contributions, the employer is subject to a 35% tax on the aggregate amount contributed by the employer to HSAs for that period.
Distribution
HSA distributions can be made to pay for qualified medical expenses, which generally mean those expenses that would qualify for the medical expense itemized deduction. They include expenses such as doctors’ visits, prescriptions, chiropractic care and premiums for long-term care insurance. If funds are withdrawn from the HSA for other reasons, the withdrawal is taxable. Additionally, an extra 20% tax will apply to the withdrawal, unless it’s made after reaching age 65, or in the event of death or disability. As you can see, HSAs offer a flexible option for providing health care coverage, but the rules are somewhat complex. Contact us if you’d like to discuss offering this benefit to your employees.
© 2019
Watch out for tax-related scams

“Thousands of people have lost millions of dollars and their personal information to tax scams,” according to the IRS. Criminals can contact victims through regular mail, telephone calls and email messages. Here are just two of the scams the tax agency has seen in recent months.
1. Fake property liens. A tax bill is sent from a fictional government agency in the mail. The fake agency may have a legitimate sounding name such as the Bureau of Tax Enforcement. The bill is accompanied by a letter threatening an IRS lien or levy based on bogus overdue taxes. (A levy is a legal seizure of property to satisfy a tax debt. A lien is a legal claim against your property to secure payment of your tax debt.)
2. Phony calls from the IRS. In this scam, criminals impersonating IRS employees call people and tell them that, if they don’t pay back taxes they owe, they will face arrest. The thieves then demand that the taxpayers pay their tax debts with a gift card, other prepaid cards or a wire transfer.
Important reminders
If you receive a text, letter, email or phone call purporting to be from the IRS, keep in mind that the IRS never calls taxpayers demanding immediate payment using a specific method of payment (such as a wire transfer or prepaid debit card). In general, the IRS sends bills or notices to taxpayers and gives them time to respond with questions or appeals. The tax agency also doesn’t threaten taxpayers with arrest.
In addition, the IRS doesn’t initiate contact by email, text message or social media channels to request information. Most contacts are initiated though regular mail delivered by the U.S. Postal Service. The IRS does use authorized private collection agencies to collect some overdue tax bills but these agencies also follow the same rules.
In some special circumstances, the IRS does call taxpayers or come to their homes or businesses. For example, the IRS may tour a business as part of an audit or during a criminal investigation. But even in those cases, taxpayers will generally receive several mailed IRS notices before the visit. And the IRS never demands that payment be made to any source other than the “United States Treasury.”
What to do if you’re contacted
You can contact us if the IRS gets in touch with you. If the contact involves a phone call, hang up immediately. You can forward an email or other tax-related scam to the IRS at phishing@irs.gov. To report an IRS impersonation scam, visit the Treasury Inspector General for Tax Administration at https://bit.ly/1ClYZbP. Be aware that criminals keep evolving their scams in an effort to steal people’s money and personal information. Remain on alert.
© 2019
Understanding and controlling the unemployment tax costs of your business

As an employer, you must pay federal unemployment (FUTA) tax on amounts up to $7,000 paid to each employee as wages during the calendar year. The rate of tax imposed is 6% but can be reduced by a credit (described below). Most employers end up paying an effective FUTA tax rate of 0.6%. An employer taxed at a 6% rate would pay FUTA tax of $420 for each employee who earned at least $7,000 per year, while an employer taxed at 0.6% pays $42.
Tax credit
Unlike FICA taxes, only employers — and not employees — are liable for FUTA tax. Most employers pay both federal and a state unemployment tax. Unemployment tax rates for employers vary from state to state. The FUTA tax may be offset by a credit for contributions paid into state unemployment funds, effectively reducing (but not eliminating) the net FUTA tax rate.
However, the amount of the credit can be reduced — increasing the effective FUTA tax rate —for employers in states that borrowed funds from the federal government to pay unemployment benefits and defaulted on repaying the loan.
Some services performed by an employee aren’t considered employment for FUTA purposes. Even if an employee’s services are considered employment for FUTA purposes, some compensation received for those services — for example, most fringe benefits — aren’t subject to FUTA tax.
Recognizing the insurance principle of taxing according to “risk,’’ states have adopted laws permitting some employers to pay less. Your unemployment tax bill may be influenced by the number of former employees who’ve filed unemployment claims with the state, the current number of employees you have and the age of your business. Typically, the more claims made against a business, the higher the unemployment tax bill.
Here are four ways to help control your unemployment tax costs:
1. If your state permits it, “buy down” your unemployment tax rate. Some states allow employers to annually buy down their rate. If you’re eligible, this could save you substantial unemployment tax dollars.
2. Hire conservatively and assess candidates. Your unemployment payments are based partly on the number of employees who file unemployment claims. You don’t want to hire employees to fill a need now, only to have to lay them off if business slows. A temporary staffing agency can help you meet short-term needs without permanently adding staff, so you can avoid layoffs. It’s often worth having job candidates undergo assessments before they’re hired to see if they’re the right match for your business and the position available. Hiring carefully can increase the likelihood that new employees will work out.
3. Train for success. Many unemployment insurance claimants are awarded benefits despite employer assertions that the employees failed to perform adequately. This may occur because the hearing officer concludes the employer didn’t provide the employee with enough training to succeed in the job.
4. Handle terminations carefully. If you must terminate an employee, consider giving him or her severance as well as outplacement benefits. Severance pay may reduce or delay the start of unemployment insurance benefits. Effective outplacement services may hasten the end of unemployment insurance benefits, because a claimant finds a new job.
If you have questions about unemployment taxes and how you can reduce them, contact us. We’d be pleased to help.
© 2019
Take advantage of the gift tax exclusion rules

As we head toward the gift-giving season, you may be considering giving gifts of cash or securities to your loved ones. Taxpayers can transfer substantial amounts free of gift taxes to their children and others each year through the use of the annual federal gift tax exclusion. The amount is adjusted for inflation annually. For 2019, the exclusion is $15,000.
The exclusion covers gifts that you make to each person each year. Therefore, if you have three children, you can transfer a total of $45,000 to them this year (and next year) free of federal gift taxes. If the only gifts made during the year are excluded in this way, there’s no need to file a federal gift tax return. If annual gifts exceed $15,000, the exclusion covers the first $15,000 and only the excess is taxable. Further, even taxable gifts may result in no gift tax liability thanks to the unified credit (discussed below).
Note: this discussion isn’t relevant to gifts made from one spouse to the other spouse, because these gifts are gift tax-free under separate marital deduction rules.
Gifts by married taxpayers
f you’re married, gifts to individuals made during a year can be treated as split between you and your spouse, even if the cash or gift property is actually given to an individual by only one of you. By “gift-splitting,” up to $30,000 a year can be transferred to each person by a married couple, because two annual exclusions are available. For example, if you’re married with three children, you and your spouse can transfer a total of $90,000 each year to your children ($30,000 × 3). If your children are married, you can transfer $180,000 to your children and their spouses ($30,000 × 6).
If gift-splitting is involved, both spouses must consent to it. We can assist you with preparing a gift tax return (or returns) to indicate consent.
“Unified” credit for taxable gifts
Even gifts that aren’t covered by the exclusion, and that are therefore taxable, may not result in a tax liability. This is because a tax credit wipes out the federal gift tax liability on the first taxable gifts that you make in your lifetime, up to $11,400,000 (for 2019). However, to the extent you use this credit against a gift tax liability, it reduces (or eliminates) the credit available for use against the federal estate tax at your death
Giving gifts of appreciated assets
Let’s say you own stocks and other marketable securities (outside of your retirement accounts) that have skyrocketed in value since they were acquired. A 15% or 20% tax rate generally applies to long-term capital gains. But there’s a 0% long-term capital gains rate for those in lower tax brackets. Even if your income is high, your family members in lower tax brackets may be able to benefit from the 0% long-term capital gains rate. Giving them appreciated stock instead of cash might allow you to eliminate federal tax liability on the appreciation, or at least significantly reduce it. The recipients can sell the assets at no or a low federal tax cost. Before acting, make sure the recipients won’t be subject to the “kiddie tax,” and consider any gift and generation-skipping transfer (GST) tax consequences
Plan ahead
Annual gifts are only one way to transfer wealth to your loved ones. There may be other effective tax and estate planning tools. Contact us before year end to discuss your options.
© 2019
The chances of an IRS audit are low, but business owners should be prepared

Many business owners ask: How can I avoid an IRS audit? The good news is that the odds against being audited are in your favor. In fiscal year 2018, the IRS audited approximately 0.6% of individuals. Businesses, large corporations and high-income individuals are more likely to be audited but, overall, audit rates are historically low.
There’s no 100% guarantee that you won’t be picked for an audit, because some tax returns are chosen randomly. However, completing your returns in a timely and accurate fashion with our firm certainly works in your favor. And it helps to know what might catch the attention of the IRS.
Audit red flags
A variety of tax-return entries may raise red flags with the IRS and may lead to an audit. Here are a few examples:
- Significant inconsistencies between previous years’ filings and your most current filing,
- Gross profit margin or expenses markedly different from those of other businesses in your industry, and
- Miscalculated or unusually high deductions.
Certain types of deductions may be questioned by the IRS because there are strict recordkeeping requirements for them • for example, auto and travel expense deductions. In addition, an owner-employee salary that’s inordinately higher or lower than those in similar companies in his or her location can catch the IRS’s eye, especially if the business is structured as a corporation.
How to respond
If you’re selected for an audit, you’ll be notified by letter. Generally, the IRS won’t make initial contact by phone. But if there’s no response to the letter, the agency may follow up with a call.
Many audits simply request that you mail in documentation to support certain deductions you’ve taken. Others may ask you to take receipts and other documents to a local IRS office. Only the harshest version, the field audit, requires meeting with one or more IRS auditors. (Note: Ignore unsolicited email messages about an audit. The IRS doesn’t contact people in this manner. These are scams.)
Keep in mind that the tax agency won’t demand an immediate response to a mailed notice. You’ll be informed of the discrepancies in question and given time to prepare. You’ll need to collect and organize all relevant income and expense records. If any records are missing, you’ll have to reconstruct the information as accurately as possible based on other documentation.
If the IRS chooses you for an audit, our firm can help you:
Determining the correct amount
- Understand what the IRS is disputing (it’s not always crystal clear),
- Gather the specific documents and information needed, and
- Respond to the auditor’s inquiries in the most expedient and effective manner.
Don’t panic if you’re contacted by the IRS. Many audits are routine. By taking a meticulous, proactive approach to how you track, document and file your company’s tax-related information, you’ll make an audit much less painful and even decrease the chances that one will happen in the first place.
© 2019
When is tax due on Series EE savings bonds?

|
How to treat your business website costs for tax purposes
|
5 ways to withdraw cash from your corporation while avoiding dividend treatment
Do you want to withdraw cash from your closely held corporation at a low tax cost? The easiest way is to distribute cash as a dividend. However, a dividend distribution isn’t tax-efficient, since it’s taxable to you to the extent of your corporation’s “earnings and profits.” But it’s not deductible by the corporation.
Different approaches
Fortunately, there are several alternative methods that may allow you to withdraw cash from a corporation while avoiding dividend treatment. Here are five ideas:
1. Capital repayments. To the extent that you’ve capitalized the corporation with debt, including amounts that you’ve advanced to the business, the corporation can repay the debt without the repayment being treated as a dividend. Additionally, interest paid on the debt can be deducted by the corporation. This assumes that the debt has been properly documented with terms that characterize debt and that the corporation doesn’t have an excessively high debt-to-equity ratio. If not, the “debt” repayment may be taxed as a dividend. If you make cash contributions to the corporation in the future, consider structuring them as debt to facilitate later withdrawals on a tax-advantaged basis.
2. Salary. Reasonable compensation that you, or family members, receive for services rendered to the corporation is deductible by the business. However, it’s also taxable to the recipient. The same rule applies to any compensation (in the form of rent) that you receive from the corporation for the use of property. In either case, the amount of compensation must be reasonable in relation to the services rendered or the value of the property provided. If it’s excessive, the excess will be nondeductible and treated as a corporate distribution.
3. Loans. You may withdraw cash from the corporation tax-free by borrowing money from it. However, to avoid having the loan characterized as a corporate distribution, it should be properly documented in a loan agreement or a note and be made on terms that are comparable to those on which an unrelated third party would lend money to you. This should include a provision for interest and principal. All interest and principal payments should be made when required under the loan terms. Also, consider the effect of the corporation’s receipt of interest income.
4. Fringe benefits. Consider obtaining the equivalent of a cash withdrawal in fringe benefits that are deductible by the corporation and not taxable to you. Examples are life insurance, certain medical benefits, disability insurance and dependent care. Most of these benefits are tax-free only if provided on a nondiscriminatory basis to other employees of the corporation. You can also establish a salary reduction plan that allows you (and other employees) to take a portion of your compensation as nontaxable benefits, rather than as taxable compensation.
5. Property sales. You can withdraw cash from the corporation by selling property to it. However, certain sales should be avoided. For example, you shouldn’t sell property to a more than 50% owned corporation at a loss, since the loss will be disallowed. And you shouldn’t sell depreciable property to a more than 50% owned corporation at a gain, since the gain will be treated as ordinary income, rather than capital gain. A sale should be on terms that are comparable to those on which an unrelated third party would purchase the property. You may need to obtain an independent appraisal to establish the property’s value.
Minimize taxes
If you’re interested in discussing any of these ideas, contact us. We can help you get the maximum out of your corporation at the minimum tax cost.
© 2019
Uncle Sam may provide relief from college costs on your tax return

We all know the cost of college is expensive. The latest figures from the College Board show that the average annual cost of tuition and fees was $10,230 for in-state students at public four-year universities — and $35,830 for students at private not-for-profit four-year institutions. These amounts don’t include room and board, books, supplies, transportation and other expenses that a student may incur.
Two tax credits,
Fortunately, the federal government offers two sizable tax credits for higher education costs that you may be able to claim:
1. The American Opportunity credit. This tax break generally provides the biggest benefit to most taxpayers. The American Opportunity credit provides a maximum benefit of $2,500. That is, you may qualify for a credit equal to 100% of the first $2,000 of expenses for the year and 25% of the next $2,000 of expenses. It applies only to the first four years of postsecondary education and is available only to students who attend at least half time.
Basically, tuition, course materials and fees qualify for this credit. The credit is per eligible student and is subject to phaseouts based on modified adjusted gross income (MAGI). For 2019, the MAGI phaseout ranges are:
- Between $80,000 and $90,000 for unmarried individuals, and
- Between $160,000 and $180,000 for married joint filers.
2. The Lifetime Learning credit. This credit equals 20% of qualified education expenses for up to <00 per tax return. There are fewer restrictions to qualify for this credit than for the American Opportunity credit.
The Lifetime Learning credit can be applied to education beyond the first four years, and qualifying students may attend school less than half time. The student doesn’t even need to be part of a degree program. So, the credit works well for graduate studies and part-time students who take a qualifying course at a local college to improve job skills. It applies to tuition, fees and materials.
It’s also subject to phaseouts based on MAGI, however. For 2019, the MAGI phaseout ranges are:,
- Between $58,000 and $68,000 for unmarried individuals, and
- Between $116,000 and $136,000 for married joint filers.
Note: You can’t claim either the American Opportunity Credit or the Lifetime Learning Credit for the same student or for the same expense in the same year.
Credit for what you’ve paid
So which higher education tax credit is right for you? A number of factors need to be reviewed before determining the answer to that question. Contact us for more information about how to take advantage of tax-favored ways to save or pay for college.
© 2019
Getting a divorce? There are tax issues you need to understand
|
2019 Q4 tax calendar: Key deadlines for businesses and other employers
|
The next estimated tax deadline is September 16: Do you have to make a payment?

If you’re self-employed and don’t have withholding from paychecks, you probably have to make estimated tax payments. These payments must be sent to the IRS on a quarterly basis. The third 2019 estimated tax payment deadline for individuals is Monday, September 16. Even if you do have some withholding from paychecks or payments you receive, you may still have to make estimated payments if you receive other types of income such as Social Security, prizes, rent, interest, and dividends.
Pay-as-you-go system
You must make sufficient federal income tax payments long before the April filing deadline through withholding, estimated tax payments, or a combination of the two. If you fail to make the required payments, you may be subject to an underpayment penalty, as well as interest.
In general, you must make estimated tax payments for 2019 if both of these statements apply:
- You expect to owe at least $1,000 in tax after subtracting tax withholding and credits, and
- You expect withholding and credits to be less than the smaller of 90% of your tax for 2019 or 100% of the tax on your 2018 return — 110% if your 2018 adjusted gross income was more than $150,000 ($75,000 for married couples filing separately).
If you’re a sole proprietor, partner or S corporation shareholder, you generally have to make estimated tax payments if you expect to owe $1,000 or more in tax when you file your return.
Quarterly due dates
Estimated tax payments are spread out through the year. The due dates are April 15, June 15, September 15 and January 15 of the following year. However, if the date falls on a weekend or holiday, the deadline is the next business day (which is why the third deadline is September 16 this year).
Estimated tax is calculated by factoring in expected gross income, taxable income, deductions and credits for the year. The easiest way to pay estimated tax is electronically through the Electronic Federal Tax Payment System. You can also pay estimated tax by check or money order using the Estimated Tax Payment Voucher or by credit or debit card.
Seasonal businesses
Most individuals make estimated tax payments in four installments. In other words, you can determine the required annual payment, divide the number by four and make four equal payments by the due dates. But you may be able to make smaller payments under an “annualized income method.” This can be useful to people whose income isn’t uniform over the year, perhaps because of a seasonal business. For example, let’s say your income comes exclusively from a business that you operate in a beach town during June, July and August. In this case, with the annualized income method, no estimated payment would be required before the usual September 15 deadline. You may also want to use the annualized income method if a large portion of your income comes from capital gains on the sale of securities that you sell at various times during the year.
Determining the correct amount
Contact us if you think you may be eligible to determine your estimated tax payments under the annualized income method, or you have any other questions about how the estimated tax rules apply to you.
© 2019
The key to retirement security is picking the right plan for your business

If you’re a small business owner or you’re involved in a start-up, you may want to set up a tax-favored retirement plan for yourself and any employees. Several types of plans are eligible for tax advantages.
401(k) plan
One of the best-known retirement plan options is the 401(k) plan. It provides for employer contributions made at the direction of employees. Specifically, the employee elects to have a certain amount of pay deferred and contributed by the employer on his or her behalf to an individual account. Employee contributions can be made on a pretax basis, saving employees current income tax on the amount contributed.
Employers may, or may not, provide matching contributions on behalf of employees who make elective deferrals to 401(k) plans. Establishing and operating a 401(k) plan means some up-front paperwork and ongoing administrative effort. Matching contributions may be subject to a vesting schedule. 401(k) plans are subject to testing requirements, so that highly compensated employees don’t contribute too much more than non-highly compensated employees. However, these tests can be avoided if you adopt a “safe harbor” 401(k) plan.
Within limits, participants can borrow from a 401(k) account (assuming the plan document permits it).
For 2019, the maximum amount you can contribute to a 401(k) is $19,000, plus a $6,000 “catch-up” amount for those age 50 or older as of December 31, 2019.
Other tax-favored plans
Of course, a 401(k) isn’t your only option. Here’s a quick rundown of two other alternatives that are simpler to set up and administer:
1. A Simplified Employee Pension (SEP) IRA. For 2019, the maximum amount of deductible contributions that you can make to an employee’s SEP plan, and that he or she can exclude from income, is the lesser of 25% of compensation or $56,000. Your employees control their individual IRAs and IRA investments.
2. A SIMPLE IRA. SIMPLE stands for “savings incentive match plan for employees.” A business with 100 or fewer employees can establish a SIMPLE. Under one, an IRA is established for each employee, and the employer makes matching contributions based on contributions elected by participating employees under a qualified salary reduction arrangement. The maximum amount you can contribute to a SIMPLE in 2019 is $13,000, plus a $3,000 “catch-up” amount if you’re age 50 or older as of December 31, 2019.
Annual contributions to a SEP plan and a SIMPLE are controlled by special rules and aren’t tied to the normal IRA contribution limits. Neither type of plan requires annual filings or discrimination testing. You can’t borrow from a SEP plan or a SIMPLE.
Many choices
These are only some of the retirement savings options that may be available to your business. We can discuss the alternatives and help find the best option for your situation.
© 2019
Expenses that teachers can and can't deduct on their tax returns

As teachers head back for a new school year, they often pay for various expenses for which they don’t receive reimbursement. Fortunately, they may be able to deduct them on their tax returns. However, there are limits on this special deduction, and some expenses can’t be written off.
For 2019, qualifying educators can deduct some of their unreimbursed out-of-pocket classroom costs under the educator expense deduction. This is an “above-the-line” deduction, which means you don’t have to itemize your deductions in order to claim it.
Eligible deductionsHere are some details about the educator expense deduction:
- For 2019, educators can deduct up to $250 of trade or business expenses that weren’t reimbursed. (The deduction is $500 if both taxpayers are eligible educators who file a joint tax return, but these taxpayers can’t deduct more than $250 each.)
- Qualified expenses are amounts educators paid themselves during the tax year.
- Examples of expenses that educators can deduct include books, supplies, computer equipment (including software), other materials used in the classroom, and professional development courses.
- To be eligible, taxpayers must be kindergarten through grade 12 teachers, instructors, counselors, principals or aides. They must also work at least 900 hours a school year in a school that provides elementary or secondary education as determined under state law.
Educators should keep receipts when they make eligible expenses and note the date, amount and purpose of each purchase.
Ineligible deductionsTeachers or professors may see advertisements for job-related courses in out-of-town or exotic locations. You may have wondered whether traveling to these courses is tax-deductible on teachers’ tax returns. The bad news is that, for tax years 2018–2025, it isn’t, because the outlays are employee business expenses.
Prior to 2018, employee business expenses could be claimed as miscellaneous itemized deductions. However, under the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act, miscellaneous itemized deductions aren’t deductible by individuals for tax years 2018–2025.
© 2019
The tax implications of a company car

|
Taking distributions from your traditional IRA
|
Should you elect S corporation status?
|
“Innocent spouses” may get relief from tax liability

|
What to do if your business receives a “no-match” letter

|
The IRS is targeting business transactions in bitcoin and other virtual currencies

|
The tax implications of being a winner

|
The “kiddie tax” hurts families more than ever
|
Take a closer look at home office deductions
|
The “nanny tax” must be paid for more than just nannies

You may have heard of the “nanny tax.” But even if you don’t employ a nanny, it may apply to you. Hiring a housekeeper, gardener or other household employee (who isn’t an independent contractor) may make you liable for federal income and other taxes. You may also have state tax obligations.
If you employ a household worker, you aren’t required to withhold federal income taxes from pay. But you may choose to withhold if the worker requests it. In that case, ask the worker to fill out a Form W-4. However, you may be required to withhold Social Security and Medicare (FICA) taxes and to pay federal unemployment (FUTA) tax.
FICA and FUTA tax
In 2019, you must withhold and pay FICA taxes if your household worker earns cash wages of $2,100 or more (excluding the value of food and lodging). If you reach the threshold, all the wages (not just the excess) are subject to FICA.
However, if a nanny is under age 18 and child care isn’t his or her principal occupation, you don’t have to withhold FICA taxes. So, if you have a part-time babysitter who is a student, there’s no FICA tax liability.
Both an employer and a household worker may have FICA tax obligations. As an employer, you’re responsible for withholding your worker’s FICA share. In addition, you must pay a matching amount. FICA tax is divided between Social Security and Medicare. The Social Security tax rate is 6.2% for the employer and 6.2% for the worker (12.4% total). Medicare tax is 1.45% each for both the employer and the worker (2.9% total).
If you want, you can pay your worker’s share of Social Security and Medicare taxes. If you do, your payments aren’t counted as additional cash wages for Social Security and Medicare purposes. However, your payments are treated as additional income to the worker for federal tax purposes, so you must include them as wages on the W-2 form that you must provide.
You also must pay FUTA tax if you pay $1,000 or more in cash wages (excluding food and lodging) to your worker in any calendar quarter. FUTA tax applies to the first $7,000 of wages paid and is only paid by the employer.
Reporting and paying
You pay household worker obligations by increasing your quarterly estimated tax payments or increasing withholding from wages, rather than making an annual lump-sum payment.
As a household worker employer, you don’t have to file employment tax returns, even if you’re required to withhold or pay tax (unless you own your own business). Instead, employment taxes are reported on your tax return on Schedule H.
When you report the taxes on your return, you include your employer identification number (not the same as your Social Security number). You must file Form SS-4 to get one.
However, if you own a business as a sole proprietor, you include the taxes for a household worker on the FUTA and FICA forms (940 and 941) that you file for your business. And you use your sole proprietorship EIN to report the taxes.
Keep careful records
Keep related tax records for at least four years from the later of the due date of the return or the date the tax was paid. Records should include the worker’s name, address, Social Security number, employment dates, dates and amount of wages paid and taxes withheld, and copies of forms filed.
Contact us for assistance or questions about how to comply with these employment tax requirements.
© 2019
Businesses can utilize the same information IRS auditors use to examine tax returns
|
Summer: A good time to review your investments

You may have heard about a proposal in Washington to cut the taxes paid on investments by indexing capital gains to inflation. Under the proposal, the purchase price of assets would be adjusted so that no tax is paid on the appreciation due to inflation.
While the fate of such a proposal is unknown, the long-term capital gains tax rate is still historically low on appreciated securities that have been held for more than 12 months. And since we’re already in the second half of the year, it’s a good time to review your portfolio for possible tax-saving strategies.
The federal income tax rate on long-term capital gains recognized in 2019 is 15% for most taxpayers. However, the maximum rate of 20% plus the 3.8% net investment income tax (NIIT) can apply at higher income levels. For 2019, the 20% rate applies to single taxpayers with taxable income exceeding $425,800 ($479,000 for joint filers or $452,400 for heads of households).
You also may be able to plan for the NIIT. It can affect taxpayers with modified AGI (MAGI) over $200,000 for singles and heads of households, or $250,000 for joint filers. You may be able to lower your tax liability by reducing your MAGI, reducing net investment income or both.
What about losing investments that you’d like to sell? Consider selling them and using the resulting capital losses to shelter capital gains, including high-taxed short-term gains, from other sales this year. You may want to repurchase those investments, so long as you wait at least 31 days to avoid the “wash sale” rule.
If your capital losses exceed your capital gains, the result would be a net capital loss for the year. A net capital loss can also be used to shelter up to $3,000 of 2019 ordinary income (or up to $1,500 if you’re married and file separately). Ordinary income includes items including salaries, bonuses, self-employment income, interest income and royalties. Any excess net capital loss from 2019 can be carried forward to 2020 and later years.
Consider gifting to young relatives
While most taxpayers with long-term capital gains pay a 15% rate, those in the 0% federal income tax bracket only pay a 0% federal tax rate on gains from investments that were held for more than a year. Let’s say you’re feeling generous and want to give some money to your children, grandchildren, nieces, nephews, or others. Instead of making cash gifts to young relatives in lower federal tax brackets, give them appreciated investments. That way, they’ll pay less tax than you’d pay if you sold the same shares.
(You can count your ownership period plus the gift recipient’s ownership period for purposes of meeting the more-than-one-year rule.)
Even if the appreciated shares have been held for a year or less before being sold, your relative will probably pay a much lower tax rate on the gain than you would.
Increase your return
Paying capital gains taxes on your investment profits reduces your total return. Look for strategies to grow your portfolio by minimizing the amount you must pay to the federal and state governments. These are only a few strategies that may be available to you. Contact us about your situation.
© 2019
It’s a good time to buy business equipment and other depreciable property
|
Volunteering for charity: Do you get a tax break?

If you’re a volunteer who works for charity, you may be entitled to some tax breaks if you itemize deductions on your tax return. Unfortunately, they may not amount to as much as you think your generosity is worth.
Because donations to charity of cash or property generally are tax deductible for itemizers, it may seem like donations of something more valuable for many people — their time — would also be deductible. However, no tax deduction is allowed for the value of time you spend volunteering or the services you perform for a charitable organization.
It doesn’t matter if the services you provide require significant skills and experience, such as construction, which a charity would have to pay dearly for if it went out and obtained itself. You still don’t get to deduct the value of your time.
However, you potentially can deduct out-of-pocket costs associated with your volunteer work.
The basic rules
As with any charitable donation, to be able to deduct your volunteer expenses, the first requirement is that the organization be a qualified charity. You can check by using the IRS’s “Tax Exempt Organization Search” tool at https://www.irs.gov/charities-non-profits/tax-exempt-organization-search.
If the charity is qualified, you may be able to deduct out-of-pocket costs that are unreimbursed; directly connected with the services you’re providing; incurred only because of your charitable work; and not “personal, living or family” expenses.
Expenses that may qualify
A wide variety of expenses can qualify for the deduction. For example, supplies you use in the activity may be deductible. And the cost of a uniform you must wear during the activity may also be deductible (if it’s required and not something you’d wear when not volunteering).
Transportation costs to and from the volunteer activity generally are deductible — either the actual expenses (such as gas costs) or 14 cents per charitable mile driven. The cost of entertaining others (such as potential contributors) on behalf of a charity may also be deductible. However, the cost of your own entertainment or meal isn’t deductible.
Deductions are permitted for away-from-home travel expenses while performing services for a charity. This includes out-of-pocket round-trip travel expenses, taxi fares and other costs of transportation between the airport or station and hotel, plus lodging and meals. However, these expenses aren’t deductible if there’s a significant element of personal pleasure associated with the travel, or if your services for a charity involve lobbying activities.
Recordkeeping is important
The IRS may challenge charitable deductions for out-of-pocket costs, so it’s important to keep careful records and receipts. You must meet the other requirements for charitable donations. For example, no charitable deduction is allowed for a contribution of $250 or more unless you substantiate the contribution with a written acknowledgment from the organization. The acknowledgment generally must include the amount of cash, a description of any property contributed, and whether you got anything in return for your contribution.
And, in order to get a charitable deduction, you must itemize. Under the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act, fewer people are itemizing because the law significantly increased the standard deduction amounts. So even if you have expenses from volunteering that qualify for a deduction, you may not get any tax benefit if you don’t have enough itemized deductions.
If you have questions about charitable deductions and volunteer expenses, please contact us.
© 2019
M&A transactions: Avoid surprises from the IRS

If you’re considering buying or selling a business — or you’re in the process of a merger or acquisition — it’s important that both parties report the transaction to the IRS in the same way. Otherwise, you may increase your chances of being audited.
If a sale involves business assets (as opposed to stock or ownership interests), the buyer and the seller must generally report to the IRS the purchase price allocations that both use. This is done by attaching IRS Form 8594, “Asset Acquisition Statement,” to each of their respective federal income tax returns for the tax year that includes the transaction.
What’s reported?
When buying business assets in an M&A transaction, you must allocate the total purchase price to the specific assets that are acquired. The amount allocated to each asset then becomes its initial tax basis. For depreciable and amortizable assets, the initial tax basis of each asset determines the depreciation and amortization deductions for that asset after the acquisition. Depreciable and amortizable assets include:
- Equipment,
- Buildings and improvements,
- Software,
- Furniture, fixtures and
- Intangibles (including customer lists, licenses, patents, copyrights and goodwill).
In addition to reporting the items above, you must also disclose on Form 8594 whether the parties entered into a noncompete agreement, management contract or similar agreement, as well as the monetary consideration paid under it.
IRS scrutiny
The IRS may inspect the forms that are filed to see if the buyer and the seller use different allocations. If the IRS finds that different allocations are used, auditors may dig deeper and the investigation could expand beyond just the transaction. So, it’s in your best interest to ensure that both parties use the same allocations. Consider including this requirement in your asset purchase agreement at the time of the sale.
The tax implications of buying or selling a business are complicated. Price allocations are important because they affect future tax benefits. Both the buyer and the seller need to report them to the IRS in an identical way to avoid unwanted attention. To lock in the best postacquisition results, consult with us before finalizing any transaction.
© 2019
You may have to pay tax on Social Security benefits

During your working days, you pay Social Security tax in the form of withholding from your salary or self-employment tax. And when you start receiving Social Security benefits, you may be surprised to learn that some of the payments may be taxed.
If you’re getting close to retirement age, you may be wondering if your benefits are going to be taxed. And if so, how much will you have to pay? The answer depends on your other income. If you are taxed, between 50% and 85% of your payments will be hit with federal income tax. (There could also be state tax.)
Important: This doesn’t mean you pay 50% to 85% of your benefits back to the government in taxes. It means that you have to include 50% to 85% of them in your income subject to your regular tax rates.
Calculate provisional income
To determine how much of your benefits are taxed, you must calculate your provisional income. It starts with your adjusted gross income on your tax return. Then, you add certain amounts (for example, tax-exempt interest from municipal bonds). Add to that the income of your spouse, if you file jointly. To this, add half of the Social Security benefits you and your spouse received during the year. The figure you come up with is your provisional income. Now apply the following rules:
- If you file a joint tax return and your provisional income, plus half your benefits, isn’t above $32,000 ($25,000 for single taxpayers), none of your Social Security benefits are taxed.
- If your provisional income is between $32,001 and $44,000, and you file jointly with your spouse, you must report up to 50% of your Social Security benefits as income. For single taxpayers, if your provisional income is between $25,001 and $34,000, you must report up to 50% of your Social Security benefits as income.
- If your provisional income is more than $44,000, and you file jointly, you must report up to 85% of your Social Security benefits as income on Form 1040. For single taxpayers, if your provisional income is more than $34,000, the general rule is that you must report up to 85% of your Social Security benefits as income.
Caution: If you aren’t paying tax on your Social Security benefits now because your income is below the floor, or you’re paying tax on only 50% of those benefits, an unplanned increase in your income can have a significant tax cost. You’ll have to pay tax on the additional income, you’ll also have to pay tax on (or on more of) your Social Security benefits, and you may get pushed into a higher tax bracket.
For example, this might happen if you receive a large retirement plan distribution during the year or you receive large capital gains. With careful planning, you might be able to avoid this tax result.
Avoid a large tax bill
If you know your Social Security benefits will be taxed, you may want to voluntarily arrange to have tax withheld from the payments by filing a Form W-4V with the IRS. Otherwise, you may have to make estimated tax payments.
Contact us to help you with the exact calculations on whether your Social Security will be taxed. We can also help you with tax planning to keep your taxes as low as possible during retirement.
© 2019
Bartering: A taxable transaction even if your business exchanges no cash
Small businesses may find it beneficial to barter for goods and services instead of paying cash for them. If your business engages in bartering, be aware that the fair market value of goods that you receive in bartering is taxable income. And if you exchange services with another business, the transaction results in taxable income for both parties.
Income is also realized if services are exchanged for property. For example, if a construction firm does work for a retail business in exchange for unsold inventory, it will have income equal to the fair market value of the inventory.
Barter clubs
Many business owners join barter clubs that facilitate barter exchanges. In general, these clubs use a system of “credit units” that are awarded to members who provide goods and services. The credits can be redeemed for goods and services from other members.
Bartering is generally taxable in the year it occurs. But if you participate in a barter club, you may be taxed on the value of credit units at the time they’re added to your account, even if you don’t redeem them for actual goods and services until a later year. For example, let’s say that you earn 2,000 credit units one year, and that each unit is redeemable for $1 in goods and services. In that year, you’ll have $2,000 of income. You won’t pay additional tax if you redeem the units the next year, since you’ve already been taxed once on that income.
If you join a barter club, you’ll be asked to provide your Social Security number or employer identification number. You’ll also be asked to certify that you aren’t subject to backup withholding. Unless you make this certification, the club will withhold tax from your bartering income at a 24% rate.
Required forms
By January 31 of each year, the barter club will send you a Form 1099-B, “Proceeds from Broker and Barter Exchange Transactions,” which shows the value of cash, property, services, and credits that you received from exchanges during the previous year. This information will also be reported to the IRS.
If you don’t contract with a barter exchange but you do trade services, you don’t file Form 1099-B. But you may have to file a form 1099-MISC.
Many benefits
By bartering, you can trade away excess inventory or provide services during slow times, all while hanging onto your cash. You may also find yourself bartering when a customer doesn’t have the money on hand to complete a transaction. As long as you’re aware of the federal and state tax consequences, these transactions can benefit all parties. Contact us for more information.
© 2019
If your kids are off to day camp, you may be eligible for a tax break

Now that most schools are out for the summer, you might be sending your children to day camp. It’s often a significant expense. The good news: You might be eligible for a tax break for the cost.
The value of a credit
Day camp is a qualified expense under the child and dependent care credit, which is worth 20% to 35% of qualifying expenses, subject to a cap. Note: Sleep-away camp does not qualify.
For 2019, the maximum expenses allowed for the credit are $3,000 for one qualifying child and $6,000 for two or more. Other expenses eligible for the credit include payments to a daycare center, nanny, or nursery school.
Keep in mind that tax credits are especially valuable because they reduce your tax liability dollar-for-dollar — $1 of tax credit saves you $1 of taxes. This differs from deductions, which simply reduce the amount of income subject to tax.
For example, if you’re in the 32% tax bracket, $1 of deduction saves you only $0.32 of taxes. So it’s important to take maximum advantage of all tax credits available to you.
Work-related expenses
For an expense to qualify for the credit, it must be related to employment. In other words, it must enable you to work — or look for work if you’re unemployed. It must also be for the care of your child, stepchild, foster child, or other qualifying relative who is under age 13, lives in your home for more than half the year and meets other requirements.
There’s no age limit if the dependent child is physically or mentally unable to care for him- or herself. Special rules apply if the child’s parents are divorced or separated or if the parents live apart.
Credit vs. FSA
If you participate in an employer-sponsored child and dependent care Flexible Spending Account (FSA), you can’t use expenses paid from or reimbursed by the FSA to claim the credit.
If your employer offers a child and dependent care FSA, you may wish to consider participating in the FSA instead of taking the credit. With an FSA for child and dependent care, you can contribute up to $5,000 on a pretax basis. If your marginal tax rate is more than 15%, participating in the FSA is more beneficial than taking the credit. That’s because the exclusion from income under the FSA gives a tax benefit at your highest tax rate, while the credit rate for taxpayers with adjusted gross income over $43,000 is limited to 20%.
Proving your eligibility
On your tax return, you must include the Social Security number of each child who attended the camp or received care. There’s no credit without it. You must also identify the organizations or persons that provided care for your child. So make sure to obtain the name, address and taxpayer identification number of the camp.
Additional rules apply to the child and dependent care credit. Contact us if you have questions. We can help determine your eligibility for the credit and other tax breaks for parents.
© 2019Which entity is most suitable for your new or existing business?

The Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA) has changed the landscape for business taxpayers. That’s because the law introduced a flat 21% federal income tax rate for C corporations. Under prior law, profitable C corporations paid up to 35%.
The TCJA also cut individual income tax rates, which apply to sole proprietorships and pass-through entities, including partnerships, S corporations, and LLCs (treated as partnerships for tax purposes). However, the top rate dropped from 39.6% to only 37%.
These changes have caused many business owners to ask: What’s the optimal entity choice for me?
Entity tax basics
Before the TCJA, conventional wisdom was that most small businesses should be set up as sole proprietorships or pass-through entities to avoid the double taxation of C corporations. A C corporation pays entity-level income tax and then shareholders pay tax on dividends — and on capital gains when they sell the stock. For pass-through entities, there’s no federal income tax at the entity level.
Although C corporations are still potentially subject to double taxation, their current 21% tax rate helps make up for it. This issue is further complicated, however, by another tax provision that allows noncorporate owners of pass-through entities to take a deduction equal to as much as 20% of qualified business income (QBI), subject to various limits. But, unless Congress extends it, that deduction is available only through 2025.
Many factors to consider
The best entity choice for your business depends on many factors. Keep in mind that one form of doing business might be more appropriate at one time (say, when you’re launching), while another form might be better after you’ve been operating for a few years. Here are a few examples:
- Suppose a business consistently generates losses. There’s no tax advantage to operating as a C corporation. C corporation losses can’t be deducted by their owners. A pass-through entity would generally make more sense in this scenario because losses would pass through to the owners’ personal tax returns.
- What about a profitable business that pays out all income to the owners? In this case, operating as a pass-through entity would generally be better if significant QBI deductions are available. If not, there’s probably not a clear entity-choice answer in terms of tax liability.
- Finally, what about a business that’s profitable but holds on to its profits to fund future projects? In this case, operating as a C corporation generally would be beneficial if the corporation is a qualified small business (QSB). Reason: A 100% gain exclusion may be available for QSB stock sale gains. Even if QSB status isn’t available, C corporation status is still probably preferred — unless significant QBI deductions would be available at the owner level.
As you can see, there are many issues involved and taxes are only one factor.
For example, one often-cited advantage of certain entities is that they allow a business to be treated as an entity separate from the owner. A properly structured corporation can protect you from business debts. But to ensure that the corporation is treated as a separate entity, it’s important to observe various formalities required by the state. These include filing articles of incorporation, adopting by-laws, electing a board of directors, holding organizational meetings and keeping minutes.
The best long-term choice
The TCJA has far-reaching effects on businesses. Contact us to discuss how your business should be set up to lower its tax bill over the long run. But remember that entity choice is easier when starting up a business. Converting from one type of entity to another adds complexity. We can help you examine the ins and outs of making a change.
Is an HSA right for you?

To help defray health care costs, many people now contribute to, or are thinking about setting up, Health Savings Accounts (HSAs). With these accounts, individuals can pay for certain medical expenses on a tax advantaged basis.
The basics
With HSAs, you take more responsibility for your health care costs. If you’re covered by a qualified high-deductible health plan, you can contribute pretax income to an employer-sponsored HSA — or make deductible contributions to an HSA you set up yourself.
You own the account, which can bear interest or be invested. It can grow tax-deferred, similar to an IRA. Withdrawals for qualified medical expenses are tax-free, and you can carry over a balance from year to year. So, unlike Flexible Spending Accounts (FSAs), undistributed balances in HSAs aren’t forfeited at year end.
For the 2019 tax year, you can make a tax-deductible HSA contribution of up to $3,500 if you have qualifying self-only coverage or up to $7,000 if you have qualifying family coverage (anything other than self-only coverage). If you’re age 55 or older as of December 31, the maximum contribution increases by $1,000.
To be eligible to contribute to an HSA, you must have a qualifying high deductible health insurance policy and no other general health coverage. For 2019, a high deductible health plan is defined as one with a deductible of at least $1,350 for self-only coverage or $2,700 for family coverage.
For 2019, qualifying policies must have had out-of-pocket maximums of no more than $6,750 for self-only coverage or $13,500 for family coverage.
Account balances
If you still have an HSA balance after reaching Medicare eligibility age (generally age 65), you can empty the account for any reason without a tax penalty. If you don’t use the withdrawal to cover qualified medical expenses, you’ll owe federal income tax and possibly state income tax. But the 20% tax penalty that generally applies to withdrawals not used for medical expenses won’t apply. There’s no tax penalty on withdrawals made after disability or death.
Alternatively, you can use your HSA balance to pay uninsured medical expenses incurred after reaching Medicare eligibility age. If your HSA still has a balance when you die, your surviving spouse can take over the account tax-free and treat it as his or her own HSA, if he or she is named as the beneficiary. In other cases, the date-of-death HSA balance must generally be included in taxable income on that date by the person who inherits the account.
Deadlines and deductions
If you’re eligible to make an HSA contribution, the deadline is April 15 of the following year (adjusted for weekends and holidays) to open an account and make a tax-deductible contribution for the previous year.
So, if you’re eligible, there’s plenty of time to make a deductible contribution for 2019. The deadline for making 2019 contributions is April 15, 2020.
The write-off for HSA contributions is an “above-the-line” deduction. That means you can claim it even if you don’t itemize.
In addition, an HSA contribution isn’t tied to income. Even wealthy people can make deductible HSA contributions if they have qualifying high deductible health insurance coverage and meet the other requirements.
Tax-smart opportunity
HSAs can provide a smart tax-saving opportunity for individuals with qualifying high deductible health plans. Contact us to help you set up an HSA or decide how much to contribute for 2019.
© 2019
Donating your vehicle to charity may not be a taxwise decision
|
Hiring this summer? You may qualify for a valuable tax credit

|
Thinking about moving to another state in retirement? Don’t forget about taxes

When you retire, you may consider moving to another state — say, for the weather or to be closer to your loved ones. Don’t forget to factor state and local taxes into the equation. Establishing residency for state tax purposes may be more complicated than it initially appears to be.
Identify all applicable taxes
It may seem like a no-brainer to simply move to a state with no personal income tax. But, to make a good decision, you must consider all taxes that can potentially apply to a state resident. In addition to income taxes, these may include property taxes, sales taxes and estate taxes.
If the states you’re considering have an income tax, look at what types of income they tax. Some states, for example, don’t tax wages but do tax interest and dividends. And some states offer tax breaks for pension payments, retirement plan distributions and Social Security payments.
Watch out for state estate tax
The federal estate tax currently doesn’t apply to many people. For 2019, the federal estate tax exemption is $11.4 million ($22.8 million for a married couple). But some states levy estate tax with a much lower exemption and some states may also have an inheritance tax in addition to (or in lieu of) an estate tax.
Establish domicile
If you make a permanent move to a new state and want to escape taxes in the state you came from, it’s important to establish legal domicile in the new location. The definition of legal domicile varies from state to state. In general, your domicile is your fixed and permanent home location and the place where you plan to return, even after periods of residing elsewhere.
Each state has its own rules regarding domicile. You don’t want to wind up in a worst-case scenario: Two states could claim you owe state income taxes if you established domicile in the new state but didn’t successfully terminate domicile in the old one. Additionally, if you die without clearly establishing domicile in just one state, both the old and new states may claim that your estate owes income taxes and any state estate tax.
How do you establish domicile in a new state? The more time that elapses after you change states and the more steps you take to establish domicile in the new state, the harder it will be for your old state to claim that you’re still domiciled there for tax purposes. Some ways to help lock in domicile in a new state are to:
- Buy or lease a home in the new state and sell your home in the old state (or rent it out at market rates to an unrelated party),
- Change your mailing address at the post office,
- Change your address on passports, insurance policies, will or living trust documents, and other important documents,
- Register to vote, get a driver’s license and register your vehicle in the new state, and
- Open and use bank accounts in the new state and close accounts in the old one.
If an income tax return is required in the new state, file a resident return. File a nonresident return or no return (whichever is appropriate) in the old state. We can help with these returns.
Make an informed choice
Before deciding where you want to live in retirement, do some research and contact us. We can help you avoid unpleasant tax surprises.
© 2019
Employers: Be aware (or beware) of a harsh payroll tax penalty

|
The chances of IRS audit are down but you should still be prepared

The IRS just released its audit statistics for the 2018 fiscal year, and fewer taxpayers had their returns examined as compared with prior years. However, even though a small percentage of tax returns are being chosen for audit these days, that will be little consolation if yours is one of them.
Latest statistics
Overall, just 0.59% of individual tax returns were audited in 2018, as compared with 0.62% in 2017. This was the lowest percentage of audits conducted since 2002.
However, as in the past, those with very high incomes face greater odds. For example, in 2018, 2.21% of taxpayers with adjusted gross incomes (AGIs) of between $1 million and $5 million were audited (down from 3.52% in 2017).
The richest taxpayers, those with AGIs of $10 million and more, experienced a steep decline in audits. In 2018, 6.66% of their returns were audited, compared with 14.52% in 2017.
Surviving an audit
Even though fewer audits are being performed, the IRS will still examine thousands of returns this year. With proper planning, you should fare well even if you’re one of the unlucky ones.
The easiest way to survive an IRS examination is to prepare in advance. On an ongoing basis, you should systematically maintain documentation — invoices, bills, canceled checks, receipts, or other proof — for all items reported on your tax returns.
Just because a return is selected for audit doesn’t mean that an error was made. Some returns are randomly selected based on statistical formulas. For example, IRS computers compare income and deductions on returns with what other taxpayers report. If an individual deducts a charitable contribution that’s significantly higher than what others with similar incomes report, the IRS may want to know why.
Returns can also be selected when they involve issues or transactions with other taxpayers who were previously selected for audit, such as business partners or investors.
The government generally has three years within which to conduct an audit, and often the exam won’t begin until a year or more after you file your return.
More audit details
The scope of an audit depends on the tax return’s complexity. A return reflecting business or real estate income and expenses is likely to take longer to examine than a return with only salary income.
An audit can be conducted by mail or through an in-person interview and review of records. The interview may be conducted at an IRS office or may be a “field audit” at the taxpayer’s home, business, or accountant’s office.
Important: Even if your return is audited, an IRS examination may be nothing to lose sleep over. In many cases, the IRS asks for proof of certain items and routinely “closes” the audit after the documentation is presented.
Representation
It’s advisable to have a tax professional represent you at an audit. A tax pro knows what issues the IRS is likely to scrutinize and can prepare accordingly. In addition, a professional knows that in many instances IRS auditors will take a position (for example, to disallow deduction of a certain expense) even though courts and other guidance have expressed a contrary opinion on the issue. Because pros can point to the proper authority, the IRS may be forced to throw in the towel.
If you receive an IRS audit letter or simply want to improve your recordkeeping, we’re here to assist you. Contact us to discuss this or any other aspect of your taxes.
© 2019
Tax-smart domestic travel: Combining business with pleasure

Summer is just around the corner, so you might be thinking about getting some vacation time. If you’re self-employed or a business owner, you have a golden opportunity to combine a business trip with a few extra days of vacation and offset some of the cost with a tax deduction. But be careful, or you might not qualify for the write-offs you’re expecting
Basic Rules
Business travel expenses can potentially be deducted if the travel is within the United States and the expenses are:
- “Ordinary and necessary” and
- Directly related to the business.
Note: The tax rules for foreign business travel are different from those for domestic travel.
Business owners and the self-employed are generally eligible to deduct business travel expenses if they meet the tests described above. However, under the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act, employees can no longer deduct such expenses. The potential deductions discussed in this article assume that you’re a business owner or self-employed.
A business-vacation trip
Transportation costs to and from the location of your business activity may be 100% deductible if the primary reason for the trip is business rather than pleasure. But if vacation is the primary reason for your travel, generally no transportation costs are deductible. These costs include plane or train tickets, the cost of getting to and from the airport, luggage handling tips and car expenses if you drive. Costs for driving your personal car are also eligible.
The key factor in determining whether the primary reason for domestic travel is business is the number of days you spend conducting business vs. enjoying vacation days. Any day principally devoted to business activities during normal business hours counts as a business day. In addition:
- Your travel days count as business days, as do weekends and holidays — if they fall between days devoted to business and it wouldn’t be practical to return home.
- Standby days (days when your physical presence might be required) also count as business days, even if you aren’t ultimately called upon to work on those days.
Bottom line: If your business days exceed your personal days, you should be able to claim business was the primary reason for a domestic trip and deduct your transportation costs.
What else can you deduct?
Once at the destination, your out-of-pocket expenses for business days are fully deductible. Examples of these expenses include lodging, meals (subject to the 50% disallowance rule), seminar and convention fees, and cab fare. Expenses for personal days aren’t deductible.
Keep in mind that only expenses for yourself are deductible. You can’t deduct expenses for family members traveling with you, including your spouse — unless they’re employees of your business and traveling for a bona fide business purpose.
Keep good records
Be sure to retain proof of the business nature of your trip. You must properly substantiate all of the expenses you’re deducting. If you get audited, the IRS will want to see records during travel you claim was for business. Good records are your best defense. Additional rules and limits apply to travel expense deductions. Please contact us if you have questions.
© 2019
It’s a good time to check your withholding and make changes, if necessary
|
Hire your children this summer: Everyone wins
|
Selling your home? Consider these tax implications

Spring and summer are the optimum seasons for selling a home. And interest rates are currently attractive, so buyers may be out in full force in your area. Freddie Mac reports that the average 30-year fixed mortgage rate was 4.14% during the week of May 2, 2019, while the 15-year mortgage rate was 3.6%. This is down 0.41 and 0.43%, respectively, from a year earlier.
But before you contact a realtor to sell your home, you should review the tax considerations.
Sellers can exclude some gain
If you’re selling your principal residence, and you meet certain requirements, you can exclude up to $250,000 ($500,000 for joint filers) of gain. Gain that qualifies for the exclusion is also excluded from the 3.8% net investment income tax.
To qualify for the exclusion, you must meet these tests:
- The ownership test. You must have owned the property for at least two years during the five-year period ending on the sale date.
- The use test. You must have used the property as a principal residence for at least two years during the same five-year period. (Periods of ownership and use don’t need to overlap.)
In addition, you can’t use the exclusion more than once every two years.
Handling bigger gains
What if you’re fortunate enough to have more than $250,000/$500,000 of profit when selling your home? Any gain that doesn’t qualify for the exclusion generally will be taxed at your long-term capital gains rate, provided you owned the home for at least a year. If you didn’t, the gain will be considered short term and subject to your ordinary-income rate, which could be more than double your long-term rate.
Other tax issues
Here are some additional tax considerations when selling a home:
Keep track of your basis. To support an accurate tax basis, be sure to maintain thorough records, including information on your original cost and subsequent improvements, reduced by any casualty losses and depreciation claimed based on business use.
Be aware that you can’t deduct a loss. If you sell your principal residence at a loss, it generally isn’t deductible. But if part of your home is rented out or used exclusively for your business, the loss attributable to that portion may be deductible.
If you’re selling a second home (for example, a vacation home), be aware that it won’t be eligible for the gain exclusion. But if it qualifies as a rental property, it can be considered a business asset, and you may be able to defer tax on any gains through an installment sale or a Section 1031 exchange. Or you may be able to deduct a loss.
Your home is probably your largest investment. So before selling it, make sure you understand the tax implications. We can help you plan ahead to minimize taxes and answer any questions you have about your situation.
© 2019
Consider a Roth 401(k) plan — and make sure employees use it
|
Check on your refund — and find out why the IRS might not send it

It’s that time of year when many people who filed their tax returns in April are checking their mail or bank accounts to see if their refunds have landed. According to the IRS, most refunds are issued in less than 21 calendar days. However, it may take longer — and in rare cases, refunds might not come at all.
Your refund statusIf you’re curious about when your refund will arrive, you can use the IRS “Where’s My Refund?” tool. Go to https://bit.ly/2cl5MZo and click “Check My Refund Status.” You’ll need your Social Security number, your filing status (single, married joint filer, etc.) and your exact refund amount.
In some cases, taxpayers who are expecting a refund may be notified that all or part of their refunds aren’t going to be paid. A number of situations can cause this to happen.
Refunds settle debtsThe Treasury Offset Program can use all, or part, of a refund to settle certain debts, including:
- Past-due federal tax debts,
- State income tax obligations,
- Past-due child and spousal support,
- Federal agency debts such as a delinquent student loan, and
- Certain unemployment compensation owed to a state.
If the federal government is going to “offset” a refund to pay past-due debts, a letter is sent to the taxpayer listing the original refund, the offset amount and the agency that received the payment. If the taxpayer wants to dispute the offset, he or she should contact the relevant federal agency.
Spousal reliefIf you file a joint tax return and your tax refund is applied to the past-due debts of your spouse, you may be able to get back your share of the joint refund. For example, let’s say a husband has back child support debt from before he was married. After he and his new spouse file a joint tax return, their joint refund is applied to his child support. His wife can apply for injured spouse relief to get her portion of the refund. This is done by filing Form 8379, “Injured Spouse Allocation.”
No passports in significant casesBeyond having a refund taken by the government, owing a significant amount of back federal taxes can now also cause a taxpayer to have passport problems. Last year, the IRS began enforcing a tax law provision that gives the IRS the authority to notify the State Department about individuals who have “seriously delinquent tax debts.” The State Department is then tasked with denying the individuals new passports or revoking existing passports.
For these purposes, a seriously delinquent tax debt is defined as an inflation-adjusted $50,000 or more. For 2019, the threshold is $52,000.
Refund questions?In most cases, refunds are routinely sent to taxpayers within a few weeks. However, there may be some delays, or, in worst-case scenarios, refunds may be applied to debts owed to the federal or state governments. If you have questions about your refund, contact us.
© 2019
What type of expenses can’t be written off by your business?

If you read the Internal Revenue Code (and you probably don’t want to!), you may be surprised to find that most business deductions aren’t specifically listed. It doesn’t explicitly state that you can deduct office supplies and certain other expenses.
Some expenses are detailed in the tax code, but the general rule is contained in the first sentence of Section 162, which states you can write off “all the ordinary and necessary expenses paid or incurred during the taxable year in carrying on any trade or business.”
Basic definitions
In general, an expense is ordinary if it’s considered common or customary in the particular trade or business. For example, insurance premiums to protect a store would be an ordinary business expense in the retail industry.
A necessary expense is defined as one that’s helpful or appropriate. For example, let’s say a car dealership purchases an automatic defibrillator. It may not be necessary for the operation of the business, but it might be helpful and appropriate if an employee or customer suffers a heart attack.
It’s possible for an ordinary expense to be unnecessary — but, in order to be deductible, an expense must be ordinary and necessary.
In addition, a deductible amount must be reasonable in relation to the benefit expected. For example, if you’re attempting to land a $3,000 deal, a $65 lunch with a potential client should be OK with the IRS. (Keep in mind that the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act eliminated most deductions for entertainment expenses but retains the 50% deduction for business meals.)
Examples of not ordinary and unnecessary
Not surprisingly, the IRS and courts don’t always agree with taxpayers about what qualifies as ordinary and necessary expenditures.
In one case, a man engaged in a business with his brother was denied deductions for his private airplane expenses. The U.S. Tax Court noted that the taxpayer had failed to prove the expenses were ordinary and necessary to the business. In addition, only one brother used the plane and the flights were to places that the taxpayer could have driven to or flown to on a commercial airline. And, in any event, the stated expenses including depreciation expenses, weren’t adequately substantiated, the court added. (TC Memo 2018-108)
In another case, the Tax Court ruled that a business owner wasn’t entitled to deduct legal and professional fees he’d incurred in divorce proceedings defending his ex-wife’s claims to his interest in, or portion of, distributions he received from his LLC. The IRS and the court ruled the divorce legal fees were nondeductible personal expenses and weren’t ordinary and necessary. (TC Memo 2018-80)
Proceed with caution
The deductibility of some expenses is clear. But for other expenses, it can get more complicated. Generally, if an expense seems like it’s not normal in your industry — or if it could be considered fun, personal or extravagant in nature — you should proceed with caution. And keep records to substantiate the expenses you’re deducting. Consult with us for guidance.
© 2019
Plug in tax savings for electric vehicles

|
Employee vs. independent contractor: How should you handle worker classification?

Many employers prefer to classify workers as independent contractors to lower costs, even if it means having less control over a worker’s day-to-day activities. But the government is on the lookout for businesses that classify workers as independent contractors simply to reduce taxes or avoid their employee benefit obligations.
Why it matters
When your business classifies a worker as an employee, you generally must withhold federal income tax and the employee’s share of Social Security and Medicare taxes from his or her wages. Your business must then pay the employer’s share of these taxes, pay federal unemployment tax, file federal payroll tax returns and follow other burdensome IRS and U.S. Department of Labor rules.
You may also have to pay state and local unemployment and workers’ compensation taxes and comply with more rules. Dealing with all this can cost a bundle each year.
On the other hand, with independent contractor status, you don’t have to worry about employment tax issues. You also don’t have to provide fringe benefits like health insurance, retirement plans and paid vacations. If you pay $600 or more to an independent contractor during the year, you must file a Form 1099-MISC with the IRS and send a copy to the worker to report what you paid. That’s basically the extent of your bureaucratic responsibilities.
But if you incorrectly treat a worker as an independent contractor — and the IRS decides the worker is actually an employee — your business could be assessed unpaid payroll taxes plus interest and penalties. You also could be liable for employee benefits that should have been provided but weren’t, including penalties under federal laws.
Filing an IRS form
To find out if a worker is an employee or an independent contractor, you can file optional IRS Form SS-8, “Determination of Worker Status for Purposes of Federal Employment Taxes and Income Tax Withholding.” Then, the IRS will let you know how to classify a worker. However, be aware that the IRS has a history of classifying workers as employees rather than independent contractors.
Businesses should consult with us before filing Form SS-8 because it may alert the IRS that your business has worker classification issues — and inadvertently trigger an employment tax audit.
It can be better to simply treat independent contractors so the relationships comply with the tax rules. This generally includes not controlling how the workers perform their duties, ensuring that you’re not the workers’ only customer, providing annual Forms 1099 and, basically, not treating the workers like employees.
Workers can also ask for a determination
Workers who want an official determination of their status can also file Form SS-8. Disgruntled independent contractors may do so because they feel entitled to employee benefits and want to eliminate self-employment tax liabilities.
If a worker files Form SS-8, the IRS will send a letter to the business. It identifies the worker and includes a blank Form SS-8. The business is asked to complete and return the form to the IRS, which will render a classification decision.
Defending your position
If your business properly handles independent contractors, don’t panic if a worker files a Form SS-8. Contact us before replying to the IRS. With a proper response, you may be able to continue to classify the worker as a contractor. We also can assist you in setting up independent contractor relationships that stand up to IRS scrutiny.
© 2019
Casualty loss deductions: You can claim one only for a federally declared disaster

Unforeseen disasters happen all the time and they may cause damage to your home or personal property. Before the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act, eligible casualty loss victims could claim a deduction on their tax returns. But there are new restrictions that make these deductions much more difficult to take.
What’s considered a casualty for tax purposes? It’s a sudden, unexpected or unusual event, such as a hurricane, tornado, flood, earthquake, or fire; an accident or act of vandalism; or even a terrorist attack.
Unfavorable change
For losses incurred in 2018 through 2025, the TCJA generally eliminates deductions for personal casualty losses, except for losses due to federally declared disasters. For example, during 2019, there were presidential declarations of major disasters in parts of Iowa and Nebraska after severe storms and flooding. So victims there would be eligible for casualty loss deductions.
Note: There’s an exception to the general rule of allowing casualty loss deductions only in federally declared disaster areas. If you have personal casualty gains because your insurance proceeds exceed the tax basis of the damaged or destroyed property, you can deduct personal casualty losses that aren’t due to a federally declared disaster up to the amount of your personal casualty gains.
Special timing election
If your casualty loss is due to a federally declared disaster, a special election allows you to deduct the loss on your tax return for the preceding year. If you’ve already filed your return for the preceding year, you can file an amended return to make the election and claim the deduction in the earlier year. This can help you get extra cash when you need it.
This election must be made by no later than six months after the due date (without considering extensions) for filing your tax return for the year in which the disaster occurs. However, the election itself must be made on an original or amended return for the preceding year.
Calculating personal losses
To calculate the casualty loss deduction for personal-use property in an area declared a federal disaster, you must take the following three steps:
- Subtract any insurance proceeds.
- Subtract $100 per casualty event.
- Combine the results from the first two steps and then subtract 10% of your adjusted gross income (AGI) for the year you claim the loss deduction.
Important: Another factor that now makes it harder to claim a casualty loss is that you must itemize deductions to claim one. For 2018 through 2025, fewer people will itemize, because the TCJA significantly increased the standard deduction amounts. For 2019, they are $12,200 for single filers, $18,350 for heads of households, and $24,400 for married joint-filing couples.
So even if you qualify for a casualty deduction, you might not get any tax benefit, because you don’t have enough itemized deductions.
We can help
These are the rules for personal property. Keep in mind that the rules for business or income-producing property are different. If you have disaster-related losses, we can help you navigate the complex rules.
© 2019
How entrepreneurs must treat expenses on their tax returns

Have you recently started a new business? Or are you contemplating starting one? Launching a new venture is a hectic, exciting time. And as you know, before you even open the doors, you generally have to spend a lot of money. You may have to train workers and pay for rent, utilities, marketing and more.
Entrepreneurs are often unaware that many expenses incurred by start-ups can’t be deducted right away. You should be aware that the way you handle some of your initial expenses can make a large difference in your tax bill.
Key points on how expenses are handled
When starting or planning a new enterprise, keep these factors in mind:
-
Start-up costs include those incurred or paid while creating an active trade or business — or investigating the creation or acquisition of one.
-
Under the federal tax code, taxpayers can elect to deduct up to $5,000 of business start-up and $5,000 of organizational costs in the year the business begins. We don’t need to tell you that $5,000 doesn’t go far these days! And the $5,000 deduction is reduced dollar-for-dollar by the amount by which your total start-up or organizational costs exceed $50,000. Any remaining costs must be amortized over 180 months on a straight-line basis.
-
No deductions or amortization write-offs are allowed until the year when “active conduct” of your new business commences. That usually means the year when the enterprise has all the pieces in place to begin earning revenue. To determine if a taxpayer meets this test, the IRS and courts generally ask questions such as: Did the taxpayer undertake the activity intending to earn a profit? Was the taxpayer regularly and actively involved? Has the activity actually begun?
Examples of expenses
Start-up expenses generally include all expenses that are incurred to:
- Investigate the creation or acquisition of a business,
- Create a business, or
- Engage in a for-profit activity in anticipation of that activity becoming an active business.
To be eligible for the election, an expense also must be one that would be deductible if it were incurred after a business began. One example would be the money you spend analyzing potential markets for a new product or service.
To qualify as an “organization expense,” the outlay must be related to the creation of a corporation or partnership. Some examples of organization expenses are legal and accounting fees for services related to organizing the new business and filing fees paid to the state of incorporation.
An important decision
Time may be of the essence if you have start-up expenses that you’d like to deduct this year. You need to decide whether to take the elections described above. Recordkeeping is important. Contact us about your business start-up plans. We can help with the tax and other aspects of your new venture.
© 2019
Three questions you may have after you file your return

|
Small Business Tax Brief

Deducting business meal expenses under today’s tax rules
In the course of operating your business, you probably spend time and money “wining and dining” current or potential customers, vendors and employees. What can you deduct on your tax return for these expenses? The rules changed under the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA), but you can still claim some valuable write-offs.
No more entertainment deductions
One of the biggest changes is that you can no longer deduct most business-related entertainment expenses. Beginning in 2018, the TCJA disallows deductions for entertainment expenses, including those for sports events, theater productions, golf outings and fishing trips.
Meal deductions still allowed
You can still deduct 50% of the cost of food and beverages for meals conducted with business associates. However, you need to follow three basic rules in order to prove that your expenses are business related:
-
The expenses must be “ordinary and necessary” in carrying on your business. This means your food and beverage costs are customary and appropriate. They shouldn’t be lavish or extravagant.
-
The expenses must be directly related or associated with your business. This means that you expect to receive a concrete business benefit from them. The principal purpose for the meal must be business. You can’t go out with a group of friends for the evening, discuss business with one of them for a few minutes, and then write off the check.
-
You must be able to substantiate the expenses. There are requirements for proving that meal and beverage expenses qualify for a deduction. You must be able to establish the amount spent, the date and place where the meals took place, the business purpose and the business relationship of the people involved.
Set up detailed record keeping procedures to keep track of business meal costs. That way, you can prove them and the business connection in the event of an IRS audit.
Other considerations
What if you spend money on food and beverages at an entertainment event? The IRS clarified in guidance (Notice 2018-76) that taxpayers can still deduct 50% of food and drink expenses incurred at entertainment events, but only if business was conducted during the event or shortly before or after. The food-and-drink expenses should also be “stated separately from the cost of the entertainment on one or more bills, invoices or receipts,” according to the guidance.
Another related tax law change involves meals provided to employees on the business premises. Before the TCJA, these meals provided to an employee for the convenience of the employer were 100% deductible by the employer. Beginning in 2018, meals provided for the convenience of an employer in an on-premises cafeteria or elsewhere on the business property are only 50% deductible. After 2025, these meals won’t be deductible at all.
Plan ahead
As you can see, the treatment of meal and entertainment expenses became more complicated after the TCJA. Your tax advisor can keep you up to speed on the issues and suggest strategies to get the biggest tax-saving bang for your business meal bucks.
Seniors: Medicare premiums could lower your tax bill

Americans who are 65 and older qualify for basic Medicare insurance, and they may need to pay additional premiums to get the level of coverage they desire. The premiums can be expensive, especially if you're married and both you and your spouse are paying them. But one aspect of paying premiums might be positive: If you qualify, they may help lower your tax bill.
Medicare premium tax deductions
Premiums for Medicare health insurance can be combined with other qualifying health care expenses for purposes of claiming an itemized deduction for medical expenses on your individual tax return. This includes amounts for "Medigap" insurance and Medicare Advantage plans. Some people buy Medigap policies because Medicare Parts A and B don't cover all their health care expenses. Coverage gaps include co–payments, co–insurance, deductibles and other costs. Medigap is private supplemental insurance that's intended to cover some or all gaps.
Fewer people now itemize
Qualifying for a medical expense deduction can be difficult for a couple of reasons. For 2019, you can deduct medical expenses only if you itemize deductions and only to the extent that total qualifying expenses exceeded 10% of AGI. (This threshold was 7.5% for the 2018 tax year.)
The Tax Cuts and Jobs Act nearly doubled the standard deduction amounts for 2018 through 2025. For 2019, the standard deduction amounts are $12,200 for single filers, $24,400 for married joint-filing couples and $18,350 for heads of households. So, fewer individuals are claiming itemized deductions.
However, if you have significant medical expenses (including Medicare health insurance premiums), you may itemize and collect some tax savings.
Important note: Self–employed people and shareholder–employees of S corporations can generally claim an above–the–line deduction for their health insurance premiums, including Medicare premiums. So, they don't need to itemize to get the tax savings from their premiums.
Other deductible medical expenses
In addition to Medicare premiums, you can deduct a variety of medical expenses, including those for ambulance services, dental treatment, dentures, eyeglasses and contacts, hospital services, lab tests, qualified long–term care services, prescription medicines and others.
Keep in mind that many items that Medicare doesn't cover can be written off for tax purposes, if you qualify. You can also deduct transportation expenses to get to medical appointments. If you go by car, you can deduct a flat 20-cents-per-mile rate for 2019, or you can keep track of your actual out–of–pocket expenses for gas, oil and repairs.
Need more information?
Contact us if you have additional questions about Medicare coverage options or claiming medical expense deductions on your personal tax return. Your advisor can help determine the optimal overall tax–planning strategy based on your personal circumstances.
© 2019
Divorcing business owners need to pay attention to tax implications

If you’re getting a divorce, you know it’s a highly stressful time. But if you’re a business owner, tax issues can complicate matters even more. Your business ownership interest is one of your biggest personal assets and your marital property will include all or part of it.
Transferring property tax-free
You can generally divide most assets, including cash and business ownership interests, between you and your soon-to-be ex-spouse without any federal income or gift tax consequences. When an asset falls under this tax-free transfer rule, the spouse who receives the asset takes over its existing tax basis (for tax gain or loss purposes) and its existing holding period (for short-term or long-term holding period purposes).
For example, let’s say that, under the terms of your divorce agreement, you give your house to your spouse in exchange for keeping 100% of the stock in your business. That asset swap would be tax-free. And the existing basis and holding periods for the home and the stock would carry over to the person who receives them.
Tax-free transfers can occur before the divorce or at the time it becomes final. Tax-free treatment also applies to postdivorce transfers so long as they’re made “incident to divorce.” This means transfers that occur within:
- A year after the date the marriage ends, or
- Six years after the date the marriage ends if the transfers are made pursuant to your divorce agreement.
Future tax implications
Eventually, there will be tax implications for assets received tax-free in a divorce settlement. The ex-spouse who winds up owning an appreciated asset — when the fair market value exceeds the tax basis — generally must recognize taxable gain when it’s sold (unless an exception applies).
What if your ex-spouse receives 49% of your highly appreciated small business stock? Thanks to the tax-free transfer rule, there’s no tax impact when the shares are transferred. Your ex will continue to apply the same tax rules as if you had continued to own the shares, including carryover basis and carryover holding period. When your ex-spouse ultimately sells the shares, he or she will owe any capital gains taxes. You will owe nothing.
Note that the person who winds up owning appreciated assets must pay the built-in tax liability that comes with them. From a net-of-tax perspective, appreciated assets are worth less than an equal amount of cash or other assets that haven’t appreciated. That’s why you should always take taxes into account when negotiating your divorce agreement.
In addition, the IRS now extends the beneficial tax-free transfer rule to ordinary-income assets, not just to capital-gains assets. For example, if you transfer business receivables or inventory to your ex-spouse in divorce, these types of ordinary-income assets can also be transferred tax-free. When the asset is later sold, converted to cash or exercised (in the case of nonqualified stock options), the person who owns the asset at that time must recognize the income and pay the tax liability.
Avoid adverse tax consequences
Like many major life events, divorce can have major tax implications. For example, you may receive an unexpected tax bill if you don’t carefully handle the splitting up of qualified retirement plan accounts (such as a 401(k) plan) and IRAs. And if you own a business, the stakes are higher. Your tax advisor can help you minimize the adverse tax consequences of settling your divorce under today’s laws.
© 2019
Make a deductible IRA contribution for 2018. It’s not too late!

Do you want to save more for retirement on a tax-favored basis? If so, and if you qualify, you can make a deductible traditional IRA contribution for the 2018 tax year between now and the tax filing deadline and claim the write-off on your 2018 return. Or you can contribute to a Roth IRA and avoid paying taxes on future withdrawals.
You can potentially make a contribution of up to $5,500 (or $6,500 if you were age 50 or older as of December 31, 2018). If you’re married, your spouse can potentially do the same, thereby doubling your tax benefits.
The deadline for 2018 traditional and Roth contributions for most taxpayers is April 15, 2019 (April 17 for those in Maine and Massachusetts).
There are some ground rules. You must have enough 2018 earned income (from jobs, self-employment or alimony) to equal or exceed your IRA contributions for the tax year. If you’re married, either spouse can provide the necessary earned income. And you can’t make a deductible contribution to a traditional IRA if you were 70½ or older as of December 31, 2018. (But you can make one to a Roth IRA after that age.)
Finally, deductible IRA contributions are phased out (reduced or eliminated) if last year’s modified adjusted gross income (MAGI) is too high.
Types of contributions
If you haven’t already maxed out your 2018 IRA contribution limit, consider making one of these three types of contributions by the April deadline:
1. Deductible traditional. With traditional IRAs, account growth is tax-deferred and distributions are subject to income tax. If you and your spouse don’t participate in an employer-sponsored plan such as a 401(k), the contribution is fully deductible on your 2018 tax return. If you or your spouse do participate in an employer-sponsored plan, your deduction is subject to the following MAGI phaseout:
- For married taxpayers filing jointly, the phaseout range is specific to each spouse based on whether he or she is a participant in an employer-sponsored plan:
- For a spouse who participated in 2018: $101,000–$121,000.
- For a spouse who didn’t participate in 2018: $189,000–$199,000.
- For single and head-of-household taxpayers participating in an employer-sponsored plan: $63,000–$73,000.
Taxpayers with MAGIs within the applicable range can deduct a partial contribution. But those with MAGIs exceeding the applicable range can’t deduct any IRA contribution.
2. Roth. Roth IRA contributions aren’t deductible, but qualified distributions — including growth — are tax-free, if you satisfy certain requirements.
Your ability to contribute, however, is subject to a MAGI-based phaseout:
- For married taxpayers filing jointly: $189,000–$199,000.
- For single and head-of-household taxpayers: $120,000–$135,000.
You can make a partial contribution if your 2018 MAGI is within the applicable range, but no contribution if it exceeds the top of the range.
3. Nondeductible traditional. If your income is too high for you to fully benefit from a deductible traditional or a Roth contribution, you may benefit from a nondeductible contribution to a traditional IRA. The account can still grow tax-deferred, and when you take qualified distributions, you’ll only be taxed on the growth.
Act fast
Traditional and Roth IRAs provide a powerful way to save for retirement on a tax-advantaged basis. Contact us to learn more about making 2018 contributions and making the most of IRAs in 2019 and beyond.
© 2019
Understanding how taxes factor into an M&A transaction

|
Still working after age 70½? You may not have to begin 401(k) withdrawals

|
2019 Q2 tax calendar: Key deadlines for businesses and other employers

|
Stretch your college student’s spending money with the dependent tax credit

If you’re the parent of a child who is age 17 to 23, and you pay all (or most) of his or her expenses, you may be surprised to learn you’re not eligible for the child tax credit. But there’s a dependent tax credit that may be available to you. It’s not as valuable as the child tax credit, but when you’re saving for college or paying tuition, every dollar counts!
Background of the creditsThe Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA) increased the child credit to $2,000 per qualifying child under the age of 17. The law also substantially increased the phaseout income thresholds for the credit so more people qualify for it. Unfortunately, the TCJA eliminated dependency exemptions for older children for 2018 through 2025. But the TCJA established a new $500 tax credit for dependents who aren’t under-age-17 children who qualify for the child tax credit. However, these individuals must pass certain tests to be classified as dependents.
A qualifying dependent for purposes of the $500 credit includes:
- A dependent child who lives with you for over half the year and is over age 16 and up to age 23 if he or she is a student, and
- Other nonchild dependent relatives (such as a grandchild, sibling, father, mother, grandfather, grandmother and other relatives).
To be eligible for the $500 credit, you must provide over half of the person’s support for the year and he or she must be a U.S. citizen, U.S. national or U.S. resident.
Both the child tax credit and the dependent credit begin to phase out at $200,000 of modified adjusted gross income ($400,000 for married joint filers).
The child’s incomeAfter the TCJA passed, it was unclear if your child would qualify you for the $500 credit if he or she had any gross income for the year. Fortunately, IRS Notice 2018-70 favorably resolved the income question. According to the guidance, a dependent will pass the income test for the 2018 tax year if he or she has gross income of $4,150 or less. (The $4,150 amount will be adjusted for inflation in future years.)
More spending moneyAlthough $500 per child doesn’t cover much for today’s college student, it can help with books, clothing, software and other needs. Contact us with questions about whether you qualify for either the child or the dependent tax credits.
© 2019
Could your business benefit from the tax credit for family and medical leave?
|
The 2018 gift tax return deadline is almost here

|
There’s still time for small business owners to set up a SEP retirement plan for last year

|
Vehicle-expense deduction ins and outs for individual taxpayers
|
Will leasing equipment or buying it be more tax efficient for your business?

Recent changes to federal tax law and accounting rules could affect whether you decide to lease or buy equipment or other fixed assets. Although there’s no universal “right” choice, many businesses that formerly leased assets are now deciding to buy them.
Pros and cons of leasingFrom a cash flow perspective, leasing can be more attractive than buying. And leasing does provide some tax benefits: Lease payments generally are tax deductible as “ordinary and necessary” business expenses. (Annual deduction limits may apply.)
Leasing used to be advantageous from a financial reporting standpoint. But new accounting rules that bring leases to the lessee’s balance sheet go into effect in 2020 for calendar-year private companies. So, lease obligations will show up as liabilities, similar to purchased assets that are financed with traditional bank loans.
Leasing also has some potential drawbacks. Over the long run, leasing an asset may cost you more than buying it, and leasing doesn’t provide any buildup of equity. What’s more, you’re generally locked in for the entire lease term. So, you’re obligated to keep making lease payments even if you stop using the equipment. If the lease allows you to opt out before the term expires, you may have to pay an early-termination fee.
Pros and cons of buyingHistorically, the primary advantage of buying over leasing has been that you’re free to use the assets as you see fit. But an advantage that has now come to the forefront is that Section 179 expensing and first-year bonus depreciation can provide big tax savings in the first year an asset is placed in service.
These two tax breaks were dramatically enhanced by the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA) — enough so that you may be convinced to buy assets that your business might have leased in the past. Many businesses will be able to write off the full cost of most equipment in the year it’s purchased. Any remainder is eligible for regular depreciation deductions over IRS-prescribed schedules.
The primary downside of buying fixed assets is that you’re generally required to pay the full cost upfront or in installments, although the Sec. 179 and bonus depreciation tax benefits are still available for property that’s financed. If you finance a purchase through a bank, a down payment of at least 20% of the cost is usually required. This could tie up funds and affect your credit rating. If you decide to finance fixed asset purchases, be aware that the TCJA limits interest expense deductions (for businesses with more than $25 million in average annual gross receipts) to 30% of adjusted taxable income.
Decision timeWhen deciding whether to lease or buy a fixed asset, there are a multitude of factors to consider, including tax implications. We can help you determine the approach that best suits your circumstances.
© 2019
Careful tax planning required for incentive stock options
|
Beware the Ides of March — if you own a pass-through entity

|
Some of your deductions may be smaller (or nonexistent) when you file your 2018 tax return

While the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA) reduces most income tax rates and expands some tax breaks, it limits or eliminates several itemized deductions that have been valuable to many individual taxpayers. Here are five deductions you may see shrink or disappear when you file your 2018 income tax return:
1. State and local tax deduction.For 2018 through 2025, your total itemized deduction for all state and local taxes combined — including property tax — is limited to $10,000 ($5,000 if you’re married and filing separately). You still must choose between deducting income and sales tax; you can’t deduct both, even if your total state and local tax deduction wouldn’t exceed $10,000.
2. Mortgage interest deduction. You generally can claim an itemized deduction for interest on mortgage debt incurred to purchase, build or improve your principal residence and a second residence. Points paid related to your principal residence also may be deductible. For 2018 through 2025, the TCJA reduces the mortgage debt limit from $1 million to $750,000 for debt incurred after Dec. 15, 2017, with some limited exceptions.
3. Home equity debt interest deduction. Before the TCJA, an itemized deduction could be claimed for interest on up to $100,000 of home equity debt used for any purpose, such as to pay off credit cards (for which interest isn’t deductible). The TCJA effectively limits the home equity interest deduction for 2018 through 2025 to debt that would qualify for the home mortgage interest deduction.
4. Miscellaneous itemized deductions subject to the 2% floor. This deduction for expenses such as certain professional fees, investment expenses and unreimbursed employee business expenses is suspended for 2018 through 2025. If you’re an employee and work from home, this includes the home office deduction. (Business owners and the self-employed may still be able to claim a home office deduction against their business or self-employment income.)
5. Personal casualty and theft loss deduction. For 2018 through 2025, this itemized deduction is suspended except if the loss was due to an event officially declared a disaster by the President.
Be aware that additional rules and limits apply to many of these deductions. Also keep in mind that the TCJA nearly doubles the standard deduction. The combination of a much larger standard deduction and the reduction or elimination of many itemized deductions means that, even if itemizing has typically benefited you in the past, you might be better off taking the standard deduction when you file your 2018 return. Please contact us with any questions you have.
© 2019
The home office deduction: Actual expenses vs. the simplified method

If you run your business from your home or perform certain functions at home that are related to your business, you might be able to claim a home office deduction against your business income on your 2018 income tax return. There are now two methods for claiming this deduction: the actual expenses method and the simplified method.
Basics of the deductionIn general, you’ll qualify for a home office deduction if part of your home is used “regularly and exclusively” as your principal place of business.
If your home isn’t your principal place of business, you may still be able to deduct home office expenses if 1) you physically meet with patients, clients or customers on your premises, or 2) you use a storage area in your home (or a separate free-standing structure, such as a garage) exclusively and regularly for your business.
Actual expensesTraditionally, taxpayers have deducted actual expenses when they claim a home office deduction.
Deductible home office expenses may include:
- Direct expenses, such as the cost of painting and carpeting a room used exclusively for business,
- A proportionate share of indirect expenses, such as mortgage interest, property taxes, utilities, repairs and insurance, and
- A depreciation allowance.
But keeping track of actual expenses can be time consuming.
The simplified methodFortunately, there’s a simplified method that’s been available since 2013: You can deduct $5 for each square foot of home office space, up to a maximum total of $1,500.
For example, if you’ve converted a 300-square-foot bedroom to an office you use exclusively and regularly for business, you can write off $1,500 under the simplified method (300 square feet x $5). However, if your business is located in a 600-square-foot finished basement, the deduction will still be only $1,500 because of the cap on the deduction under this method.
As you can see, the cap can make the simplified method less beneficial for larger home office spaces. But even for spaces of 300 square feet or less, taxpayers may qualify for a bigger deduction using the actual expense method. So, tracking your actual expenses can be worth the extra hassle.
Flexibility in filingWhen claiming the home office deduction, you’re not locked into a particular method. For instance, you might choose the actual expense method on your 2018 return, use the simplified method when you file your 2019 return next year and then switch back to the actual expense method thereafter. The choice is yours.
Unsure whether you qualify for the home office deduction? Or wondering whether you should deduct actual expenses or use the simplified method? Contact us. We can help you determine what’s right for your specific situation.
© 2019
3 big TCJA changes affecting 2018 individual tax returns and beyond

When you file your 2018 income tax return, you’ll likely find that some big tax law changes affect you — besides the much-discussed tax rate cuts and reduced itemized deductions. For 2018 through 2025, the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA) makes significant changes to personal exemptions, standard deductions and the child credit. The degree to which these changes will affect you depends on whether you have dependents and, if so, how many. It also depends on whether you typically itemize deductions.
1. No more personal exemptionsFor 2017, taxpayers could claim a personal exemption of $4,050 each for themselves, their spouses and any dependents. For families with children and/or other dependents, such as elderly parents, these exemptions could really add up.
For 2018 through 2025, the TCJA suspends personal exemptions. This will substantially increase taxable income for large families. However, enhancements to the standard deduction and child credit, combined with lower tax rates and other changes, might mitigate this increase.
2. Nearly doubled standard deductionTaxpayers can choose to itemize certain deductions or take the standard deduction based on their filing status. Itemizing deductions when the total will be larger than the standard deduction saves tax, but it makes filing more complicated.
For 2017, the standard deductions were $6,350 for singles and separate filers, $9,350 for head of household filers, and $12,700 for married couples filing jointly.
The TCJA nearly doubles the standard deductions for 2018 to $12,000 for singles and separate filers, $18,000 for heads of households, and $24,000 for joint filers. For 2019, they’re $12,200, $18,350 and $24,400, respectively. (These amounts will continue to be adjusted for inflation annually through 2025.)
For some taxpayers, the increased standard deduction could compensate for the elimination of the exemptions, and perhaps provide some additional tax savings. But for those with many dependents or who itemize deductions, these changes might result in a higher tax bill — depending in part on the extent to which they can benefit from enhancements to the child credit.
3. Enhanced child creditCredits can be more powerful than exemptions and deductions because they reduce taxes dollar-for-dollar, rather than just reducing the amount of income subject to tax. For 2018 through 2025, the TCJA doubles the child credit to $2,000 per child under age 17.
The TCJA also makes the child credit available to more families. For 2018 through 2025, the credit doesn’t begin to phase out until adjusted gross income exceeds $400,000 for joint filers or $200,000 for all other filers, compared with the 2017 phaseout thresholds of $110,000 and $75,000, respectively.
The TCJA also includes, for 2018 through 2025, a $500 credit for qualifying dependents other than qualifying children.
Maximize your tax savingsThese are just some of the TCJA changes that may affect you when you file your 2018 tax return and for the next several years. We can help ensure you claim all of the breaks available to you on your 2018 return and implement TCJA-smart tax-saving strategies for 2019.
© 2019
When are LLC members subject to self-employment tax?

Limited liability company (LLC) members commonly claim that their distributive shares of LLC income — after deducting compensation for services in the form of guaranteed payments — aren’t subject to self-employment (SE) tax. But the IRS has been cracking down on LLC members it claims have underreported SE income, with some success in court.
SE tax backgroundSelf-employment income is subject to a 12.4% Social Security tax (up to the wage base) and a 2.9% Medicare tax. Generally, if you’re a member of a partnership — including an LLC taxed as a partnership — that conducts a trade or business, you’re considered self-employed.
General partners pay SE tax on all their business income from the partnership, whether it’s distributed or not. Limited partners, however, are subject to SE tax only on any guaranteed payments for services they provide to the partnership. The rationale is that limited partners, who have no management authority, are more akin to passive investors.
(Note, however, that “service partners” in service partnerships, such as law firms, medical practices, and architecture and engineering firms, generally may not claim limited partner status regardless of their level of participation.)
LLC uncertaintyOver the years, many LLC members have taken the position that they’re equivalent to limited partners and, therefore, exempt from SE tax (except on guaranteed payments for services). But there’s a big difference between limited partners and LLC members. Both enjoy limited personal liability, but, unlike limited partners, LLC members can actively participate in management without jeopardizing their liability protection.
Arguably, LLC members who are active in management or perform substantial services related to the LLC’s business are subject to SE tax, while those who more closely resemble passive investors should be treated like limited partners. The IRS issued proposed regulations to that effect in 1997, but hasn’t finalized them — although it follows them as a matter of internal policy.
Some LLC members have argued that the IRS’s failure to finalize the regulations supports the claim that their distributive shares aren’t subject to SE tax. But the IRS routinely rejects this argument and has successfully litigated its position. The courts generally have imposed SE tax on LLC members unless, like traditional limited partners, they lack management authority and don’t provide significant services to the business.
Review your situationThe law in this area remains uncertain, particularly with regard to capital-intensive businesses. But given the IRS’s aggressiveness in collecting SE taxes from LLCs, LLC members should assess whether the IRS might claim that they’ve underpaid SE taxes.
Those who wish to avoid or reduce these taxes in the future may have some options, including converting to an S corporation or limited partnership, or restructuring their ownership interests. When evaluating these strategies, there are issues to consider beyond taxes. Contact us to discuss your specific situation.
© 2019
Why you shouldn’t wait to file your 2018 income tax return

The IRS opened the 2018 income tax return filing season on January 28. Even if you typically don’t file until much closer to the April 15 deadline, this year consider filing as soon as you can. Why? You can potentially protect yourself from tax identity theft — and reap other benefits, too.
What is tax identity theft?
In a tax identity theft scheme, a thief uses your personal information to file a fraudulent tax return early in the filing season and claim a bogus refund.
You discover the fraud when you file your return and are informed by the IRS that the return has been rejected because one with your Social Security number has already been filed for the same tax year. While you should ultimately be able to prove that your return is the legitimate one, tax identity theft can cause major headaches to straighten out and significantly delay your refund.
Filing early may be your best defense: If you file first, it will be the tax return filed by a would-be thief that will be rejected — not yours.
What if you haven’t received your W-2s and 1099s?
To file your tax return, you must have received all of your W-2s and 1099s. January 31 was the deadline for employers to issue 2018 Form W-2 to employees and, generally, for businesses to issue Form 1099 to recipients of any 2018 interest, dividend or reportable miscellaneous income payments.
If you haven’t received a W-2 or 1099, first contact the entity that should have issued it. If that doesn’t work, you can contact the IRS for help.
What are other benefits of filing early?
Besides protecting yourself from tax identity theft, the most obvious benefit of filing early is that, if you’re getting a refund, you’ll get that refund sooner. The IRS expects more than nine out of ten refunds to be issued within 21 days.
But even if you owe tax, filing early can be beneficial. You still won’t need to pay your tax bill until April 15, but you’ll know sooner how much you owe and can plan accordingly. Keep in mind that some taxpayers who typically have gotten refunds in the past could find themselves owing tax when they file their 2018 return due to tax law changes under the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA) and reduced withholding from 2018 paychecks.
Need help?
If you have questions about tax identity theft or would like help filing your 2018 return early, please contact us. While the new Form 1040 essentially does fit on a postcard, many taxpayers will also have to complete multiple schedules along with the form. And the TCJA has changed many tax breaks. We can help you ensure you file an accurate return that takes advantage of all of the breaks available to you.
Fundamental tax truths for C corporations

The flat 21% federal income tax rate for C corporations under the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA) has been great news for these entities and their owners. But some fundamental tax truths for C corporations largely remain the same:
C corporations are subject to double taxation. Double taxation occurs when corporate income is taxed once at the corporate level and again at the shareholder level as dividends are paid out. The cost of double taxation, however, is now generally less because of the 21% corporate rate.
And double taxation isn’t a problem when a C corporation needs to retain all its earnings to finance growth and capital investments. Because all the earnings stay “inside” the corporation, no dividends are paid to shareholders, and, therefore, there’s no double taxation.
Double taxation also isn’t an issue when a C corporation’s taxable income levels are low. This can often be achieved by paying reasonable salaries and bonuses to shareholder-employees and providing them with tax-favored fringe benefits (deductible by the corporation and tax-free to the recipient shareholder-employees).
C corporation status isn’t generally advisable for ventures with appreciating assets or certain depreciable assets. If assets such as real estate are eventually sold for substantial gains, it may be impossible to extract the profits from the corporation without being subject to double taxation. In contrast, if appreciating assets are held by a pass-through entity (such as an S corporation, partnership or limited liability company treated as a partnership for tax purposes), gains on such sales will be taxed only once, at the owner level.
But assets held by a C corporation don’t necessarily have to appreciate in value for double taxation to occur. Depreciation lowers the tax basis of the property, so a taxable gain results whenever the sale price exceeds the depreciated basis. In effect, appreciation can be caused by depreciation when depreciable assets hold their value.
To avoid this double-taxation issue, you might consider using a pass-through entity to lease to your C corporation appreciating assets or depreciable assets that will hold their value.
C corporation status isn’t generally advisable for ventures that will incur ongoing tax losses. When a venture is set up as a C corporation, losses aren’t passed through to the owners (the shareholders) like they would be in a pass-through entity. Instead, they create corporate net operating losses (NOLs) that can be carried over to future tax years and then used to offset any corporate taxable income.
This was already a potential downside of C corporations, because it can take many years for a start-up to be profitable. Now, under the TCJA, NOLs that arise in tax years beginning after 2017 can’t offset more than 80% of taxable income in the NOL carryover year. So it may take even longer to fully absorb tax losses.
Do you have questions about C corporation tax issues post-TCJA? Contact us.
Investment interest expense is still deductible, but that doesn’t necessarily mean you’ll benefit

|
There’s still time to get substantiation for 2018 donations

If you’re like many Americans, letters from your favorite charities have been appearing in your mailbox in recent weeks acknowledging your 2018 year-end donations. But what happens if you haven’t received such a letter — can you still claim an itemized deduction for the gift on your 2018 income tax return? It depends.
Basic requirements
To support a charitable deduction, you need to comply with IRS substantiation requirements. This generally includes obtaining a contemporaneous written acknowledgment from the charity stating the amount of the donation, whether you received any goods or services in consideration for the donation, and the value of any such goods or services.
“Contemporaneous” means the earlier of 1) the date you file your tax return, or 2) the extended due date of your return. So if you made a donation in 2018 but haven’t yet received substantiation from the charity, it’s not too late — as long as you haven’t filed your 2018 return. Contact the charity and request a written acknowledgment.
Keep in mind that, if you made a cash gift of under $250 with a check or credit card, generally a canceled check, bank statement or credit card statement is sufficient. However, if you received something in return for the donation, you generally must reduce your deduction by its value — and the charity is required to provide you a written acknowledgment as described earlier.
Substantiation is serious business
Don’t take the substantiation requirements lightly. In one U.S. Tax Court case, the taxpayers substantiated a donation deduction with canceled checks and a written acknowledgment. The IRS denied the deduction, however, because the acknowledgment failed to state whether the taxpayers received goods or services in consideration for their donation.
The taxpayers obtained a second acknowledgment including the required statement. But the Tax Court didn’t accept it because it wasn’t contemporaneous (that is, it was obtained after the tax return was filed).
2018 and 2019 deductions
Additional substantiation requirements apply to some types of donations. We can help you determine whether you have sufficient substantiation for the donations you hope to deduct on your 2018 income tax return — and guide you on the substantiation you’ll need for gifts you’re planning this year to ensure you can enjoy the desired deductions on your 2019 return.
© 2019
Many tax-related limits affecting businesses increase for 2019

A variety of tax-related limits affecting businesses are annually indexed for inflation, and many have gone up for 2019. Here’s a look at some that may affect you and your business.
Deductions
- Section 179 expensing:
- Limit: $1.02 million (up from $1 million)
- Phaseout: $2.55 million (up from $2.5 million)
- Income-based phase-ins for certain limits on the Sec. 199A qualified business income deduction:
- Married filing jointly: $321,400-$421,400 (up from $315,000-$415,000)
- Married filing separately: $160,725-$210,725 (up from $157,500-$207,500)
- Other filers: $160,700-$210,700 (up from $157,500-$207,500)
Retirement plans
- Employee contributions to 401(k) plans: $19,000 (up from $18,500)
- Catch-up contributions to 401(k) plans: $6,000 (no change)
- Employee contributions to SIMPLEs: $13,000 (up from $12,500)
- Catch-up contributions to SIMPLEs: $3,000 (no change)
- Combined employer/employee contributions to defined contribution plans (not including catch-ups): $56,000 (up from $55,000)
- Maximum compensation used to determine contributions: $280,000 (up from $275,000)
- Annual benefit for defined benefit plans: $225,000 (up from $220,000)
- Compensation defining “highly compensated employee”: $125,000 (up from $120,000)
- Compensation defining “key employee”: $180,000 (up from $175,000)
Other employee benefits
- Qualified transportation fringe-benefits employee income exclusion: $265 per month (up from $260)
- Health Savings Account contributions:
- Individual coverage: $3,500 (up from $3,450)
- Family coverage: $7,000 (up from $6,900)
- Catch-up contribution: $1,000 (no change)
- Flexible Spending Account contributions:
- Health care: $2,700 (up from $2,650)
- Dependent care: $5,000 (no change)
Additional rules apply to these limits, and they are only some of the limits that may affect your business. Please contact us for more information.
© 2019
What will your marginal income tax rate be?

While the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA) generally reduced individual tax rates for 2018 through 2025, some taxpayers could see their taxes go up due to reductions or eliminations of certain tax breaks — and, in some cases, due to their filing status. But some may see additional tax savings due to their filing status.
Unmarried vs. married taxpayers
In an effort to further eliminate the marriage “penalty,” the TCJA made changes to some of the middle tax brackets. As a result, some single and head of household filers could be pushed into higher tax brackets more quickly than pre-TCJA. For example, the beginning of the 32% bracket for singles for 2018 is $157,501, whereas it was $191,651 for 2017 (though the rate was 33%). For heads of households, the beginning of this bracket has decreased even more significantly, to $157,501 for 2018 from $212,501 for 2017.
Married taxpayers, on the other hand, won’t be pushed into some middle brackets until much higher income levels for 2018 through 2025. For example, the beginning of the 32% bracket for joint filers for 2018 is $315,001, whereas it was $233,351 for 2017 (again, the rate was 33% then).
2018 filing and 2019 brackets
Because there are so many variables, it will be hard to tell exactly how specific taxpayers will be affected by TCJA changes, including changes to the brackets, until they file their 2018 tax returns. In the meantime, it’s a good idea to begin to look at 2019. As before the TCJA, the tax brackets are adjusted annually for inflation.
Below is a look at the 2019 brackets under the TCJA. Contact us for help assessing what your tax rate likely will be for 2019 — and for help filing your 2018 tax return.
Single individuals
10%: $0 - $9,700
12%: $9,701 - $39,475
22%: $39,476 - $84,200
24%: $84,201 - $160,725
32%: $160,726 - $204,100
35%: $204,101 - $510,300
37%: Over $510,300
Heads of households
10%: $0 - $13,850
12%: $13,851 - $52,850
22%: $52,851 - $84,200
24%: $84,201 - $160,700
32%: $160,701 - $204,100
35%: $204,101 - $510,300
37%: Over $510,300
Married individuals filing joint returns and surviving spouses
10%: $0 - $19,400
12%: $19,401 - $78,950
22%: $78,951 - $168,400
24%: $168,401 - $321,450
32%: $321,451 - $408,200
35%: $408,201 - $612,350
37%: Over $612,350
Married individuals filing separate returns
10%: $0 - $9,700
12%: $9,701 - $39,475
22%: $39,476 - $84,200
24%: $84,201 - $160,725
32%: $160,726 - $204,100
35%: $204,101 - $306,175
37%: Over $306,175
© 2019
Higher mileage rate may mean larger tax deductions for business miles in 2019

This year, the optional standard mileage rate used to calculate the deductible costs of operating an automobile for business increased by 3.5 cents, to the highest level since 2008. As a result, you might be able to claim a larger deduction for vehicle-related expense for 2019 than you can for 2018.
Actual costs vs. mileage rateBusinesses can generally deduct the actual expenses attributable to business use of vehicles. This includes gas, oil, tires, insurance, repairs, licenses and vehicle registration fees. In addition, you can claim a depreciation allowance for the vehicle. However, in many cases depreciation write-offs on vehicles are subject to certain limits that don’t apply to other types of business assets.
The mileage rate comes into play when taxpayers don’t want to keep track of actual vehicle-related expenses. With this approach, you don’t have to account for all your actual expenses, although you still must record certain information, such as the mileage for each business trip, the date and the destination.
The mileage rate approach also is popular with businesses that reimburse employees for business use of their personal automobiles. Such reimbursements can help attract and retain employees who’re expected to drive their personal vehicle extensively for business purposes. Why? Under the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act, employees can no longer deduct unreimbursed employee business expenses, such as business mileage, on their individual income tax returns.
But be aware that you must comply with various rules. If you don’t, you risk having the reimbursements considered taxable wages to the employees.
The 2019 rateBeginning on January 1, 2019, the standard mileage rate for the business use of a car (van, pickup or panel truck) is 58 cents per mile. For 2018, the rate was 54.5 cents per mile.
The business cents-per-mile rate is adjusted annually. It is based on an annual study commissioned by the IRS about the fixed and variable costs of operating a vehicle, such as gas, maintenance, repair and depreciation. Occasionally, if there is a substantial change in average gas prices, the IRS will change the mileage rate midyear.
More considerationsThere are certain situations where you can’t use the cents-per-mile rate. It depends in part on how you’ve claimed deductions for the same vehicle in the past or, if the vehicle is new to your business this year, whether you want to take advantage of certain first-year depreciation breaks on it.
As you can see, there are many variables to consider in determining whether to use the mileage rate to deduct vehicle expenses. Contact us if you have questions about tracking and claiming such expenses in 2019 — or claiming them on your 2018 income tax return.
© 2019
2 major tax law changes for individuals in 2019

|
Is there still time to pay 2018 bonuses and deduct them on your 2018 return?
|
A review of significant TCJA provisions impacting individual taxpayers

Now that 2019 has begun, there isn’t too much you can do to reduce your 2018 income tax liability. But it’s smart to begin preparing for filing your 2018 return. Because the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA), which was signed into law at the end of 2017, likely will have a major impact on your 2018 taxes, it’s a good time to review the most significant provisions impacting individual taxpayers.
Generally, taxpayers will be subject to lower tax rates for 2018. But a couple of rates stay the same, and changes to some of the brackets for certain types of filers (individuals and heads of households) could cause them to be subject to higher rates. Some exemptions are eliminated, while others increase. Here are some of the specific changes:
- Drops of individual income tax rates ranging from 0 to 4 percentage points (depending on the bracket) to 10%, 12%, 22%, 24%, 32%, 35% and 37%
- Elimination of personal and dependent exemptions
- AMT exemption increase, to $109,400 for joint filers, $70,300 for singles and heads of households, and $54,700 for separate filers for 2018
- Approximate doubling of the gift and estate tax exemption, to $11.18 million for 2018
Generally, tax breaks are reduced for 2018. However, a few are enhanced. Here’s a closer look:
- Doubling of the child tax credit to $2,000 and other modifications intended to help more taxpayers benefit from the credit
- Near doubling of the standard deduction, to $24,000 (married couples filing jointly), $18,000 (heads of households) and $12,000 (singles and married couples filing separately) for 2018
- Reduction of the adjusted gross income (AGI) threshold for the medical expense deduction to 7.5% for regular and AMT purposes
- New $10,000 limit on the deduction for state and local taxes (on a combined basis for property and income or sales taxes; $5,000 for separate filers)
- Reduction of the mortgage debt limit for the home mortgage interest deduction to $750,000 ($375,000 for separate filers), with certain exceptions
- Elimination of the deduction for interest on home equity debt
- Elimination of the personal casualty and theft loss deduction (with an exception for federally declared disasters)
- Elimination of miscellaneous itemized deductions subject to the 2% floor (such as certain investment expenses, professional fees and unreimbursed employee business expenses)
- Elimination of the AGI-based reduction of certain itemized deductions
- Elimination of the moving expense deduction (with an exception for members of the military in certain circumstances)
- Expansion of tax-free Section 529 plan distributions to include those used to pay qualifying elementary and secondary school expenses, up to $10,000 per student per tax year
As you can see, the TCJA changes for individuals are dramatic. Many rules and limits apply, so contact us to find out exactly how you’re affected. We can also tell you if any other provisions affect you, and help you begin preparing for your 2018 tax return filing and 2019 tax planning.
© 2019
A refresher on major tax law changes for small-business owners

The dawning of 2019 means the 2018 income tax filing season will soon be upon us. After year end, it’s generally too late to take action to reduce 2018 taxes. Business owners may, therefore, want to shift their focus to assessing whether they’ll likely owe taxes or get a refund when they file their returns this spring, so they can plan accordingly.
With the biggest tax law changes in decades — under the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA) — generally going into effect beginning in 2018, most businesses and their owners will be significantly impacted. So, refreshing yourself on the major changes is a good idea.
Taxation of pass-through entitiesThese changes generally affect owners of S corporations, partnerships and limited liability companies (LLCs) treated as partnerships, as well as sole proprietors:
- Drops of individual income tax rates ranging from 0 to 4 percentage points (depending on the bracket) to 10%, 12%, 22%, 24%, 32%, 35% and 37%
- A new 20% qualified business income deduction for eligible owners (the Section 199A deduction)
- Changes to many other tax breaks for individuals that will impact owners’ overall tax liability
These changes generally affect C corporations, personal service corporations (PSCs) and LLCs treated as C corporations:
- Replacement of graduated corporate rates ranging from 15% to 35% with a flat corporate rate of 21%
- Replacement of the flat PSC rate of 35% with a flat rate of 21%
- Repeal of the 20% corporate alternative minimum tax (AMT)
These changes generally apply to both pass-through entities and corporations:
- Doubling of bonus depreciation to 100% and expansion of qualified assets to include used assets
- Doubling of the Section 179 expensing limit to $1 million and an increase of the expensing phaseout threshold to $2.5 million
- A new tax credit for employer-paid family and medical leave
These changes generally also apply to both pass-through entities and corporations:
- A new disallowance of deductions for net interest expense in excess of 30% of the business’s adjusted taxable income (exceptions apply)
- New limits on net operating loss (NOL) deductions
- Elimination of the Section 199 deduction (not to be confused with the new Sec.199A deduction), which was for qualified domestic production activities and commonly referred to as the “manufacturers’ deduction”
- A new rule limiting like-kind exchanges to real property that is not held primarily for sale (generally no more like-kind exchanges for personal property)
- New limitations on deductions for certain employee fringe benefits, such as entertainment and, in certain circumstances, meals and transportation
Keep in mind that additional rules and limits apply to the rates and breaks covered here. Also, these are only some of the most significant and widely applicable TCJA changes; you and your business could be affected by other changes as well. Contact us to learn precisely how you might be affected and for help preparing for your 2018 tax return filing — and beginning to plan for 2019, too.
© 2018
You may be able to save more for retirement in 2019
|
Business owners: An exit strategy should be part of your tax planning
Tax planning is a juggling act for business owners. You have to keep your eye on your company’s income and expenses and applicable tax breaks (especially if you own a pass-through entity). But you also must look out for your own financial future.
For example, you need to develop an exit strategy so that taxes don’t trip you up when you retire or leave the business for some other reason. An exit strategy is a plan for passing on responsibility for running the company, transferring ownership and extracting your money from the business.
Buy-sell agreement
When a business has more than one owner, a buy-sell agreement can be a powerful tool. The agreement controls what happens to the business when a specified event occurs, such as an owner’s retirement, disability or death. Among other benefits, a well-drafted agreement:
- Provides a ready market for the departing owner’s shares,
- Prescribes a method for setting a price for the shares, and
- Allows business continuity by preventing disagreements caused by new owners.
A key issue with any buy-sell agreement is providing the buyer(s) with a means of funding the purchase. Life or disability insurance often helps fulfill this need and can give rise to several tax issues and opportunities. One of the biggest advantages of life insurance as a funding method is that proceeds generally are excluded from the beneficiary’s taxable income.
Succession within the family
You can pass your business on to family members by giving them interests, selling them interests or doing some of each. Be sure to consider your income needs, the tax consequences, and how family members will feel about your choice.
Under the annual gift tax exclusion, you can gift up to $15,000 of ownership interests without using up any of your lifetime gift and estate tax exemption. Valuation discounts may further reduce the taxable value of the gift.
With the gift and estate tax exemption approximately doubled through 2025 ($11.4 million for 2019), gift and estate taxes may be less of a concern for some business owners. But others may want to make substantial transfers now to take maximum advantage of the high exemption. What’s right for you will depend on the value of your business and your timeline for transferring ownership.
Plan ahead
If you don’t have co-owners or want to pass the business to family members, other options include a management buyout, an employee stock ownership plan (ESOP) or a sale to an outsider. Each involves a variety of tax and nontax considerations.
Please contact us to discuss your exit strategy. To be successful, your strategy will require planning well in advance of the transition.
© 2018
Act soon to save 2018 taxes on your investments

Do you have investments outside of tax-advantaged retirement plans? If so, you might still have time to shrink your 2018 tax bill by selling some investments • you just need to carefully select which investments you sell.
Try balancing gains and losses
If you’ve sold investments at a gain this year, consider selling some losing investments to absorb the gains. This is commonly referred to as “harvesting” losses.
If, however, you’ve sold investments at a loss this year, consider selling other investments in your portfolio that have appreciated, to the extent the gains will be absorbed by the losses. If you believe those appreciated investments have peaked in value, essentially you’ll lock in the peak value and avoid tax on your gains.
Review your potential tax ratesAt the federal level, long-term capital gains (on investments held more than one year) are taxed at lower rates than short-term capital gains (on investments held one year or less). The Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA) retains the 0%, 15% and 20% rates on long-term capital gains. But, for 2018 through 2025, these rates have their own brackets, instead of aligning with various ordinary-income brackets.
For example, these are the thresholds for the top long-term gains rates for 2018:
- Singles: $425,800
- Heads of households: $452,400
- Married couples filing jointly: $479,000
But the top ordinary-income rate of 37%, which also applies to short-term capital gains, doesn’t go into effect until income exceeds $500,000 for singles and heads of households or $600,000 for joint filers. The TCJA also retains the 3.8% net investment income tax (NIIT) and its $200,000 and $250,000 thresholds.
Don't forget the netting rules
Before selling investments, consider the netting rules for gains and losses, which depend on whether gains and losses are long term or short term. To determine your net gain or loss for the year, long-term capital losses offset long-term capital gains before they offset short-term capital gains. In the same way, short-term capital losses offset short-term capital gains before they offset long-term capital gains.
You may use up to $3,000 of total capital losses in excess of total capital gains as a deduction against ordinary income in computing your adjusted gross income. Any remaining net losses are carried forward to future years.
Time is running out
By reviewing your investment activity year-to-date and selling certain investments by year end, you may be able to substantially reduce your 2018 taxes. But act soon, because time is running out.
Keep in mind that tax considerations shouldn’t drive your investment decisions. You also need to consider other factors, such as your risk tolerance and investment goals.
We can help you determine what makes sense for you. Please contact us.
© 2018
6 last-minute tax moves for your business

|
Year-end tax and financial to-do list for individuals

|
Can a PTO contribution arrangement help your employees and your business?

|
Check deductibility before making year-end charitable gifts

|
2019 Q1 tax calendar: Key deadlines for businesses and other employers

|
Does prepaying property taxes make sense anymore?
|
When holiday gifts and parties are deductible or taxable

The holiday season is a great time for businesses to show their appreciation for employees and customers by giving them gifts or hosting holiday parties. Before you begin shopping or sending out invitations, though, it’s a good idea to find out whether the expense is tax deductible and whether it’s taxable to the recipient. Here’s a brief review of the rules.
Gifts to customers
When you make gifts to customers, the gifts are deductible up to $25 per recipient per year. For purposes of the $25 limit, you need not include “incidental” costs that don’t substantially add to the gift’s value, such as engraving, gift-wrapping, packaging or shipping. Also excluded from the $25 limit is branded marketing collateral — such as pens or stress balls imprinted with your company’s name and logo — provided they’re widely distributed and cost less than $4.
The $25 limit is for gifts to individuals. There’s no set limit on gifts to a company (a gift basket for all to share, for example) as long as they’re “reasonable.”
Gifts to employees
Generally anything of value that you transfer to an employee is included in the employee’s taxable income (and, therefore, subject to income and payroll taxes) and deductible by you. But there’s an exception for noncash gifts that constitute “de minimis fringe benefits.”
These are items so small in value and given so infrequently that it would be administratively impracticable to account for them. Common examples include holiday turkeys or hams, gift baskets, occasional sports or theater tickets (but not season tickets), and other low-cost merchandise.
De minimis fringe benefits are not included in an employee’s taxable income yet are still deductible by you. Unlike gifts to customers, there’s no specific dollar threshold for de minimis gifts. However, many businesses use an informal cutoff of $75.
Keep in mind that cash gifts — as well as cash equivalents, such as gift cards — are included in an employee’s income and subject to payroll tax withholding regardless of how small and infrequent.
Holiday parties
The Tax Cuts and Jobs Act reduced certain deductions for business-related meals and eliminated the deduction for business entertainment altogether. There’s an exception, however, for certain recreational activities, including holiday parties.
Holiday parties are fully deductible (and excludible from recipients’ income) provided they’re primarily for the benefit of non-highly-compensated employees and their families. If customers also attend, holiday parties may be partially deductible.
Gifts that give back
If you’re thinking about giving holiday gifts to employees or customers or throwing a holiday party, contact us. With a little tax planning, you may receive a gift of your own from Uncle Sam.
Catch-up retirement plan contributions can be particularly advantageous post-TCJA

|
Tax reform expands availability of cash accounting
|
Mutual funds: Handle with care at year end

|
It's not too late: You can still set up a retirement plan for 2018

|
Time for NQDC plan deferral elections

Time for NQDC plan deferral elections
If you’re an executive or other key employee, your employer may offer you a nonqualified deferred compensation (NQDC) plan. As the name suggests, NQDC plans pay employees in the future for services currently performed. The plans allow deferral of the income tax associated with the compensation.
But to receive this attractive tax treatment, NQDC plans must meet many requirements. One is that employees must make the deferral election before the year they perform the services for which the compensation is earned. So, if you wish to defer part of your 2019 compensation, you generally must make the election by the end of 2018.
NQDC plans vs. qualified plans
NQDC plans differ from qualified plans, such as 401(k)s, in that:
- NQDC plans can favor highly compensated employees,
- Although your income tax liability can be deferred, your employer can’t deduct the NQDC until you recognize it as income, and
- Any NQDC plan funding isn’t protected from your employer’s creditors.
While some rules are looser for NQDC plans, there are also many rules that apply to them that don’t apply to qualified plans.
2 more NQDC rules
In addition to the requirement that deferral elections be made before the start of the year, there are two other important NQDC rules to be aware of:
1. Distributions. Benefits must be paid on a specified date, according to a fixed payment schedule or after the occurrence of a specified event — such as death, disability, separation from service, change in ownership or control of the employer, or an unforeseeable emergency.
2. Elections to make certain changes. The timing of benefits can be delayed but not accelerated. Elections to change the timing or form of a payment must be made at least 12 months in advance. Also, new payment dates must be at least five years after the date the payment would otherwise have been made.
Be aware that the penalties for noncompliance with NQDC rules can be severe: You can be taxed on plan benefits at the time of vesting, and a 20% penalty and interest charges also may apply. So if you’re receiving NQDC, check with your employer to make sure it’s addressing any compliance issues.
No deferral of employment tax
Another important NQDC tax issue is that employment taxes are generally due when services are performed or when there’s no longer a substantial risk of forfeiture, whichever is later. This is true even though the compensation isn’t actually paid or recognized for income tax purposes until later years.
So your employer may withhold your portion of the tax from your salary or ask you to write a check for the liability. Or your employer might pay your portion, in which case you’ll have additional taxable income.
Next steps
Questions about NQDC — or other executive comp, such as incentive stock options or restricted stock? Contact us. We can answer them and help you determine what, if any, steps you need to take before year end to defer taxes and avoid interest and penalties.
© 2018
Buy business assets before year end to reduce your 2018 tax liability

|
Donate appreciated stock for twice the tax benefits
|
Research credit available to some businesses for the first time
|
Could “bunching” medical expenses into 2018 save you tax?

Some of your medical expenses may be tax deductible, but only if you itemize deductions and have enough expenses to exceed the applicable floor for deductibility. With proper planning, you may be able to time controllable medical expenses to your tax advantage. The Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA) could make bunching such expenses into 2018 beneficial for some taxpayers. At the same time, certain taxpayers who’ve benefited from the deduction in previous years might no longer benefit because of the TCJA’s increase to the standard deduction.
The ChangesVarious limits apply to most tax deductions, and one type of limit is a “floor,” which means expenses are deductible only to the extent that they exceed that floor (typically a specific percentage of your income). One example is the medical expense deduction.
Because it can be difficult to exceed the floor, a common strategy is to “bunch” deductible medical expenses into a particular year where possible. The TCJA reduced the floor for the medical expense deduction for 2017 and 2018 from 10% to 7.5%. So, it might be beneficial to bunch deductible medical expenses into 2018.
Medical expenses that aren’t reimbursable by insurance or paid through a tax-advantaged account (such as a Health Savings Account or Flexible Spending Account) may be deductible.
However, if your total itemized deductions won’t exceed your standard deduction, bunching medical expenses into 2018 won’t save tax. The TCJA nearly doubled the standard deduction. For 2018, it’s $12,000 for singles and married couples filing separately, $18,000 for heads of households, and $24,000 for married couples filing jointly.
If your total itemized deductions for 2018 will exceed your standard deduction, bunching nonurgent medical procedures and other controllable expenses into 2018 may allow you to exceed the applicable floor and benefit from the medical expense deduction. Controllable expenses might include prescription drugs, eyeglasses and contact lenses, hearing aids, dental work, and elective surgery.
Planning for uncertaintyKeep in mind that legislation could be signed into law that extends the 7.5% threshold for 2019 and even beyond. For help determining whether you could benefit from bunching medical expenses into 2018, please contact us.
© 2018
Selling your business? Defer — and possibly reduce — tax with an installment sale

|
Consider all the tax consequences before making gifts to loved ones
|
Now’s the time to review your business expenses

As we approach the end of the year, it’s a good idea to review your business’s expenses for deductibility. At the same time, consider whether your business would benefit from accelerating certain expenses into this year.
Be sure to evaluate the impact of the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA), which reduces or eliminates many deductions. In some cases, it may be necessary or desirable to change your expense and reimbursement policies.
What’s deductible, anyway?There’s no master list of deductible business expenses in the Internal Revenue Code (IRC). Although some deductions are expressly authorized or excluded, most are governed by the general rule of IRC Sec. 162, which permits businesses to deduct their “ordinary and necessary” expenses.
An ordinary expense is one that is common and accepted in your industry. A necessary expense is one that is helpful and appropriate for your business. (It need not be indispensable.) Even if an expense is ordinary and necessary, it may not be deductible if the IRS considers it lavish or extravagant.
What did the TCJA change?The TCJA contains many provisions that affect the deductibility of business expenses. Significant changes include these deductions:
Meals and entertainment.The act eliminates most deductions for entertainment expenses, but retains the 50% deduction for business meals. What about business meals provided in connection with nondeductible entertainment? In a recent notice, the IRS clarified that such meals continue to be 50% deductible, provided they’re purchased separately from the entertainment or their cost is separately stated on invoices or receipts.
TransportationThe act eliminates most deductions for qualified transportation fringe benefits, such as parking, vanpooling and transit passes. This change may lead some employers to discontinue these benefits, although others will continue to provide them because 1) they’re a valuable employee benefit (they’re still tax-free to employees) or 2) they’re required by local law.
Employee expenses. The act suspends employee deductions for unreimbursed job expenses — previously treated as miscellaneous itemized deductions — through 2025. Some businesses may want to implement a reimbursement plan for these expenses. So long as the plan meets IRS requirements, reimbursements are deductible by the business and tax-free to employees.
Need Help?The deductibility of certain expenses, such as employee wages or office supplies, is obvious. In other cases, it may be necessary to consult IRS rulings or court cases for guidance. For assistance, please contact us.
© 2018
529 plans offer two tax-advantaged education funding options

Section 529 plans are a popular education-funding tool because of tax and other benefits. Two types are available: 1) prepaid tuition plans, and 2) savings plans. And one of these plans got even better under the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA).
Enjoy valuable benefits529 plans provide a tax-advantaged way to help pay for qualifying education expenses. First and foremost, although contributions aren’t deductible for federal purposes, plan assets can grow tax-deferred. In addition, some states offer tax incentives for contributing in the form of deductions or credits.
But that’s not all. 529 plans also usually offer high contribution limits. And there are no income limits for contributing.
Lock in current tuition ratesWith a 529 prepaid tuition plan, if your contract is for four years of tuition, tuition is guaranteed regardless of its cost at the time the beneficiary actually attends the school. This can provide substantial savings if you invest when the child is still very young.
One downside is that there’s uncertainty in how benefits will be applied if the beneficiary attends a different school. Another is that the plan doesn’t cover costs other than tuition, such as room and board.
Fund more than just college tuitionA 529 savings plan can be used to pay a student’s expenses at most postsecondary educational institutions. Distributions used to pay qualified expenses (such as tuition, mandatory fees, books, supplies, computer equipment, software, Internet service and, generally, room and board) are income-tax-free for federal purposes and typically for state purposes as well, thus making the tax deferral a permanent savings.
In addition, the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act expands the definition of qualified expenses to generally include elementary and secondary school tuition. However, tax-free distributions used for such tuition are limited to $10,000 per year.
The biggest downside may be that you don’t have direct control over investment decisions; you’re limited to the options the plan offers. Additionally, for funds already in the plan, you can make changes to your investment options only twice during the year or when you change beneficiaries.
But each time you make a contribution to a 529 savings plan, you can select a different option for that contribution, regardless of how many times you contribute throughout the year. And every 12 months you can make a tax-free rollover to a different 529 plan for the same child.
Picking your planBoth prepaid tuition plans and savings plans offer attractive benefits. We can help you determine which one is a better fit for you or explore other tax-advantaged education-funding options.
© 2018
Tax-free fringe benefits help small businesses and their employees

|
Charitable IRA rollovers may be especially beneficial in 2018

If you’re age 70½ or older, you can make direct contributions — up to $100,000 annually — from your IRA to qualified charitable organizations without owing any income tax on the distributions. This break may be especially beneficial now because of Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA) changes that affect who can benefit from the itemized deduction for charitable donations.
Counts toward your RMDA charitable IRA rollover can be used to satisfy required minimum distributions (RMDs). You must begin to take annual RMDs from your traditional IRAs in the year you reach age 70½. If you don’t comply, you can owe a penalty equal to 50% of the amount you should have withdrawn but didn’t. (Deferral is allowed for the initial year, but you’ll have to take two RMDs the next year.)
So if you don’t need the RMD for your living expenses, a charitable IRA rollover can be a great way to comply with the RMD requirement without triggering the tax liability that would occur if the RMD were paid to you.
Doesn’t require itemizingYou might be able to achieve a similar tax result from taking the RMD and then contributing that amount to charity. But it’s more complex because you must report the RMD as income and then take an itemized deduction for the donation.
And, with the TCJA’s near doubling of the standard deduction, fewer taxpayers will benefit from itemizing. Itemizing saves tax only when itemized deductions exceed the standard deduction. For 2018, the standard deduction is $12,000 for singles, $18,000 for heads of households, and $24,000 for married couples filing jointly.
Doesn’t have other deduction downsidesEven if you have enough other itemized deductions to exceed your standard deduction, taking your RMD and contributing that amount to charity has two more possible downsides.
First, the reported RMD income might increase your income to the point that you’re pushed into a higher tax bracket, certain additional taxes are triggered and/or the benefits of certain tax breaks are reduced or eliminated. It could even cause Social Security payments to become taxable or increase income-based Medicare premiums and prescription drug charges.
Second, if your donation would equal a large portion of your income for the year, your deduction might be reduced due to the percentage-of-income limit. You generally can’t deduct cash donations that exceed 60% of your adjusted gross income for the year. (The TCJA raised this limit from 50%, but if the cash donation is to a private nonoperating foundation, the limit is only 30%.) You can carry forward the excess up to five years, but if you make large donations every year, that won’t help you.
A charitable IRA rollover avoids these potential negative tax consequences.
Have questions?The considerations involved in deciding whether to make a direct IRA rollover have changed in light of the TCJA. So contact us to go over your particular situation and determine what’s right for you.
© 2018
Could a cost segregation study help you accelerate depreciation deductions?
|
Tax planning for investments gets more complicated

For investors, fall is a good time to review year-to-date gains and losses. Not only can it help you assess your financial health, but it also can help you determine whether to buy or sell investments before year end to save taxes. This year, you also need to keep in mind the impact of the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA). While the TCJA didn’t change long-term capital gains rates, it did change the tax brackets for long-term capital gains and qualified dividends.
For 2018 through 2025, these brackets are no longer linked to the ordinary-income tax brackets for individuals. So, for example, you could be subject to the top long-term capital gains rate even if you aren’t subject to the top ordinary-income tax rate.
Old rulesFor the last several years, individual taxpayers faced three federal income tax rates on long-term capital gains and qualified dividends: 0%, 15% and 20%. The rate brackets were tied to the ordinary-income rate brackets.
Specifically, if the long-term capital gains and/or dividends fell within the 10% or 15% ordinary-income brackets, no federal income tax was owed. If they fell within the 25%, 28%, 33% or 35% ordinary-income brackets, they were taxed at 15%. And, if they fell within the maximum 39.6% ordinary-income bracket, they were taxed at the maximum 20% rate.
In addition, higher-income individuals with long-term capital gains and dividends were also hit with the 3.8% net investment income tax (NIIT). It kicked in when modified adjusted gross income exceeded $200,000 for singles and heads of households and $250,000 for married couples filing jointly. So, many people actually paid 18.8% (15% + 3.8%) or 23.8% (20% + 3.8%) on their long-term capital gains and qualified dividends.
New RulesThe TCJA retains the 0%, 15% and 20% rates on long-term capital gains and qualified dividends for individual taxpayers. However, for 2018 through 2025, these rates have their own brackets. Here are the 2018 brackets:
- Singles:
- 0%: $0 – $38,600
- 15%: $38,601 – $425,800
- 20%: $425,801 and up
- Head of Households:
- 0%: $0 – $51,700
- 15%: $51,701 – $452,400
- 20%: $452,401 and up
- Married couples filing jointly
- 0%: $0 – $77,200
- 15%: $77,201 – $479,000
- 20%: $479,001 and up
For 2018, the top ordinary-income rate of 37%, which also applies to short-term capital gains and nonqualified dividends, doesn’t go into effect until income exceeds $500,000 for singles and heads of households or $600,000 for joint filers. (Both the long-term capital gains brackets and the ordinary-income brackets will be indexed for inflation for 2019 through 2025.) The new tax law also retains the 3.8% NIIT and its $200,000 and $250,000 thresholds.
More thresholds, more complexityWith more tax rate thresholds to keep in mind, year-end tax planning for investments is especially complicated in 2018. If you have questions, please contact us.
© 2018
Businesses aren’t immune to tax identity theft

Businesses aren’t immune to tax identity theft
Tax identity theft may seem like a problem only for individual taxpayers. But, according to the IRS, increasingly businesses are also becoming victims. And identity thieves have become more sophisticated, knowing filing practices, the tax code and the best ways to get valuable data.
How it works
In tax identity theft, a taxpayer’s identifying information (such as Social Security number) is used to fraudulently obtain a refund or commit other crimes. Business tax identity theft occurs when a criminal uses the identifying information of a business to obtain tax benefits or to enable individual tax identity theft schemes.
For example, a thief could use an Employer Identification Number (EIN) to file a fraudulent business tax return and claim a refund. Or a fraudster may report income and withholding for fake employees on false W-2 forms. Then, he or she can file fraudulent individual tax returns for these “employees” to claim refunds.
The consequences can include significant dollar amounts, lost time sorting out the mess and damage to your reputation.
Red flags
There are some red flags that indicate possible tax identity theft. For example, your business’s identity may have been compromised if:
- Your business doesn’t receive expected or routine mailings from the IRS,
- You receive an IRS notice that doesn’t relate to anything your business submitted, that’s about fictitious employees or that’s related to a defunct, closed or dormant business after all account balances have been paid,
- The IRS rejects an e-filed return or an extension-to-file request, saying it already has a return with that identification number — or the IRS accepts it as an amended return,
- You receive an IRS letter stating that more than one tax return has been filed in your business’s name, or
- You receive a notice from the IRS that you have a balance due when you haven’t yet filed a return.
Keep in mind, though, that some of these could be the result of a simple error, such as an inadvertent transposition of numbers. Nevertheless, you should contact the IRS immediately if you receive any notices or letters from the agency that you believe might indicate that someone has fraudulently used your Employer Identification Number.
Prevention tips
Businesses should take steps such as the following to protect their own information as well as that of their employees:
- Provide training to accounting, human resources and other employees to educate them on the latest tax fraud schemes and how to spot phishing emails.
- Use secure methods to send W-2 forms to employees.
- Implement risk management strategies designed to flag suspicious communications.
Of course identity theft can go beyond tax identity theft, so be sure to have a comprehensive plan in place to protect the data of your business, your employees and your customers. If you’re concerned your business has become a victim, or you have questions about prevention, please contact us.
© 2018
The tax deduction ins and outs of donating artwork to charity
|
Be sure your employee travel expense reimbursements will pass muster with the IRS

Does your business reimburse employees’ work-related travel expenses? If you do, you know that it can help you attract and retain employees. If you don’t, you might want to start, because changes under the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA) make such reimbursements even more attractive to employees. Travel reimbursements also come with tax benefits, but only if you follow a method that passes muster with the IRS.
The TCJA’s impactBefore the TCJA, unreimbursed work-related travel expenses generally were deductible on an employee’s individual tax return (subject to a 50% limit for meals and entertainment) as a miscellaneous itemized deduction. However, many employees weren’t able to benefit from the deduction because either they didn’t itemize deductions or they didn’t have enough miscellaneous itemized expenses to exceed the 2% of adjusted gross income (AGI) floor that applied.
For 2018 through 2025, the TCJA suspends miscellaneous itemized deductions subject to the 2% of AGI floor. That means even employees who itemize deductions and have enough expenses that they would exceed the floor won’t be able to enjoy a tax deduction for business travel. Therefore, business travel expense reimbursements are now more important to employees.
The potential tax benefitsYour business can deduct qualifying reimbursements, and they’re excluded from the employee’s taxable income. The deduction is subject to a 50% limit for meals. But, under the TCJA, entertainment expenses are no longer deductible.
To be deductible and excludable, travel expenses must be legitimate business expenses and the reimbursements must comply with IRS rules. You can use either an accountable plan or the per diem method to ensure compliance.
Reimbursing actual expensesAn accountable plan is a formal arrangement to advance, reimburse or provide allowances for business expenses. To qualify as “accountable,” your plan must meet the following criteria:
- Payments must be for “ordinary and necessary” business expenses.
- Employees must substantiate these expenses — including amounts, times and places — ideally at least monthly.
- Employees must return any advances or allowances they can’t substantiate within a reasonable time, typically 120 days.
The IRS will treat plans that fail to meet these conditions as nonaccountable, transforming all reimbursements into wages taxable to the employee, subject to income taxes (employee) and employment taxes (employer and employee).
Keeping it simpleWith the per diem method, instead of tracking actual expenses, you use IRS tables to determine reimbursements for lodging, meals and incidental expenses, or just for meals and incidental expenses, based on location. (If you don’t go with the per diem method for lodging, you’ll need receipts to substantiate those expenses.)
Be sure you don’t pay employees more than the appropriate per diem amount. The IRS imposes heavy penalties on businesses that routinely overpay per diems.
What’s right for your business?To learn more about business travel expense deductions and reimbursements post-TCJA, contact us. We can help you determine whether you should reimburse such expenses and which reimbursement option is better for you.
© 2018
You might save tax if your vacation home qualifies as a rental property

Do you own a vacation home? If you both rent it out and use it personally, you might save tax by taking steps to ensure it qualifies as a rental property this year. Vacation home expenses that qualify as rental property expenses aren’t subject to the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act’s (TCJA’s) new limit on the itemized deduction for state and local taxes (SALT) or the lower debt limit for the itemized mortgage interest deduction.
Rental or personal property?
If you rent out your vacation home for 15 days or more, what expenses you can deduct depends on how the home is classified for tax purposes, based on the amount of personal vs. rental use:
Rental property. If you (or your immediate family) use the home for 14 days or less, or under 10% of the days you rent out the property, whichever is greater, the IRS will classify the home as a rental property. You can deduct rental expenses, including losses, subject to the real estate activity rules. Your deduction for property tax attributable to the rental use of the home isn’t subject to the TCJA’s new SALT deduction limit. And your deduction for mortgage interest on the home isn’t subject to the debt limit that applies to the itemized deduction for mortgage interest. You can’t deduct any interest that’s attributable to your personal use of the home, but you can take the personal portion of property tax as an itemized deduction (subject to the new SALT limit).
Nonrental property. If you (or your immediate family) use the home for more than 14 days or 10% of the days you rent out the property, whichever is greater, the IRS will classify the home as a personal residence. You can deduct rental expenses only to the extent of your rental income. Any excess can be carried forward to offset rental income in future years.
If you itemize deductions, you also can deduct the personal portion of both property tax and mortgage interest, subject to the TCJA’s new limits on those deductions. The SALT deduction limit is $10,000 for the combined total of state and local property taxes and either income taxes or sales taxes ($5,000 for married taxpayers filing separately). For mortgage interest debt incurred after December 15, 2017, the debt limit (with some limited exceptions) has been reduced to $750,000.
Be aware that many taxpayers who have itemized in the past will no longer benefit from itemizing because of the TCJA’s near doubling of the standard deduction. Itemizing saves tax only if total itemized deductions exceed the standard deduction for the taxpayer’s filing status.
Year-to-date review
Keep in mind that, if you rent out your vacation home for less than 15 days, you don’t have to report the income. But expenses associated with the rental (such as advertising and cleaning) won’t be deductible.
Now is a good time to review your vacation home use year-to-date to project how it will be classified for tax purposes. By increasing the number of days you rent it out and/or reducing the number of days you use it personally between now and year end, you might be able to ensure it’s classified as a rental property and save some tax. But there also could be circumstances where personal property treatment would be beneficial. Please contact us to discuss your particular situation.
© 2018
2018 Q4 tax calendar: Key deadlines for businesses and other employers

Here are some of the key tax-related deadlines affecting businesses and other employers during the fourth quarter of 2018. Keep in mind that this list isn’t all-inclusive, so there may be additional deadlines that apply to you. Contact us to ensure you’re meeting all applicable deadlines and to learn more about the filing requirements.
October 15
- If a calendar-year C corporation that filed an automatic six-month extension:
- File a 2017 income tax return (Form 1120) and pay any tax, interest and penalties due.
- Make contributions for 2017 to certain employer-sponsored retirement plans.
October 31
- Report income tax withholding and FICA taxes for third quarter 2018 (Form 941) and pay any tax due. (See exception below under “November 13.”)
November 13
- Report income tax withholding and FICA taxes for third quarter 2018 (Form 941), if you deposited on time and in full all of the associated taxes due.
December 17
- If a calendar-year C corporation, pay the fourth installment of 2018 estimated income taxes.
© 2018
Do you need to make an estimated tax payment by September 17?

|
How to reduce the tax risk of using independent contractors

|
Back-to-school time means a tax break for teachers

|
Keep it SIMPLE: A tax-advantaged retirement plan solution for small businesses

|
Play your tax cards right with gambling wins and losses

If you gamble, be sure you understand the tax consequences. Both wins and losses can affect your income tax bill. And changes under the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA) could also have an impact.
Wins and taxable income
You must report 100% of your gambling winnings as taxable income. The value of complimentary goodies (“comps”) provided by gambling establishments must also be included in taxable income as winnings.
Winnings are subject to your regular federal income tax rate. You might pay a lower rate on gambling winnings this year because of rate reductions under the TCJA.
Amounts you win may be reported to you on IRS Form W-2G (“Certain Gambling Winnings”). In some cases, federal income tax may be withheld, too. Anytime a Form W-2G is issued, the IRS gets a copy. So if you’ve received such a form, remember that the IRS will expect to see the winnings on your tax return.
Losses and tax deductions
You can write off gambling losses as a miscellaneous itemized deduction. While miscellaneous deductions subject to the 2% of adjusted gross income floor are not allowed for 2018 through 2025 under the TCJA, the deduction for gambling losses isn’t subject to that floor. So gambling losses are still deductible.
But the TCJA’s near doubling of the standard deduction for 2018 (to $24,000 for married couples filing jointly, $18,000 for heads of households and $12,000 for singles and separate filers) means that, even if you typically itemized deductions in the past, you may no longer benefit from itemizing. Itemizing saves tax only when total itemized deductions exceed the applicable standard deduction.
Also be aware that the deduction for gambling losses is limited to your winnings for the year, and any excess losses cannot be carried forward to future years. Also, out-of-pocket expenses for transportation, meals, lodging and so forth can’t be deducted unless you qualify as a gambling professional.
And, for 2018 through 2025, the TCJA modifies the limit on gambling losses for professional gamblers so that all deductions for expenses incurred in carrying out gambling activities, not just losses, are limited to the extent of gambling winnings.
Tracking your activities
To claim a deduction for gambling losses, you must adequately document them, including:
- 1. The date and type of gambling activity.
- 2. The name and address or location of the gambling establishment.
- 3. The names of other persons (if any) present with you at the gambling establishment. (Obviously, this is not possible when the gambling occurs at a public venue such as a casino, race track, or bingo parlor.)
- 4. The amount won or lost.
You can document income and losses from gambling on table games by recording the number of the table you played and keeping statements showing casino credit issued to you. For lotteries, you can use winning statements and unredeemed tickets as documentation.
Please contact us if you have questions or want more information about the tax treatment of gambling wins and losses.
Assessing the S corp

The S corporation business structure offers many advantages, including limited liability for owners and no double taxation (at least at the federal level). But not all businesses are eligible • and, with the new 21% flat income tax rate that now applies to C corporations, S corps may not be quite as attractive as they once were.
Tax comparison
The primary reason for electing S status is the combination of the limited liability of a corporation and the ability to pass corporate income, losses, deductions and credits through to shareholders. In other words, S corps generally avoid double taxation of corporate income — once at the corporate level and again when distributed to the shareholder. Instead, S corp tax items pass through to the shareholders’ personal returns and the shareholders pay tax at their individual income tax rates.
But now that the C corp rate is only 21% and the top rate on qualified dividends remains at 20%, while the top individual rate is 37%, double taxation might be less of a concern. On the other hand, S corp owners may be able to take advantage of the new qualified business income (QBI) deduction, which can be equal to as much as 20% of QBI.
You have to run the numbers with your tax advisor, factoring in state taxes, too, to determine which structure will be the most tax efficient for you and your business.
S eligibility requirements
If S corp status makes tax sense for your business, you need to make sure you qualify • and stay qualified. To be eligible to elect to be an S corp or to convert to S status, your business must:
- Be a domestic corporation and have only one class of stock,
- Have no more than 100 shareholders, and
- Have only “allowable” shareholders, including individuals, certain trusts and estates. Shareholders can’t include partnerships, corporations and nonresident alien shareholders.
In addition, certain businesses are ineligible, such as insurance companies.
Reasonable compensation
Another important consideration when electing S status is shareholder compensation. The IRS is on the lookout for S corps that pay shareholder-employees an unreasonably low salary to avoid paying Social Security and Medicare taxes and then make distributions that aren’t subject to payroll taxes.
Compensation paid to a shareholder should be reasonable considering what a nonowner would be paid for a comparable position. If a shareholder’s compensation doesn’t reflect the fair market value of the services he or she provides, the IRS may reclassify a portion of distributions as unpaid wages. The company will then owe payroll taxes, interest and penalties on the reclassified wages.
Pros and cons
S corp status isn’t the best option for every business. To ensure that you’ve considered all the pros and cons, contact us. Assessing the tax differences can be tricky — especially with the tax law changes going into effect this year.
© 2018
Keep an eye out for extenders legislation

The pieces of tax legislation garnering the most attention these days are the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA) signed into law last December and the possible “Tax Reform 2.0” that Congress might pass this fall. But for certain individual taxpayers, what happens with “extenders” legislation is also important.
Recent history
Back in December of 2015, Congress passed the PATH Act, which made a multitude of tax breaks permanent. However, there were a few valuable breaks for individuals that it extended only through 2016. The TCJA didn’t address these breaks, but they were retroactively extended through December 31, 2017, by the Bipartisan Budget Act of 2018 (BBA), which was signed into law on February 9, 2018.
Now the question is whether Congress will extend them for 2018 and, if so, when. In July, House Ways and Means Committee Chair Kevin Brady (R-TX) released a broad outline of what Tax Reform 2.0 legislation may contain. And he indicated that it probably wouldn’t include the so-called “extenders” but that they would likely be addressed by separate legislation.
Mortgage insurance and loan forgiveness
Under the BBA, through 2017, you could treat qualified mortgage insurance premiums as interest for purposes of the mortgage interest deduction. This was an itemized deduction that phased out for taxpayers with AGI of $100,000 to $110,000.
The BBA likewise extended through 2017 the exclusion from gross income for mortgage loan forgiveness. It also allowed the exclusion to apply to mortgage forgiveness that occurs in 2018 as long as it’s granted pursuant to a written agreement entered into in 2017. So even if this break isn’t extended, you might still be able to benefit from it on your 2018 income tax return.
Tuition and related expenses
Also available through 2017 under the BBA was the above-the-line deduction for qualified tuition and related expenses for higher education. It was capped at $4,000 for taxpayers whose adjusted gross income (AGI) didn’t exceed $65,000 ($130,000 for joint filers) or, for those beyond those amounts, $2,000 for taxpayers whose AGI didn’t exceed $80,000 ($160,000 for joint filers).
You couldn’t take the American Opportunity credit, its cousin the Lifetime Learning credit and the tuition deduction in the same year for the same student. If you were eligible for all three breaks, the American Opportunity credit would typically be the most valuable in terms of tax savings.
But in some situations, the AGI reduction from the tuition deduction might prove more beneficial than taking the Lifetime Learning credit. For example, a lower AGI might help avoid having other tax breaks reduced or eliminated due to AGI-based phaseouts.
Still time …
There’s still plenty of time for Congress to extend these breaks for 2018. And, if you qualify and you haven’t filed your 2017 income tax return yet, there’s even still time to take advantage of these breaks on that tax return. The deadline for individual extended 2017 returns is October 15, 2018. Contact us with questions about these breaks and whether you can benefit.
© 2018
Choosing the right accounting method for tax purposes

The Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA) liberalized the eligibility rules for using the cash method of accounting, making this method — which is simpler than the accrual method — available to more businesses. Now the IRS has provided procedures a small business taxpayer can use to obtain automatic consent to change its method of accounting under the TCJA. If you have the option to use either accounting method, it pays to consider whether switching methods would be beneficial.
Cash vs. accrual
Generally, cash-basis businesses recognize income when it’s received and deduct expenses when they’re paid. Accrual-basis businesses, on the other hand, recognize income when it’s earned and deduct expenses when they’re incurred, without regard to the timing of cash receipts or payments.
In most cases, a business is permitted to use the cash method of accounting for tax purposes unless it’s:
- Expressly prohibited from using the cash method, or
- Expressly required to use the accrual method.
Cash method advantages
The cash method offers several advantages, including:
Simplicity. It’s easier and cheaper to implement and maintain.
Tax-planning flexibility. It offers greater flexibility to control the timing of income and deductible expenses. For example, it allows you to defer income to next year by delaying invoices or to shift deductions into this year by accelerating the payment of expenses. An accrual-basis business doesn’t enjoy this flexibility. For example, to defer income, delaying invoices wouldn’t be enough; the business would have to put off shipping products or performing services.
Cash flow benefits. Because income is taxed in the year it’s received, the cash method does a better job of ensuring that a business has the funds it needs to pay its tax bill.
Accrual method advantages
In some cases, the accrual method may offer tax advantages. For example, accrual-basis businesses may be able to use certain tax-planning strategies that aren’t available to cash-basis businesses, such as deducting year-end bonuses that are paid within the first 2½ months of the following year and deferring income on certain advance payments.
The accrual method also does a better job of matching income and expenses, so it provides a more accurate picture of a business’s financial performance. That’s why it’s required under Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP).
If your business prepares GAAP-compliant financial statements, you can still use the cash method for tax purposes. But weigh the cost of maintaining two sets of books against the potential tax benefits.
Making a change
Keep in mind that cash and accrual are the two primary tax accounting methods, but they’re not the only ones. Some businesses may qualify for a different method, such as a hybrid of the cash and accrual methods.
If your business is eligible for more than one method, we can help you determine whether switching methods would make sense and can execute the change for you if appropriate.
© 2018
The TCJA prohibits undoing 2018 Roth IRA conversions, but 2017 conversions are still eligible
Converting a traditional IRA to a Roth IRA can provide tax-free growth and tax-free withdrawals in retirement. But what if you convert your traditional IRA — subject to income taxes on all earnings and deductible contributions — and then discover you would have been better off if you hadn’t converted it?
Before the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA), you could undo a Roth IRA conversion using a “recharacterization.” Effective with 2018 conversions, the TCJA prohibits recharacterizations — permanently. But if you executed a conversion in 2017, you may still be able to undo it.
Reasons to recharacterize
Generally, if you converted to a Roth IRA in 2017, you have until October 15, 2018, to undo it and avoid the tax hit.
Here are some reasons you might want to recharacterize a 2017 Roth IRA conversion:
- The conversion combined with your other income pushed you into a higher tax bracket in 2017.
- Your marginal income tax rate will be lower in 2018 than it was in 2017.
- The value of your account has declined since the conversion, so you owe taxes partially on money you no longer have.
If you recharacterize your 2017 conversion but would still like to convert your traditional IRA to a Roth IRA, you must wait until the 31st day after the recharacterization. If you undo a conversion because your IRA’s value declined, there’s a risk that your investments will bounce back during the waiting period, causing you to reconvert at a higher tax cost.
Recharacterization in action
Sally had a traditional IRA with a balance of $100,000 when she converted it to a Roth IRA in 2017. Her 2017 tax rate was 33%, so she owed $33,000 in federal income taxes on the conversion.
However, by August 1, 2018, the value of her account had dropped to $80,000. So Sally recharacterizes the account as a traditional IRA and amends her 2017 tax return to exclude the $100,000 in income.
On September 1, she reconverts the traditional IRA, whose value remains at $80,000, to a Roth IRA. She will report that amount when she files her 2018 tax return. The 33% rate has dropped to 32% under the TCJA. Assuming Sally is still in this bracket, this time she’ll owe $25,600 ($80,000 × 32%) — deferred for a year and resulting in a tax savings of $7,400.
(Be aware that the thresholds for the various brackets have changed for 2018, in some cases increasing but in others decreasing. This, combined with other TCJA provisions and changes in your income, could cause you to be in a higher or lower bracket in 2018.)
Know your options
If you converted a traditional IRA to a Roth IRA in 2017, it’s worthwhile to see if you could save tax by undoing the conversion. If you’re considering a Roth conversion in 2018, keep in mind that you won’t have the option to recharacterize. We can help you assess whether recharacterizing a 2017 conversion or executing a 2018 conversion makes sense for you.
© 2018
An FLP can save tax in a family business succession

|
Do you still need to worry about AMT?

|
Do you qualify for the home office deduction?

|
Why the “kiddie tax” is more dangerous than ever

Once upon a time, some parents and grandparents would attempt to save tax by putting investments in the names of their young children or grandchildren in lower income tax brackets. To discourage such strategies, Congress created the “kiddie” tax back in 1986. Since then, this tax has gradually become more far-reaching. Now, under the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA), the kiddie tax has become more dangerous than ever.
A short history
Years ago, the kiddie tax applied only to children under age 14 — which still provided families with ample opportunity to enjoy significant tax savings from income shifting. In 2006, the tax was expanded to children under age 18. And since 2008, the kiddie tax has generally applied to children under age 19 and to full-time students under age 24 (unless the students provide more than half of their own support from earned income).
What about the kiddie tax rate? Before the TCJA, for children subject to the kiddie tax, any unearned income beyond a certain amount ($2,100 for 2017) was taxed at their parents’ marginal rate (assuming it was higher), rather than their own likely low rate.
A fiercer kiddie tax
The TCJA doesn’t further expand who’s subject to the kiddie tax. But it will effectively increase the kiddie tax rate in many cases.
For 2018–2025, a child’s unearned income beyond the threshold ($2,100 again for 2018) will be taxed according to the tax brackets used for trusts and estates. For ordinary income (such as interest and short-term capital gains), trusts and estates are taxed at the highest marginal rate of 37% once 2018 taxable income exceeds $12,500. In contrast, for a married couple filing jointly, the highest rate doesn’t kick in until their 2018 taxable income tops $600,000.
Similarly, the 15% long-term capital gains rate takes effect at $77,201 for joint filers but at only $2,601 for trusts and estates. And the 20% rate kicks in at $479,001 and $12,701, respectively.
In other words, in many cases, children’s unearned income will be taxed at higher rates than their parents’ income. As a result, income shifting to children subject to the kiddie tax will not only not save tax, but it could actually increase a family’s overall tax liability.
The moral of the story
To avoid inadvertently increasing your family’s taxes, be sure to consider the big, bad kiddie tax before transferring income-producing or highly appreciated assets to a child or grandchild who’s a minor or college student. If you’d like to shift income and you have adult children or grandchildren who’re no longer subject to the kiddie tax but in a lower tax bracket, consider transferring such assets to them.
Please contact us for more information about the kiddie tax — or other TCJA changes that may affect your family.
© 2018
Business deductions for meal, vehicle and travel expenses: Document, document, document

Meal, vehicle and travel expenses are common deductions for businesses. But if you don’t properly document these expenses, you could find your deductions denied by the IRS.
A critical requirement
Subject to various rules and limits, business meal (generally 50%), vehicle and travel expenses may be deductible, whether you pay for the expenses directly or reimburse employees for them. Deductibility depends on a variety of factors, but generally the expenses must be “ordinary and necessary” and directly related to the business.
Proper documentation, however, is one of the most critical requirements. And all too often, when the IRS scrutinizes these deductions, taxpayers don’t have the necessary documentation.
What you need to do
Following some simple steps can help ensure you have documentation that will pass muster with the IRS:
Keep receipts or similar documentation. You generally must have receipts, canceled checks or bills that show amounts and dates of business expenses. If you’re deducting vehicle expenses using the standard mileage rate (54.5 cents for 2018), log business miles driven.
Track business purposes. Be sure to record the business purpose of each expense. This is especially important if on the surface an expense could appear to be a personal one. If the business purpose of an expense is clear from the surrounding circumstances, the IRS might not require a written explanation — but it’s probably better to err on the side of caution and document the business purpose anyway.
Require employees to comply. If you reimburse employees for expenses, make sure they provide you with proper documentation. Also be aware that the reimbursements will be treated as taxable compensation to the employee (and subject to income tax and FICA withholding) unless you make them via an “accountable plan.”
Don’t re-create expense logs at year end or when you receive an IRS deficiency notice. Take a moment to record the details in a log or diary at the time of the event or soon after. The IRS considers timely kept records more reliable, plus it’s easier to track expenses as you go than try to re-create a log later. For expense reimbursements, require employees to submit monthly expense reports (which is also generally a requirement for an accountable plan).
Addressing uncertainty
You’ve probably heard that, under the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act, entertainment expenses are no longer deductible. There’s some debate as to whether this includes business meals with actual or prospective clients. Until there’s more certainty on that issue, it’s a good idea to document these expenses. That way you’ll have what you need to deduct them if Congress or the IRS provides clarification that these expenses are indeed still deductible.
For more information about what meal, vehicle and travel expenses are and aren’t deductible — and how to properly document deductible expenses — please contact us.
© 2018
3 traditional midyear tax planning strategies for individuals that hold up post-TCJA

With its many changes to individual tax rates, brackets and breaks, the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA) means taxpayers need to revisit their tax planning strategies. Certain strategies that were once tried-and-true will no longer save or defer tax. But there are some that will hold up for many taxpayers. And they’ll be more effective if you begin implementing them this summer, rather than waiting until year end. Take a look at these three ideas, and contact us to discuss what midyear strategies make sense for you.
1. Look at your bracket
Under the TCJA, the top income tax rate is now 37% (down from 39.6%) for taxpayers with taxable income over $500,000 (single and head-of-household filers) or $600,000 (married couples filing jointly). These thresholds are higher than for the top rate in 2017 ($418,400, $444,550 and $470,700, respectively). So the top rate might be less of a concern.
However, singles and heads of households in the middle and upper brackets could be pushed into a higher tax bracket much more quickly this year. For example, for 2017 the threshold for the 33% tax bracket was $191,650 for singles and $212,500 for heads of households. For 2018, the rate for this bracket has been reduced slightly to 32% — but the threshold for the bracket is now only $157,500 for both singles and heads of households.
So a lot more of these filers could find themselves in this bracket. (Fortunately for joint filers, their threshold for this bracket has increased from $233,350 to $315,000.)
If you expect this year’s income to be near the threshold for a higher bracket, consider strategies for reducing your taxable income and staying out of the next bracket. For example, you could take steps to accelerate deductible expenses.
2. Incur medical expenses
One itemized deduction the TCJA has retained and — temporarily — enhanced is the medical expense deduction. If you expect to benefit from itemizing on your 2018 return, take a look at whether you can accelerate deductible medical expenses into this year.
You can deduct only expenses that exceed a floor based on your adjusted gross income (AGI). Under the TCJA, the floor has dropped from 10% of AGI to 7.5%. But it’s scheduled to return to 10% for 2019 and beyond.
Deductible expenses may include:
- Health insurance premiums,
- Long-term care insurance premiums,
- Medical and dental services and prescription drugs, and
- Mileage driven for health care purposes.
You may be able to control the timing of some of these expenses so you can bunch them into 2018 and exceed the floor while it’s only 7.5%.
3. Review your investments
The TCJA didn’t make changes to the long-term capital gains rate, so the top rate remains at 20%. However, that rate now kicks in before the top ordinary-income tax rate. For 2018, the 20% rate applies to taxpayers with taxable income exceeding $425,800 (singles), $452,400 (heads of households), or $479,000 (joint filers).
If you’ve realized, or expect to realize, significant capital gains, consider selling some depreciated investments to generate losses you can use to offset those gains. It may be possible to repurchase those investments, so long as you wait at least 31 days to avoid the “wash sale” rule.
You also may need to plan for the 3.8% net investment income tax (NIIT). It can affect taxpayers with modified AGI (MAGI) over $200,000 for singles and heads of households, $250,000 for joint filers. You may be able to lower your tax liability by reducing your MAGI, reducing net investment income or both.
© 2018
Close-up on the new QBI deduction’s wage limit

The Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA) provides a valuable new tax break to noncorporate owners of pass-through entities: a deduction for a portion of qualified business income (QBI). The deduction generally applies to income from sole proprietorships, partnerships, S corporations and, typically, limited liability companies (LLCs). It can equal as much as 20% of QBI. But once taxable income exceeds $315,000 for married couples filing jointly or $157,500 for other filers, a wage limit begins to phase in.
Full vs. partial phase-in
When the wage limit is fully phased in, at $415,000 for joint filers and $207,500 for other filers, the QBI deduction generally can’t exceed the greater of the owner’s share of:
- 50% of the amount of W-2 wages paid to employees during the tax year, or
- The sum of 25% of W-2 wages plus 2.5% of the cost of qualified business property (QBP).
When the wage limit applies but isn’t yet fully phased in, the amount of the limit is reduced and the final deduction is calculated as follows:
- The difference between taxable income and the applicable threshold is divided by $100,000 for joint filers or $50,000 for other filers.
- The resulting percentage is multiplied by the difference between the gross deduction and the fully wage-limited deduction.
- The result is subtracted from the gross deduction to determine the final deduction.
Some examples
Let’s say Chris and Leslie have taxable income of $600,000. This includes $300,000 of QBI from Chris’s pass-through business, which pays $100,000 in wages and has $200,000 of QBP. The gross deduction would be $60,000 (20% of $300,000), but the wage limit applies in full because the married couple’s taxable income exceeds the $415,000 top of the phase-in range for joint filers. Computing the deduction is fairly straightforward in this situation.
The first option for the wage limit calculation is $50,000 (50% of $100,000). The second option is $30,000 (25% of $100,000 + 2.5% of $200,000). So the wage limit — and the deduction — is $50,000.
What if Chris and Leslie’s taxable income falls within the phase-in range? The calculation is a bit more complicated. Let’s say their taxable income is $400,000. The full wage limit is still $50,000, but only 85% of the full limit applies:
($400,000 taxable income - $315,000 threshold)/$100,000 = 85%
To calculate the amount of their deduction, the couple must first calculate 85% of the difference between the gross deduction of $60,000 and the fully wage-limited deduction of $50,000:
($60,000 - $50,000) × 85% = $8,500
That amount is subtracted from the $60,000 gross deduction for a final deduction of $51,500.
That's not all
Be aware that another restriction may apply: For income from “specified service businesses,” the QBI deduction is reduced if an owner’s taxable income falls within the applicable income range and eliminated if income exceeds it. Please contact us to learn whether your business is a specified service business or if you have other questions about the QBI deduction.
© 2018
What you can deduct when volunteering

Because donations to charity of cash or property generally are tax deductible (if you itemize), it only seems logical that the donation of something even more valuable to you — your time — would also be deductible. Unfortunately, that’s not the case.
Donations of time or services aren’t deductible. It doesn’t matter if it’s simple administrative work, such as checking in attendees at a fundraising event, or if it’s work requiring significant experience and expertise that would be much more costly to the charity if it had to pay for it, such as skilled carpentry or legal counsel.
However, you potentially can deduct out-of-pocket costs associated with your volunteer work.
The basic rules
As with any charitable donation, for you to be able to deduct your volunteer expenses, the first requirement is that the organization be a qualified charity. You can use the IRS’s “Tax Exempt Organization Search” tool (formerly “Select Check”) at https://www.irs.gov/charities-non-profits/tax-exempt-organization-search to find out.
Assuming the charity is qualified, you may be able to deduct out-of-pocket costs that are:
- Unreimbursed,
- Directly connected with the services you’re providing,
- Incurred only because of your charitable work, and
- Not “personal, living or family” expenses.
Supplies, uniforms and transportation
A wide variety of expenses can qualify for the deduction. For example, supplies you use in the activity may be deductible. And the cost of a uniform you must wear during the activity may also be deductible (if it’s required and not something you’d wear when not volunteering).
Transportation costs to and from the volunteer activity generally are deductible, either the actual cost or 14 cents per charitable mile driven. But you have to be the volunteer. If, say, you drive your elderly mother to the nature center where she’s volunteering, you can’t deduct the cost.
You also can’t deduct transportation costs you’d be incurring even if you weren’t volunteering. For example, if you take a commuter train downtown to work, then walk to a nearby volunteer event after work and take the train back home afterwards, you won’t be able to deduct your train fares. But if you take a cab from work to the volunteer event, then you potentially can deduct the cab fare for that leg of your transportation.
Volunteer travel
Transportation costs may also be deductible for out-of-town travel associated with volunteering. This can include air, rail and bus transportation; driving expenses; and taxi or other transportation costs between an airport or train station and wherever you’re staying. Lodging and meal costs also might be deductible.
The key to deductibility is that there is no significant element of personal pleasure, recreation or vacation in the travel. That said, according to the IRS, the deduction for travel expenses won’t be denied simply because you enjoy providing services to the charitable organization. But you must be volunteering in a genuine and substantial sense throughout the trip. If only a small portion of your trip involves volunteer work, your travel expenses generally won’t be deductible.
Keep careful records
The IRS may challenge charitable deductions for out-of-pocket costs, so it’s important to keep careful records. If you have questions about what volunteer expenses are and aren’t deductible, please contact us.
© 2018
How to avoid getting hit with payroll tax penalties

For small businesses, managing payroll can be one of the most arduous tasks. Adding to the burden earlier this year was adjusting income tax withholding based on the new tables issued by the IRS. (Those tables account for changes under the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act.) But it’s crucial not only to withhold the appropriate taxes — including both income tax and employment taxes — but also to remit them on time to the federal government.
If you don’t, you, personally, could face harsh penalties. This is true even if your business is an entity that normally shields owners from personal liability, such as a corporation or limited liability company.
The 100% penalty
Employers must withhold federal income and employment taxes (such as Social Security) as well as applicable state and local taxes on wages paid to their employees. The federal taxes must then be remitted to the federal government according to a deposit schedule.
If a business makes payments late, there are escalating penalties. And if it fails to make them, the Trust Fund Recovery Penalty could apply. Under this penalty, also known as the 100% penalty, the IRS can assess the entire unpaid amount against a “responsible person.”
The corporate veil won’t shield corporate owners in this instance. The liability protections that owners of corporations — and limited liability companies — typically have don’t apply to payroll tax debts.
When the IRS assesses the 100% penalty, it can file a lien or take levy or seizure action against personal assets of a responsible person.
“Responsible person,” defined
The penalty can be assessed against a shareholder, owner, director, officer or employee. In some cases, it can be assessed against a third party. The IRS can also go after more than one person. To be liable, an individual or party must:
- Be responsible for collecting, accounting for and remitting withheld federal taxes, and
- Willfully fail to remit those taxes. That means intentionally, deliberately, voluntarily and knowingly disregarding the requirements of the law.
Prevention is the best medicine
When it comes to the 100% penalty, prevention is the best medicine. So make sure that federal taxes are being properly withheld from employees’ paychecks and are being timely remitted to the federal government. (It’s a good idea to also check state and local requirements and potential penalties.)
If you aren’t already using a payroll service, consider hiring one. A good payroll service provider relieves you of the burden of withholding the proper amounts, taking care of the tax payments and handling recordkeeping. Contact us for more information.
© 2018
Does your business have to begin collecting sales tax on all out-of-state online sales?

You’ve probably heard about the recent U.S. Supreme Court decision allowing state and local governments to impose sales taxes on more out-of-state online sales. The ruling in South Dakota v. Wayfair, Inc. is welcome news for brick-and-mortar retailers, who felt previous rulings gave an unfair advantage to their online competitors. And state and local governments are pleased to potentially be able to collect more sales tax.
What the requirements used to beEven before Wayfair, a state could require an out-of-state business to collect sales tax from its residents on online sales if the business had a “substantial nexus” — or connection — with the state. The nexus requirement is part of the Commerce Clause of the U.S. Constitution.
Previous Supreme Court rulings had found that a physical presence in a state (such as retail outlets, employees or property) was necessary to establish substantial nexus. As a result, some online retailers have already been collecting tax from out-of-state customers, while others have not had to.
What has changedIn Wayfair, South Dakota had enacted a law requiring out-of-state retailers that made at least 200 sales or sales totaling at least $100,000 in the state to collect and remit sales tax. The Supreme Court found that the physical presence rule is “unsound and incorrect,” and that the South Dakota tax satisfies the substantial nexus requirement.
The Court said that the physical presence rule puts businesses with a physical presence at a competitive disadvantage compared with remote sellers that needn’t charge customers for taxes.
In addition, the Court found that the physical presence rule treats sellers differently for arbitrary reasons. A business with a few items of inventory in a small warehouse in a state is subject to sales tax on all of its sales in the state, while a business with a pervasive online presence but no physical presence isn’t subject to the same tax for the sales of the same items.
What the decision meansWayfair doesn’t necessarily mean that you must immediately begin collecting sales tax on online sales to all of your out-of-state customers. You’ll be required to collect such taxes only if the particular state requires it. Some states already have laws on the books similar to South Dakota’s, but many states will need to revise or enact legislation.
Also keep in mind that the substantial nexus requirement isn’t the only principle in the Commerce Clause doctrine that can invalidate a state tax. The others weren’t argued in Wayfair, but the Court observed that South Dakota’s tax system included several features that seem designed to prevent discrimination against or undue burdens on interstate commerce, such as a prohibition against retroactive application and a safe harbor for taxpayers who do only limited business in the state.
Please contact us with any questions you have about sales tax collection requirements. © 2018
Home green home: Save tax by saving energy

“Going green” at home — whether it’s your principal residence or a second home — can reduce your tax bill in addition to your energy bill, all while helping the environment, too. The catch is that, to reap all three benefits, you need to buy and install certain types of renewable energy equipment in the home. Invest in green and save green For 2018 and 2019, you may be eligible for a tax credit of 30% of expenditures (including costs for site preparation, assembly, installation, piping, and wiring) for installing the following types of renewable energy equipment: • Qualified solar electricity generating equipment and solar water heating equipment, • Qualified wind energy equipment, • Qualified geothermal heat pump equipment, and • Qualified fuel cell electricity generating equipment (limited to $500 for each half kilowatt of fuel cell capacity). Because these items can be expensive, the credits can be substantial. To qualify, the equipment must be installed at your U.S. residence, including a vacation home — except for fuel cell equipment, which must be installed at your principal residence. You can’t claim credits for equipment installed at a property that’s used exclusively as a rental. To qualify for the credit for solar water heating equipment, at least 50% of the energy used to heat water for the property must be generated by the solar equipment. And no credit is allowed for solar water heating equipment unless it’s certified for performance by the nonprofit Solar Rating & Certification Corporation or a comparable entity endorsed by the state in which your residence is located. (Keep this certification with your tax records.) The credit rate for these expenditures is scheduled to drop to 26% in 2020 and then to 22% in 2021. After that, the credits are scheduled to expire. Document and explore As with all tax breaks, documentation is key when claiming credits for green investments in your home. Keep proof of how much you spend on qualifying equipment, including any extra amounts for site preparation, assembly and installation. Also keep a record of when the installation is completed, because you can claim the credit only for the year when that occurs. Be sure to look beyond the federal tax credits and explore other ways to save by going green. Your green home investments might also be eligible for state and local tax benefits, subsidized state and local financing deals, and utility company rebates. To learn more about federal, state and local tax breaks available for green home investments, contact us. © 2018
Do you know the ABCs of HSAs, FSAs and HRAs?

There continues to be much uncertainty about the Affordable Care Act and how such uncertainty will impact health care costs. So it’s critical to leverage all tax-advantaged ways to fund these expenses, including HSAs, FSAs and HRAs. Here’s how to make sense of this alphabet soup of health care accounts.
HSAs
If you’re covered by a qualified high-deductible health plan (HDHP), you can contribute pretax income to an employer-sponsored Health Savings Account — or make deductible contributions to an HSA you set up yourself — up to $3,450 for self-only coverage and $6,900 for family coverage for 2018. Plus, if you’re age 55 or older, you may contribute an additional $1,000.
You own the account, which can bear interest or be invested, growing tax-deferred similar to an IRA. Withdrawals for qualified medical expenses are tax-free, and you can carry over a balance from year to year.
FSAs
Regardless of whether you have an HDHP, you can redirect pretax income to an employer-sponsored Flexible Spending Account up to an employer-determined limit — not to exceed $2,650 in 2018. The plan pays or reimburses you for qualified medical expenses.
What you don’t use by the plan year’s end, you generally lose — though your plan might allow you to roll over up to $500 to the next year. Or it might give you a grace period of two and a half months to incur expenses to use up the previous year’s contribution. If you have an HSA, your FSA is limited to funding certain “permitted” expenses.
HRAs
A Health Reimbursement Account is an employer-sponsored account that reimburses you for medical expenses. Unlike an HSA, no HDHP is required. Unlike an FSA, any unused portion typically can be carried forward to the next year.
There’s no government-set limit on HRA contributions. But only your employer can contribute to an HRA; employees aren’t allowed to contribute.
Maximize the benefit
If you have one of these health care accounts, it’s important to understand the applicable rules so you can get the maximum benefit from it. But tax-advantaged accounts aren’t the only way to save taxes in relation to health care. If you have questions about tax planning and health care expenses, please contact us.
© 2018
Choosing the best business entity structure post-TCJA

For tax years beginning in 2018 and beyond, the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA) created a flat 21% federal income tax rate for C corporations. Under prior law, C corporations were taxed at rates as high as 35%. The TCJA also reduced individual income tax rates, which apply to sole proprietorships and pass-through entities, including partnerships, S corporations, and, typically, limited liability companies (LLCs). The top rate, however, dropped only slightly, from 39.6% to 37%.
On the surface, that may make choosing C corporation structure seem like a no-brainer. But there are many other considerations involved.
Conventional wisdom
Under prior tax law, conventional wisdom was that most small businesses should be set up as sole proprietorships or pass-through entities to avoid the double taxation of C corporations: A C corporation pays entity-level income tax and then shareholders pay tax on dividends — and on capital gains when they sell the stock. For pass-through entities, there’s no federal income tax at the entity level.
Although C corporations are still potentially subject to double taxation under the TCJA, their new 21% tax rate helps make up for it. This issue is further complicated, however, by another provision of the TCJA that allows noncorporate owners of pass-through entities to take a deduction equal to as much as 20% of qualified business income (QBI), subject to various limits. But, unless Congress extends it, the break is available only for tax years beginning in 2018 through 2025.
There’s no one-size-fits-all answer when deciding how to structure a business. The best choice depends on your business’s unique situation and your situation as an owner.
3 common scenarios
Here are three common scenarios and the entity-choice implications:;
1. Business generates tax losses. For a business that consistently generates losses, there’s no tax advantage to operating as a C corporation. Losses from C corporations can’t be deducted by their owners. A pass-through entity will generally make more sense because losses pass through to the owners’ personal tax returns.
2. Business distributes all profits to owners. For a profitable business that pays out all income to the owners, operating as a pass-through entity generally will be better if significant QBI deductions are available. If not, it’s probably a toss-up in terms of tax liability.
3. Business retains all profits to finance growth. For a business that’s profitable but holds on to its profits to fund future growth strategies, operating as a C corporation generally will be advantageous if the corporation is a qualified small business (QSB). Why? A 100% gain exclusion may be available for QSB stock sale gains. If QSB status is unavailable, operating as a C corporation is still probably preferred — unless significant QBI deductions would be available at the owner level.
Many considerations
These are only some of the issues to consider when making the C corporation vs. pass-through entity choice. We can help you evaluate your options.
© 2018
Consider the tax advantages of investing in qualified small business stock

While the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA) reduced most ordinary-income tax rates for individuals, it didn’t change long-term capital gains rates. They remain at 0%, 15% and 20%. The 0% rate generally applies to taxpayers in the bottom two ordinary-income tax brackets (now 10% and 12%), but you no longer have to be in the top ordinary-income tax bracket (now 37%) to be subject to the top long-term capital gains rate of 20%. Many taxpayers in the 35% tax bracket also will be subject to the 20% rate.
So finding ways to defer or minimize taxes on investments is still important. One way to do that — and diversify your portfolio, too — is to invest in qualified small business (QSB) stock.
QSB defined
To be a QSB, a business must be a C corporation engaged in an active trade or business and must not have assets that exceed $50 million when you purchase the shares.
The corporation must be a QSB on the date the stock is issued and during substantially all the time you own the shares. If, however, the corporation’s assets exceed the $50 million threshold while you’re holding the shares, it won’t cause QSB status to be lost in relation to your shares.
2 tax advantages
QSBs offer investors two valuable tax advantages:
1. Up to a 100% exclusion of gain. Generally, taxpayers selling QSB stock are allowed to exclude a portion of their gain if they’ve held the stock for more than five years. The amount of the exclusion depends on the acquisition date. The exclusion is 100% for stock acquired on or after Sept. 28, 2010. So if you purchase QSB stock in 2018, you can enjoy a 100% exclusion if you hold it until sometime in 2023. (The specific date, of course, depends on the date you purchase the stock.)
2. Tax-free gain rollovers. If you don’t want to hold the QSB stock for five years, you still have the opportunity to enjoy a tax benefit: Within 60 days of selling the stock, you can buy other QSB stock with the proceeds and defer the tax on your gain until you dispose of the new stock. The rolled-over gain reduces your basis in the new stock. For determining long-term capital gains treatment, the new stock’s holding period includes the holding period of the stock you sold.
More to think about
Additional requirements and limits apply to these breaks. For example, there are many types of business that don’t qualify as QSBs, ranging from various professional fields to financial services to hospitality and more.
Before investing, it’s important to also consider nontax factors, such as your risk tolerance, time horizon and overall investment goals. Contact us to learn more about QSB stock.
© 2018
2018 Q3 tax calendar: Key deadlines for businesses and other employers
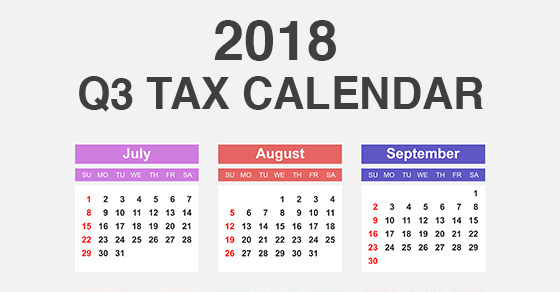
Here are some of the key tax-related deadlines affecting businesses and other employers during the second quarter of 2018. Keep in mind that this list isn’t all-inclusive, so there may be additional deadlines that apply to you. Contact us to ensure you’re meeting all applicable deadlines and to learn more about the filing requirements.
July 31
- Report income tax withholding and FICA taxes for second quarter 2018 (Form 941), and pay any tax due. (See the exception below, under “August 10.”)
- File a 2017 calendar-year retirement plan report (Form 5500 or Form 5500-EZ) or request an extension.
August 10
- Report income tax withholding and FICA taxes for second quarter 2018 (Form 941), if you deposited on time and in full all of the associated taxes due.
September 17
- If a calendar-year C corporation, pay the third installment of 2018 estimated income taxes.
- If a calendar-year S corporation or partnership that filed an automatic six-month extension:
- File a 2017 income tax return (Form 1120S, Form 1065 or Form 1065-B) and pay any tax, interest and penalties due.
- Make contributions for 2017 to certain employer-sponsored retirement plans.
© 2018
The tax impact of the TCJA on estate planning

The massive changes the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA) made to income taxes have garnered the most attention. But the new law also made major changes to gift and estate taxes. While the TCJA didn’t repeal these taxes, it did significantly reduce the number of taxpayers who’ll be subject to them, at least for the next several years. Nevertheless, factoring taxes into your estate planning is still important.
Exemption increases
The TCJA more than doubles the combined gift and estate tax exemption and the generation-skipping transfer (GST) tax exemption, from $5.49 million for 2017 to $11.18 million for 2018.
This amount will continue to be annually adjusted for inflation through 2025. Absent further congressional action, however, the exemptions will revert to their 2017 levels (adjusted for inflation) for 2026 and beyond.
The rate for all three taxes remains at 40% — only three percentage points higher than the top income tax rate.
The impact
Even before the TCJA, the vast majority of taxpayers didn’t have to worry about federal gift and estate taxes. While the TCJA protects even more taxpayers from these taxes, those with estates in the roughly $6 million to $11 million range (twice that for married couples) still need to keep potential post-2025 estate tax liability in mind in their estate planning. Although their estates would escape estate taxes if they were to die while the doubled exemption is in effect, they could face such taxes if they live beyond 2025.
Any taxpayer who could be subject to gift and estate taxes after 2025 may want to consider making gifts now to take advantage of the higher exemptions while they’re available.
Factoring taxes into your estate planning is also still important if you live in a state with an estate tax. Even before the TCJA, many states imposed estate tax at a lower threshold than the federal government did. Now the differences in some states will be even greater.
Finally, income tax planning, which became more important in estate planning back when exemptions rose to $5 million more than 15 years ago, is now an even more important part of estate planning.
For example, holding assets until death may be advantageous if estate taxes aren’t a concern. When you give away an appreciated asset, the recipient takes over your tax basis in the asset, triggering capital gains tax should he or she turn around and sell it. When an appreciated asset is inherited, on the other hand, the recipient’s basis is “stepped up” to the asset’s fair market value on the date of death, erasing the built-in capital gain. So retaining appreciating assets until death can save significant income tax.
Review your estate plan
Whether or not you need to be concerned about federal gift and estate taxes, having an estate plan in place and reviewing it regularly is important. Contact us to discuss the potential tax impact of the TCJA on your estate plan.
© 2018
2 tax law changes that may affect your business’s 401(k) plan

When you think about recent tax law changes and your business, you’re probably thinking about the new 20% pass-through deduction for qualified business income or the enhancements to depreciation-related breaks. Or you may be contemplating the reduction or elimination of certain business expense deductions. But there are also a couple of recent tax law changes that you need to be aware of if your business sponsors a 401(k) plan.
1. Plan loan repayment extensionThe Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA) gives a break to 401(k) plan participants with outstanding loan balances when they leave their employers. While plan sponsors aren’t required to allow loans, many do.
Before 2018, if an employee with an outstanding plan loan left the company sponsoring the plan, he or she would have to repay the loan (or contribute the outstanding balance to an IRA or his or her new employer’s plan) within 60 days to avoid having the loan balance deemed a taxable distribution (and be subject to a 10% early distribution penalty if the employee was under age 59½).
Under the TCJA, beginning in 2018, former employees in this situation have until their tax return filing due date — including extensions — to repay the loan (or contribute the outstanding balance to an IRA or qualified retirement plan) and avoid taxes and penalties.
2. Hardship swithdrawl limit increaseBeginning in 2019, the Bipartisan Budget Act (BBA) eases restrictions on employee 401(k) hardship withdrawals. Most 401(k) plans permit hardship withdrawals, though plan sponsors aren’t required to allow them. Hardship withdrawals are subject to income tax and the 10% early distribution tax penalty.
Currently, hardship withdrawals are limited to the funds employees contributed to the accounts. (Such withdrawals are allowed only if the employee has first taken a loan from the same account.)
Under the BBA, the withdrawal limit will also include accumulated employer matching contributions plus earnings on contributions. If an employee has been participating in your 401(k) for several years, this modification could add substantially to the amount of funds available for withdrawal.
Nest egg harmThese changes might sound beneficial to employees, but in the long run they could actually hurt those who take advantage of them. Most Americans aren’t saving enough for retirement, and taking longer to pay back a plan loan (and thus missing out on potential tax-deferred growth during that time) or taking larger hardship withdrawals can result in a smaller, perhaps much smaller, nest egg at retirement.
So consider educating your employees on the importance of letting their 401(k) accounts grow undisturbed and the potential negative tax consequences of loans and early withdrawals. Please contact us if you have questions.
© 2018
Factor in stat and local taxes when deciding where to live in retirement

Many Americans relocate to another state when they retire. If you’re thinking about such a move, state and local taxes should factor into your decision.
Income, property and sales taxChoosing a state that has no personal income tax may appear to be the best option. But that might not be the case once you consider property taxes and sales taxes.
For example, suppose you’ve narrowed your decision down to two states: State 1 has no individual income tax, and State 2 has a flat 5% individual income tax rate. At first glance, State 1 might appear to be much less expensive from a tax perspective. What happens when you factor in other state and local taxes?
Let’s say the property tax rate in your preferred locality in State 1 is 5%, while it’s only 1% in your preferred locality in State 2. That difference could potentially cancel out any savings in state income taxes in State 1, depending on your annual income and the assessed value of the home.
Also keep in mind that home values can vary dramatically from location to location. So if home values are higher in State 1, there’s an even greater chance that State 1’s overall tax cost could be higher than State 2’s, despite State 1’s lack of income tax.
The potential impact of sales tax can be harder to estimate, but it’s a good idea at minimum to look at the applicable rates in the various retirement locations you’re considering.
More to think aboutIf states you’re considering have an income tax, also look at what types of income they tax. Some states, for example, don’t tax wages but do tax interest and dividends. Others offer tax breaks for retirement plan and Social Security income.
In the past, the federal income tax deduction for state and local property and income or sales tax could help make up some of the difference between higher- and lower-tax states. But with the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA) limiting that deduction to $10,000 ($5,000 for married couples filing separately), this will be less help — at least through 2025, after which the limit is scheduled to expire.
There’s also estate tax to consider. Not all states have estate tax, but it can be expensive in states that do. While under the TJCA the federal estate tax exemption has more than doubled from the 2017 level to $11.18 million for 2018, states aren’t necessarily keeping pace with the federal exemption. So state estate tax could be levied after a much lower exemption.
Choose WiselyAs you can see, it’s important to factor in state and local taxes as you decide where to live in retirement. You might ultimately decide on a state with higher taxes if other factors are more important to you. But at least you will have made an informed decision and avoid unpleasant tax surprises. Contact us to learn more.
© 2018
Saving tax on restricted stock awards with the Sec. 83(b) election

Saving tax on restricted stock awards with the Sec. 83(b) election Today many employees receive stock-based compensation from their employer as part of their compensation and benefits package. The tax consequences of such compensation can be complex — subject to ordinary-income, capital gains, employment and other taxes. But if you receive restricted stock awards, you might have a tax-saving opportunity in the form of the Section 83(b) election. Convert ordinary income to long-term capital gains Restricted stock is stock your employer grants you subject to a substantial risk of forfeiture. Income recognition is normally deferred until the stock is no longer subject to that risk (that is, it’s vested) or you sell it. At that time, you pay taxes on the stock’s fair market value (FMV) at your ordinary-income rate. The FMV will be considered FICA income, so it also could trigger or increase your exposure to the additional 0.9% Medicare tax. But you can instead make a Sec. 83(b) election to recognize ordinary income when you receive the stock. This election, which you must make within 30 days after receiving the stock, allows you to convert future appreciation from ordinary income to long-term capital gains income and defer it until the stock is sold. The Sec. 83(b) election can be beneficial if the income at the grant date is negligible or the stock is likely to appreciate significantly. With ordinary-income rates now especially low under the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA), it might be a good time to recognize such income. Weigh the potential disadvantages There are some potential disadvantages, however: • You must prepay tax in the current year — which also could push you into a higher income tax bracket or trigger or increase the additional 0.9% Medicare tax. But if your company is in the earlier stages of development, the income recognized may be relatively small. • Any taxes you pay because of the election can’t be refunded if you eventually forfeit the stock or sell it at a decreased value. However, you’d have a capital loss in those situations. • When you sell the shares, any gain will be included in net investment income and could trigger or increase your liability for the 3.8% net investment income tax. It’s complicated As you can see, tax planning for restricted stock is complicated. Let us know if you’ve recently been awarded restricted stock or expect to be awarded such stock this year. We can help you determine whether the Sec. 83(b) election makes sense in your specific situation. © 2018
Putting your child on your business's payroll for the summer may make more tax sense than ever

If you own a business and have a child in high school or college, hiring him or her for the summer can provide a multitude of benefits, including tax savings. And hiring your child may make more sense than ever due to changes under the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA).
How it works
By shifting some of your business earnings to a child as wages for services performed, you can turn some of your high-taxed income into tax-free or low-taxed income. For your business to deduct the wages as a business expense, the work done must be legitimate and the child’s wages must be reasonable.
Here’s an example: A sole proprietor is in the 37% tax bracket. He hires his 20-year-old daughter, who’s majoring in marketing, to work as a marketing coordinator full-time during the summer. She earns $12,000 and doesn’t have any other earnings.
The father saves $4,440 (37% of $12,000) in income taxes at no tax cost to his daughter, who can use her $12,000 standard deduction (for 2018) to completely shelter her earnings. This is nearly twice as much as would have been sheltered last year, pre-TCJA, when the standard deduction was only $6,350.
The father can save an additional $2,035 in taxes if he keeps his daughter on the payroll as a part-time employee into the fall and pays her an additional $5,500. She can shelter the additional income from tax by making a tax-deductible contribution to her own traditional IRA.
Family taxes will be cut even if an employee-child’s earnings exceed his or her standard deduction and IRA deduction. Why? The unsheltered earnings will be taxed to the child beginning at a rate of 10% instead of being taxed at the parent’s higher rate.
Avoiding the "kiddie tax"
TCJA changes to the “kiddie tax” also make income-shifting through hiring your child (rather than, say, giving him or her income-producing investments) more appealing. The kiddie tax generally applies to children under age 19 and to full-time students under age 24. Before 2018, the unearned income of a child subject to the kiddie tax was generally taxed at the parents’ tax rate.
The TCJA makes the kiddie tax harsher. For 2018-2025, a child’s unearned income will be taxed according to the tax brackets used for trusts and estates, which for 2018 are taxed at the highest rate of 37% once taxable income reaches $12,500. In contrast, for a married couple filing jointly, the 37% rate doesn’t kick in until their taxable income tops $600,000. In other words, children’s unearned income often will be taxed at higher rates than their parents’ income.
But the kiddie tax doesn’t apply to earned income.
Other tax considerations
If your business isn’t incorporated or a partnership that includes nonparent partners, you might also save some employment tax dollars. Contact us to learn more about the tax rules surrounding hiring your child, how the kiddie tax works or other family-related tax-saving strategies.
The TCJA changes some rules for deducting pass-through business losses

It’s not uncommon for businesses to sometimes generate tax losses. But the losses that can be deducted are limited by tax law in some situations. The Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA) further restricts the amount of losses that sole proprietors, partners, S corporation shareholders and, typically, limited liability company (LLC) members can currently deduct — beginning in 2018. This could negatively impact owners of start-ups and businesses facing adverse conditions. Before the TCJA Under pre-TCJA law, an individual taxpayer’s business losses could usually be fully deducted in the tax year when they arose unless: • The passive activity loss (PAL) rules or some other provision of tax law limited that favorable outcome, or • The business loss was so large that it exceeded taxable income from other sources, creating a net operating loss (NOL). After the TCJA The TCJA temporarily changes the rules for deducting an individual taxpayer’s business losses. If your pass-through business generates a tax loss for a tax year beginning in 2018 through 2025, you can’t deduct an “excess business loss” in the current year. An excess business loss is the excess of your aggregate business deductions for the tax year over the sum of: • Your aggregate business income and gains for the tax year, and • $250,000 ($500,000 if you’re a married taxpayer filing jointly). The excess business loss is carried over to the following tax year and can be deducted under the rules for NOLs. For business losses passed through to individuals from S corporations, partnerships and LLCs treated as partnerships for tax purposes, the new excess business loss limitation rules apply at the owner level. In other words, each owner’s allocable share of business income, gain, deduction or loss is passed through to the owner and reported on the owner’s personal federal income tax return for the owner’s tax year that includes the end of the entity’s tax year. Keep in mind that the new loss limitation rules apply after applying the PAL rules. So, if the PAL rules disallow your business or rental activity loss, you don’t get to the new loss limitation rules. Expecting a business loss? The rationale underlying the new loss limitation rules is to restrict the ability of individual taxpayers to use current-year business losses to offset income from other sources, such as salary, self-employment income, interest, dividends and capital gains. The practical impact is that your allowable current-year business losses can’t offset more than $250,000 of income from such other sources (or more than $500,000 for joint filers). The requirement that excess business losses be carried forward as an NOL forces you to wait at least one year to get any tax benefit from those excess losses. If you’re expecting your business to generate a tax loss in 2018, contact us to determine whether you’ll be affected by the new loss limitation rules. We can also provide more information about the PAL and NOL rules. © 2018
Be aware of the tax consequences before selling your home

In many parts of the country, summer is peak season for selling a home. If you’re planning to put your home on the market soon, you’re probably thinking about things like how quickly it will sell and how much you’ll get for it. But don’t neglect to consider the tax consequences.
Home sale gain exclusion
The U.S. House of Representatives’ original version of the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act included a provision tightening the rules for the home sale gain exclusion. Fortunately, that provision didn’t make it into the final version that was signed into law.
As a result, if you’re selling your principal residence, there’s still a good chance you’ll be able to exclude up to $250,000 ($500,000 for joint filers) of gain. Gain that qualifies for exclusion also is excluded from the 3.8% net investment income tax.
To qualify for the exclusion, you must meet certain tests. For example, you generally must own and use the home as your principal residence for at least two years during the five-year period preceding the sale. (Gain allocable to a period of “nonqualified” use generally isn’t excludable.) In addition, you can’t use the exclusion more than once every two years.
More tax considerations
Any gain that doesn’t qualify for the exclusion generally will be taxed at your long-term capital gains rate, as long as you owned the home for at least a year. If you didn’t, the gain will be considered short-term and subject to your ordinary-income rate, which could be more than double your long-term rate.
Here are some additional tax considerations when selling a home:
Tax basis. To support an accurate tax basis, be sure to maintain thorough records, including information on your original cost and subsequent improvements, reduced by any casualty losses and depreciation claimed based on business use.
Losses. A loss on the sale of your principal residence generally isn’t deductible. But if part of your home is rented out or used exclusively for your business, the loss attributable to that portion may be deductible.
Second homes. If you’re selling a second home, be aware that it won’t be eligible for the gain exclusion. But if it qualifies as a rental property, it can be considered a business asset, and you may be able to defer tax on any gains through an installment sale or a Section 1031 exchange. Or you may be able to deduct a loss.
A big investment
Your home is likely one of your biggest investments, so it’s important to consider the tax consequences before selling it. If you’re planning to put your home on the market, we can help you assess the potential tax impact. Contact us to learn more.
Can you deduct business travel when it's combined with a vacation?

At this time of year, a summer vacation is on many people’s minds. If you travel for business, combining a business trip with a vacation to offset some of the cost with a tax deduction can sound appealing. But tread carefully, or you might not be eligible for the deduction you’re expecting.
General rules
Business travel expenses are potentially deductible if the travel is within the United States and the expenses are “ordinary and necessary” and directly related to the business. (Foreign travel expenses may also be deductible, but stricter rules apply than are discussed here.) Currently, business owners and the self-employed are potentially eligible to deduct business travel expenses. Under the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act, employees can no longer deduct such expenses. The potential deductions discussed below assume that you’re a business owner or self-employed.
Business vs. pleasure
Transportation costs to and from the location of your business activity may be 100% deductible if the primary reason for the trip is business rather than pleasure. But if vacation is the primary reason for your travel, generally none of those costs are deductible. The number of days spent on business vs. pleasure is the key factor in determining whether the primary reason for domestic travel is business:
- Your travel days count as business days, as do weekends and holidays — if they fall between days devoted to business and it would be impractical to return home.
- Standby days (days when your physical presence is required) also count as business days, even if you aren’t called upon to work those days.
- Any other day principally devoted to business activities during normal business hours also counts as a business day.
You should be able to claim business was the primary reason for a domestic trip if business days exceed personal days.
Deductible expenses
What transportation costs can you deduct? Travel to and from your departure airport, airfare, baggage fees, tips, cabs, etc. Costs for rail travel or driving your personal car are also eligible. Once at the destination, your out-of-pocket expenses for business days are fully deductible. Examples of these expenses include lodging, meals (subject to the 50% disallowance rule), seminar and convention fees, and cab fare. Expenses for personal days aren’t deductible. Keep in mind that only expenses for yourself are deductible. You can’t deduct expenses for family members traveling with you — unless they’re employees of your business and traveling for a bona fide business purpose.
Substantiation is critical
Be sure to accumulate proof of the business nature of your trip and keep it with your tax records. For example, if your trip is made to attend client meetings, log everything on your daily planner and copy the pages for your tax file. If you attend a convention or seminar, keep the program and take notes to show you attended the sessions. You also must properly substantiate all of the expenses you’re deducting. Additional rules and limits apply to the travel expense deduction. Please contact us if you have questions.
Do you need to adjust your withholding?

If you received a large refund after filing your 2017 income tax return, you’re probably enjoying the influx of cash. But a large refund isn’t all positive. It also means you were essentially giving the government an interest-free loan.
That’s why a large refund for the previous tax year would usually indicate that you should consider reducing the amounts you’re having withheld (and/or what estimated tax payments you’re making) for the current year. But 2018 is a little different.
The TCJA and withholding
To reflect changes under the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA) — such as the increase in the standard deduction, suspension of personal exemptions and changes in tax rates and brackets — the IRS updated the withholding tables that indicate how much employers should hold back from their employees’ paychecks, generally reducing the amount withheld.
The new tables may provide the correct amount of tax withholding for individuals with simple tax situations, but they might cause other taxpayers to not have enough withheld to pay their ultimate tax liabilities under the TCJA. So even if you received a large refund this year, you could end up owing a significant amount of tax when you file your 2018 return next year.
Perils of the new tables
The IRS itself cautions that people with more complex tax situations face the possibility of having their income taxes underwithheld. If, for example, you itemize deductions, have dependents age 17 or older, are in a two-income household or have more than one job, you should review your tax situation and adjust your withholding if appropriate.
The IRS has updated its withholding calculator (available at irs.gov) to assist taxpayers in reviewing their situations. The calculator reflects changes in available itemized deductions, the increased child tax credit, the new dependent credit and repeal of dependent exemptions.
More considerations
Tax law changes aren’t the only reason to check your withholding. Additional reviews during the year are a good idea if:
- You get married or divorced,
- You add or lose a dependent,
- You purchase a home,
- You start or lose a job, or
- Your investment income changes significantly.
You can modify your withholding at any time during the year, or even multiple times within a year. To do so, you simply submit a new Form W-4 to your employer. Changes typically will go into effect several weeks after the new Form W-4 is submitted. (For estimated tax payments, you can make adjustments each time quarterly payments are due.)
The TCJA and your tax situation
If you rely solely on the new withholding tables, you could run the risk of significantly underwithholding your federal income taxes. As a result, you might face an unexpectedly high tax bill when you file your 2018 tax return next year. Contact us for help determining whether you should adjust your withholding. We can also answer any questions you have about how the TCJA may affect your particular situation
IRS Audit Techniques Guides provide clues to what may come up if your business is audited

IRS examiners use Audit Techniques Guides (ATGs) to prepare for audits — and so can small business owners. Many ATGs target specific industries, such as construction. Others address issues that frequently arise in audits, such as executive compensation and fringe benefits. These publications can provide valuable insights into issues that might surface if your business is audited.
What do ATGs cover?
The IRS compiles information obtained from past examinations of taxpayers and publishes its findings in ATGs. Typically, these publications explain:
* The nature of the industry or issue,
* Accounting methods commonly used in an industry,
* Relevant audit examination techniques,
* Common and industry-specific compliance issues,
* Business practices,
* Industry terminology, and
* Sample interview questions.
By using a specific ATG, an examiner may, for example, be able to reconcile discrepancies when reported income or expenses aren’t consistent with what’s normal for the industry or to identify anomalies within the geographic area in which the taxpayer resides.
What do ATGs advise?
ATGs cover the types of documentation IRS examiners should request from taxpayers and what relevant information might be uncovered during a tour of the business premises. These guides are intended in part to help examiners identify potential sources of income that could otherwise slip through the cracks.
Other issues that ATGs might instruct examiners to inquire about include:
* Internal controls (or lack of controls),
* The sources of funds used to start the business,
* A list of suppliers and vendors,
* The availability of business records,
* Names of individual(s) responsible for maintaining business records,
* Nature of business operations (for example, hours and days open),
* Names and responsibilities of employees,
* Names of individual(s) with control over inventory, and
* Personal expenses paid with business funds.
For example, one ATG focuses specifically on cash-intensive businesses, such as auto repair shops, check-cashing operations, gas stations, liquor stores, restaurants and bars, and salons. It highlights the importance of reviewing cash receipts and cash register tapes for these types of businesses.
Cash-intensive businesses may be tempted to underreport their cash receipts, but franchised operations may have internal controls in place to deter such “skimming.” For instance, a franchisee may be required to purchase products or goods from the franchisor, which provides a paper trail that can be used to verify sales records.
Likewise, for gas stations, examiners must check the methods of determining income, rebates and other incentives. Restaurants and bars should be asked about net profits compared to the industry average, spillage, pouring averages and tipping.
Avoiding red flags
Although ATGs were created to enhance IRS examiner proficiency, they also can help small businesses ensure they aren’t engaging in practices that could raise red flags with the IRS. To access the complete list of ATGs, visit the IRS website https://www.irs.gov/businesses/small-businesses-self-employed/audit-techniques-guides-atgs. And for more information on the IRS red flags that may be relevant to your business, contact us.
Get started on 2018 tax planning now!

With the April 17 individual income tax filing deadline behind you (or with your 2017 tax return on the back burner if you filed for an extension), you may be hoping to not think about taxes for the next several months. But for maximum tax savings, now is the time to start tax planning for 2018. It’s especially critical to get an early start this year because the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA) has substantially changed the tax environment.
Many variables
A tremendous number of variables affect your overall tax liability for the year. Looking at these variables early in the year can give you more opportunities to reduce your 2018 tax bill.
For example, the timing of income and deductible expenses can affect both the rate you pay and when you pay. By regularly reviewing your year-to-date income, expenses and potential tax, you may be able to time income and expenses in a way that reduces, or at least defers, your tax liability.
In other words, tax planning shouldn’t be just a year-end activity.
Certainty vs. uncertainty
Last year, planning early was a challenge because it was uncertain whether tax reform legislation would be signed into law, when it would go into effect and what it would include. This year, the TCJA tax reform legislation is in place, with most of the provisions affecting individuals in effect for 2018–2025. And additional major tax law changes aren’t expected in 2018. So there’s no need to hold off on tax planning.
But while there’s more certainty about the tax law that will be in effect this year and next, there’s still much uncertainty on exactly what the impact of the TCJA changes will be on each taxpayer. The new law generally reduces individual tax rates, and it expands some tax breaks. However, it reduces or eliminates many other breaks.
The total impact of these changes is what will ultimately determine which tax strategies will make sense for you this year, such as the best way to time income and expenses. You may need to deviate from strategies that worked for you in previous years and implement some new strategies.
Getting started sooner will help ensure you don’t take actions that you think will save taxes but that actually will be costly under the new tax regime. It will also allow you to take full advantage of new tax-saving opportunities.
Now and throughout the year
To get started on your 2018 tax planning, contact us. We can help you determine how the TCJA affects you and what strategies you should implement now and throughout the year to minimize your tax liability.
A review of significant TCJA provisions affecting small businesses

Now that small businesses and their owners have filed their 2017 income tax returns (or filed for an extension), it’s a good time to review some of the provisions of the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA) that may significantly impact their taxes for 2018 and beyond. Generally, the changes apply to tax years beginning after December 31, 2017, and are permanent, unless otherwise noted.
Corporate taxation
* Replacement of graduated corporate rates ranging from 15% to 35% with a flat corporate rate of 21%
* Replacement of the flat personal service corporation (PSC) rate of 35% with a flat rate of 21%
* Repeal of the 20% corporate alternative minimum tax (AMT)
Pass-through taxation
* Drops of individual income tax rates ranging from 0 to 4 percentage points (depending on the bracket) to 10%, 12%, 22%, 24%, 32%, 35% and 37% — through 2025
* New 20% qualified business income deduction for owners — through 2025
* Changes to many other tax breaks for individuals — generally through 2025
New or expanded tax breaks
* Doubling of bonus depreciation to 100% and expansion of qualified assets to include used assets — effective for assets acquired and placed in service after September 27, 2017, and before January 1, 2023
* Doubling of the Section 179 expensing limit to $1 million and an increase of the expensing phaseout threshold to $2.5 million (these amounts will be indexed for inflation after 2018)
* New tax credit for employer-paid family and medical leave — through 2019
Reduced or eliminated tax breaks
* New disallowance of deductions for net interest expense in excess of 30% of the business’s adjusted taxable income (exceptions apply)
* New limits on net operating loss (NOL) deductions
* Elimination of the Section 199 deduction, also commonly referred to as the domestic production activities deduction or manufacturers’ deduction — effective for tax years beginning after December 31, 2017, for noncorporate taxpayers and for tax years beginning after December 31, 2018, for C corporation taxpayers
* New rule limiting like-kind exchanges to real property that is not held primarily for sale (generally no more like-kind exchanges for personal property)
* New limitations on excessive employee compensation
* New limitations on deductions for certain employee fringe
benefits, such as entertainment and, in certain circumstances, meals and transportation
Don’t wait to start 2018 tax planning
This is only a sampling of some of the most significant TCJA changes that will affect small businesses and their owners beginning this year, and additional rules and limits apply. The combined impact of these changes should inform which tax strategies you and your business implement in 2018, such as how to time income and expenses to your tax advantage. The sooner you begin the tax planning process, the more tax-saving opportunities will be open to you. So don’t wait to start; contact us today.
Tax record retention guidelines for individuals

What 2017 tax records can you toss once you’ve filed your 2017 return? The answer is simple: none. You need to hold on to all of your 2017 tax records for now. But it’s the perfect time to go through old tax records and see what you can discard.
The 3-year and 6-year rules
At minimum, keep tax records for as long as the IRS has the ability to audit your return or assess additional taxes, which generally is three years after you file your return. This means you potentially can get rid of most records related to tax returns for 2014 and earlier years. (If you filed an extension for your 2014 return, hold on to your records at least until the three-year anniversary of when you filed your extended return.)
However, the statute of limitations extends to six years for taxpayers who understate their adjusted gross income by more than 25%. What constitutes an understatement may go beyond simply not reporting items of income. So a common rule of thumb is to save tax records for six years from filing, just to be safe.
What to keep longer
You’ll need to hang on to certain tax-related records beyond the statute of limitations:
* Keep tax returns themselves forever, so you can prove to the IRS that you actually filed a legitimate return. (There’s no statute of limitations for an audit if you didn’t file a return or you filed a fraudulent one.)
* Hold on to W-2 forms until you begin receiving Social Security benefits. Questions might arise regarding your work record or earnings for a particular year, and your W-2 could provide the documentation needed.
* Retain records related to real estate or investments as long as you own the asset, plus at least three years after you sell it and report the sale on your tax return (or six years if you want to be extra safe).
* Keep records associated with retirement accounts until you’ve depleted the account and reported the last withdrawal on your tax return, plus three (or six) years.
Other documents
We’ve covered retention guidelines for some of the most common tax-related records. If you have questions about other documents, please contact us.
Tax document retention guidelines for small businesses

You may have breathed a sigh of relief after filing your 2017 income tax return (or requesting an extension). But if your office is strewn with reams of paper consisting of years’ worth of tax returns, receipts, canceled checks and other financial records (or your computer desktop is filled with a multitude of digital tax-related files), you probably want to get rid of what you can. Follow these retention guidelines as you clean up.
General rules
Retain records that support items shown on your tax return at least until the statute of limitations runs out — generally three years from the due date of the return or the date you filed, whichever is later. That means you can now potentially throw out records for the 2014 tax year if you filed the return for that year by the regular filing deadline. But some records should be kept longer.
For example, there’s no statute of limitations if you fail to file a tax return or file a fraudulent one. So you’ll generally want to keep copies of your returns themselves permanently, so you can show that you did file a legitimate return.
Also bear in mind that, if you understate your adjusted gross income by more than 25%, the statute of limitations period is six years.
Some specifics for businesses
Records substantiating costs and deductions associated with business property are necessary to determine the basis and any gain or loss when the property is sold. According to IRS guidelines, you should keep these for as long as you own the property, plus seven years.
The IRS recommends keeping employee records for three years after an employee has been terminated. In addition, you should maintain records that support employee earnings for at least four years. (This timeframe generally will cover varying state and federal requirements.) Also keep employment tax records for four years from the date the tax was due or the date it was paid, whichever is longer.
For travel and transportation expenses supported by mileage logs and other receipts, keep supporting documents for the three-year statute of limitations period.
Regulations for sales tax returns vary by state. Check the rules for the states where you file sales tax returns. Retention periods typically range from three to six years.
When in doubt, don’t throw it out
It’s easy to accumulate a mountain of paperwork (physical or digital) from years of filing tax returns. If you’re unsure whether you should retain a document, a good rule of thumb is to hold on to it for at least six years or, for property-related records, at least seven years after you dispose of the property. But, again, you should keep tax returns themselves permanently, and other rules or guidelines might apply in certain situations. Please contact us with any questions.
Individual tax calendar: Important deadlines for the remainder of 2018

While April 15 (April 17 this year) is the main tax deadline on most individual taxpayers’ minds, there are others through the rest of the year that you also need to be aware of. To help you make sure you don’t miss any important 2018 deadlines, here’s a look at when some key tax-related forms, payments and other actions are due. Keep in mind that this list isn’t all-inclusive, so there may be additional deadlines that apply to you.
Please review the calendar and let us know if you have any questions about the deadlines or would like assistance in meeting them.
June 15
- File a 2017 individual income tax return (Form 1040) or file for a four-month extension (Form 4868), and pay any tax and interest due, if you live outside the United States.
- Pay the second installment of 2018 estimated taxes, if not paying income tax through withholding (Form 1040-ES).
September 17
- Pay the third installment of 2018 estimated taxes, if not paying income tax through withholding (Form 1040-ES).
October 1
- If you’re the trustee of a trust or the executor of an estate, file an income tax return for the 2017 calendar year (Form 1041) and pay any tax, interest and penalties due, if an automatic five-and-a-half month extension was filed.
October 15
- File a 2017 income tax return (Form 1040, Form 1040A or Form 1040EZ) and pay any tax, interest and penalties due, if an automatic six-month extension was filed (or if an automatic four-month extension was filed by a taxpayer living outside the United States).
- Make contributions for 2017 to certain retirement plans or establish a SEP for 2017, if an automatic six-month extension was filed.
- File a 2017 gift tax return (Form 709) and pay any tax, interest and penalties due, if an automatic six-month extension was filed.
December 31
- Make 2018 contributions to certain employer-sponsored retirement plans.
- Make 2018 annual exclusion gifts (up to $15,000 per recipient).
- Incur various expenses that potentially can be claimed as itemized deductions on your 2018 tax return. Examples include charitable donations, medical expenses and property tax payments.
But remember that some types of expenses that were deductible on 2017 returns won’t be deductible on 2018 returns under the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act, such as unreimbursed work-related expenses, certain professional fees, and investment expenses. In addition, some deductions will be subject to new limits. Finally, with the nearly doubled standard deduction, you may no longer benefit from itemizing deductions.
TCJA changes to employee benefits tax breaks: 4 negatives and a positive

The Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA) includes many changes that affect tax breaks for employee benefits. Among the changes are four negatives and one positive that will impact not only employees but also the businesses providing the benefits.
4 breaks curtailed
Beginning with the 2018 tax year, the TCJA reduces or eliminates tax breaks in the following areas:
1. Transportation benefits. The TCJA eliminates business deductions for the cost of providing qualified employee transportation fringe benefits, such as parking allowances, mass transit passes and van pooling. (These benefits are still tax-free to recipient employees.) It also disallows business deductions for the cost of providing commuting transportation to an employee (such as hiring a car service), unless the transportation is necessary for the employee’s safety. And it suspends through 2025 the tax-free benefit of up to $20 a month for bicycle commuting.
2. On-premises meals. The TCJA reduces to 50% a business’s deduction for providing certain meals to employees on the business premises, such as when employees work late or if served in a company cafeteria. (The deduction is scheduled for elimination in 2025.) For employees, the value of these benefits continues to be tax-free.
3. Moving expense reimbursements. The TCJA suspends through 2025 the exclusion from employees’ taxable income of a business’s reimbursements of employees’ qualified moving expenses. However, businesses generally will still be able to deduct such reimbursements.
4. Achievement awards. The TCJA eliminates the business tax deduction and corresponding employee tax exclusion for employee achievement awards that are provided in the form of cash, gift coupons or certificates, vacations, meals, lodging, tickets to sporting or theater events, securities and “other similar items.” However, the tax breaks are still available for gift certificates that allow the recipient to select tangible property from a limited range of items preselected by the employer. The deduction/exclusion limits remain at up to $400 of the value of achievement awards for length of service or safety and $1,600 for awards under a written nondiscriminatory achievement plan.
1 new break
For 2018 and 2019, the TCJA creates a tax credit for wages paid to qualifying employees on family and medical leave. To qualify, a business must offer at least two weeks of annual paid family and medical leave, as described by the Family and Medical Leave Act (FMLA), to qualified employees. The paid leave must provide at least 50% of the employee’s wages. Leave required by state or local law or that was already part of the business’s employee benefits program generally doesn’t qualify.
The credit equals a minimum of 12.5% of the amount of wages paid during a leave period. The credit is increased gradually for payments above 50% of wages paid and tops out at 25%. No double-dipping: Employers can’t also deduct wages claimed for the credit.
More rules, limits and changes
Keep in mind that additional rules and limits apply to these breaks, and that the TCJA makes additional changes affecting employee benefits. Contact us for more details.
Haven’t filed your 2017 income tax return yet? Beware of these pitfalls

The federal income tax filing deadline is slightly later than usual this year — April 17 — but it’s now nearly upon us. So, if you haven’t filed your individual return yet, you may be thinking about an extension. Or you may just be concerned about meeting the deadline in the eyes of the IRS. Whatever you do, don’t get tripped up by one of these potential pitfalls.
Filing for an extension
Filing for an extension allows you to delay filing your return until the applicable extension deadline, which for 2017 individual tax returns is October 15, 2018.
While filing for an extension can provide relief from April 17 deadline stress and avoid failure-to-file penalties, there are some possible pitfalls:
- For married taxpayers filing jointly, the phaseout range is specific to each spouse based on whether he or she is a participant in an employer-sponsored plan:
- If you expect to owe tax, to avoid potential interest and penalties you still must (with a few exceptions) pay any tax due by April 17.
- If you expect a refund, remember that you’re simply extending the amount of time your money is in the government’s pockets rather than your own. (If you’re owed a refund and file late, you won’t be charged a failure-to-file penalty. However, filing for an extension may still be a good idea.)
Meeting the April 17 deadline
The IRS considers a paper return that’s due April 17 to be timely filed if it’s postmarked by midnight. Sounds straightforward, but here’s a potential pitfall: Let’s say you mail your return with a payment on April 17, but the envelope gets lost. You don’t figure this out until a couple of months later when you notice that the check still hasn’t cleared. You then refile and send a new check. Despite your efforts to timely file and pay, you can still be hit with both failure-to-file and failure-to-pay penalties.
To avoid this risk, use certified or registered mail or one of the private delivery services designated by the IRS to comply with the timely filing rule, such as:
- DHL Express 9:00, Express 10:30, Express 12:00 or Express Envelope,
- FedEx First Overnight, Priority Overnight, Standard Overnight or 2Day, or
- UPS Next Day Air Early A.M., Next Day Air, Next Day Air Saver, 2nd Day Air A.M. or 2nd Day Air.
Beware: If you use an unauthorized delivery service, your return isn’t “filed” until the IRS receives it. See IRS.gov for a complete list of authorized services.
Avoiding interest and penalties
Despite the potential pitfalls, filing for an extension can be tax-smart if you’re missing critical documents or you face unexpected life events that prevent you from devoting sufficient time to your return right now. We can help you estimate whether you owe tax and how much you should pay by April 17. Please contact us if you need help or have questions about avoiding interest and penalties.
A net operating loss on your 2017 tax return isn’t all bad news

Tax-advantaged retirement plans like IRAs allow your money to grow tax-deferred — or, in the case of Roth accounts, tax-free. The deadline for 2017 contributions is April 17, 2018. Deductible contributions will lower your 2017 tax bill, but even nondeductible contributions can be beneficial.
When a company’s deductible expenses exceed its income, generally a net operating loss (NOL) occurs. If when filing your 2017 income tax return you found that your business had an NOL, there is an upside: tax benefits. But beware — the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA) makes some significant changes to the tax treatment of NOLs.
Pre-TCJA law
Under pre-TCJA law, when a business incurs an NOL, the loss can be carried back up to two years, and then any remaining amount can be carried forward up to 20 years. The carryback can generate an immediate tax refund, boosting cash flow.
The business can, however, elect instead to carry the entire loss forward. If cash flow is strong, this may be more beneficial, such as if the business’s income increases substantially, pushing it into a higher tax bracket — or if tax rates increase. In both scenarios, the carryforward can save more taxes than the carryback because deductions are more powerful when higher tax rates apply.
But the TCJA has established a flat 21% tax rate for C corporation taxpayers beginning with the 2018 tax year, and the rate has no expiration date. So C corporations don’t have to worry about being pushed into a higher tax bracket unless Congress changes the corporate rates again.
Also keep in mind that the rules are more complex for pass-through entities, such as partnerships, S corporations and limited liability companies (if they elected partnership tax treatment). Each owner’s allocable share of the entity’s loss is passed through to the owners and reported on their personal returns. The tax benefit depends on each owner’s particular tax situation.
The TCJA changes
The changes the TCJA made to the tax treatment of NOLs generally aren’t favorable to taxpayers:
- For NOLs arising in tax years ending after December 31, 2017, a qualifying NOL can’t be carried back at all. This may be especially detrimental to start-up businesses, which tend to generate NOLs in their early years and can greatly benefit from the cash-flow boost of a carried-back NOL. (On the plus side, the TCJA allows NOLs to be carried forward indefinitely, as opposed to the previous 20-year limit.
- For NOLs arising in tax years beginning after December 31, 2017, an NOL carryforward generally can’t be used to shelter more than 80% of taxable income in the carryforward year. (Under prior law, generally up to 100% could be sheltered.)
The differences between the effective dates for these changes may have been a mistake, and a technical correction might be made by Congress. Also be aware that, in the case of pass-through entities, owners’ tax benefits from the entity’s net loss might be further limited under the TCJA’s new “excess business loss” rules.
Complicated rules get more complicated
NOLs can provide valuable tax benefits. The rules, however, have always been complicated, and the TCJA has complicated them further. Please contact us if you’d like more information on the NOL rules and how you can maximize the tax benefit of an NOL.
You still have time to make 2017 IRA contributions

Tax-advantaged retirement plans like IRAs allow your money to grow tax-deferred — or, in the case of Roth accounts, tax-free. The deadline for 2017 contributions is April 17, 2018. Deductible contributions will lower your 2017 tax bill, but even nondeductible contributions can be beneficial.
Don’t lose the opportunity
The 2017 limit for total contributions to all IRAs generally is $5,500 ($6,500 if you were age 50 or older on December 31, 2017). But any unused limit can’t be carried forward to make larger contributions in future years.
This means that, once the contribution deadline has passed, the tax-advantaged savings opportunity is lost forever. So to maximize your potential for tax-deferred or tax-free savings, it’s a good idea to use up as much of your annual limit as possible.
3 types of contributions
If you haven’t already maxed out your 2017 IRA contribution limit, consider making one of these types of contributions by April 17:
1. Deductible traditional. With traditional IRAs, account growth is tax-deferred and distributions are subject to income tax. If you and your spouse don’t participate in an employer-sponsored plan such as a 401(k), the contribution is fully deductible on your 2017 tax return. If you or your spouse does participate in an employer-sponsored plan, your deduction is subject to a modified adjusted gross income (MAGI) phaseout:
- For married taxpayers filing jointly, the phaseout range is specific to each spouse based on whether he or she is a participant in an employer-sponsored plan:
- For a spouse who participates: $99,000–$119,000.
- For a spouse who doesn’t participate: $186,000–$196,000.
- For single and head-of-household taxpayers participating in an employer-sponsored plan: $62,000–$72,000.
Taxpayers with MAGIs within the applicable range can deduct a partial contribution; those with MAGIs exceeding the applicable range can’t deduct any IRA contribution.
2. Roth. With Roth IRAs, contributions aren’t deductible, but qualified distributions — including growth — are tax-free. Your ability to contribute, however, is subject to a MAGI-based phaseout:
- For married taxpayers filing jointly: $186,000–$196,000.
- For single and head-of-household taxpayers: $118,000–$133,000.
You can make a partial contribution if your MAGI falls within the applicable range, but no contribution if it exceeds the top of the range.
3. Nondeductible traditional. If your income is too high for you to fully benefit from a deductible traditional or a Roth contribution, you may benefit from a nondeductible contribution to a traditional IRA. The account can still grow tax-deferred, and when you take qualified distributions you’ll be taxed only on the growth.
Alternatively, shortly after contributing, you may be able to convert the account to a Roth IRA with minimal tax liability.
Maximize your tax-advantaged savings
Traditional and Roth IRAs provide a powerful way to save for retirement on a tax-advantaged basis. Contact us to learn more about making 2017 contributions and making the most of IRAs in 2018 and beyond.
Should you file Form SS-8 to ask the IRS to determine a worker’s status?

Classifying workers as independent contractors — rather than employees — can save businesses money and provide other benefits. But the IRS is on the lookout for businesses that do this improperly to avoid taxes and employee benefit obligations.
To find out how the IRS will classify a particular worker, businesses can file optional IRS Form SS-8, “Determination of Worker Status for Purposes of Federal Employment Taxes and Income Tax Withholding.” However, the IRS has a history of reflexively classifying workers as employees, and filing this form may alert the IRS that your business has classification issues — and even inadvertently trigger an employment tax audit.
Contractor vs. employee status
A business enjoys several advantages when it classifies a worker as an independent contractor rather than as an employee. For example, it isn’t required to pay payroll taxes, withhold taxes, pay benefits or comply with most wage and hour laws.
On the downside, if the IRS determines that you’ve improperly classified employees as independent contractors, you can be subject to significant back taxes, interest and penalties. That’s why filing IRS Form SS-8 for an up-front determination may sound appealing.
But because of the risks involved, instead of filing the form, it can be better to simply properly treat independent contractors so they meet the tax code rules. Among other things, this generally includes not controlling how the worker performs his or her duties, ensuring you’re not the worker’s only client, providing Form 1099 and, overall, not treating the worker like an employee.
Be prepared for workers filing the form
Workers seeking determination of their status can also file Form SS-8. Disgruntled independent contractors may do so because they feel entitled to health, retirement and other employee benefits and want to eliminate self-employment tax liabilities.
After a worker files Form SS-8, the IRS sends a letter to the business. It identifies the worker and includes a blank Form SS-8. The business is asked to complete and return it to the IRS, which will render a classification decision. But the Form SS-8 determination process doesn’t constitute an official IRS audit.
Passing IRS muster
If your business properly classifies workers as independent contractors, don’t panic if a worker files a Form SS-8. Contact us before replying to the IRS. With a proper response, you may be able to continue to classify the worker as a contractor. We also can assist you in setting up independent contractor relationships that can pass muster with the IRS.
Can you claim your elderly parent as a dependent on your tax return?

Perhaps. It depends on several factors, such as your parent’s income and how much financial support you provided. If you qualify for the adult-dependent exemption on your 2017 income tax return, you can deduct up to $4,050 per qualifying adult dependent. However, for 2018, under the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act, the dependency exemption is eliminated.
Income and support
For you to qualify for the adult-dependent exemption, in most cases your parent must have less gross income for the tax year than the exemption amount. (Exceptions may apply if your parent is permanently and totally disabled.) Generally Social Security is excluded, but payments from dividends, interest and retirement plans are included.
In addition, you must have contributed more than 50% of your parent’s financial support. If you shared caregiving duties with a sibling and your combined support exceeded 50%, the exemption can be claimed even though no one individually provided more than 50%. However, only one of you can claim the exemption.
Keep in mind that, even though Social Security payments can usually be excluded from the adult dependent’s income, they can still affect your ability to qualify. Why? If your parent is using Social Security money to pay for medicine or other expenses, you may find that you aren’t meeting the 50% test.
Housing
Don’t forget about your home. If your parent lived with you, the amount of support you claim under the 50% test can include the fair market rental value of part of your residence.
If the parent lived elsewhere — in his or her own residence or in an assisted-living facility or nursing home — any amount of financial support you contributed to that housing expense counts toward the 50% test.
Other savings opportunities
Sometimes caregivers fall just short of qualifying for the exemption. Should this happen, you may still be able to claim an itemized deduction for the medical expenses that you pay for the parent. To receive a tax benefit on your 2017 (or 2018) return, you must itemize deductions and the combined medical expenses paid for you, your dependents and your parent for the year must exceed 7.5% of your adjusted gross income.
The adult-dependent exemption is just one tax break that you may be able to employ to ease the financial burden of caring for an elderly parent. For 2018 through 2025, while the exemption is suspended, you might be eligible for a $500 “family” tax credit for your adult dependent. We’d be happy to provide additional information. Contact us to learn more.
2018 Q2 tax calendar: Key deadlines for businesses and other employers
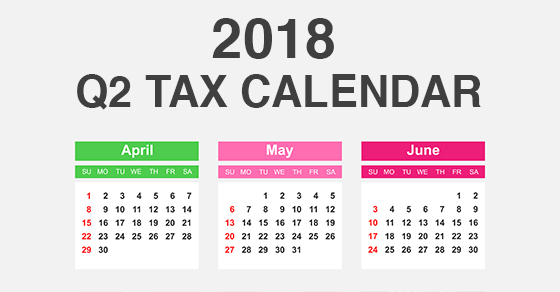
Here are some of the key tax-related deadlines affecting businesses and other employers during the second quarter of 2018. Keep in mind that this list isn’t all-inclusive, so there may be additional deadlines that apply to you. Contact us to ensure you’re meeting all applicable deadlines and to learn more about the filing requirements.
April 2
- Electronically file 2017 Form 1096, Form 1098, Form 1099 (except if an earlier deadline applies) and Form W-2G.
April 17
- If a calendar-year C corporation, file a 2017 income tax return (Form 1120) or file for an automatic six-month extension (Form 7004), and pay any tax due. If the return isn’t extended, this is also the last day to make 2017 contributions to pension and profit-sharing plans.
- If a calendar-year C corporation, pay the first installment of 2018 estimated income taxes.
April 30
- Report income tax withholding and FICA taxes for first quarter 2018 (Form 941), and pay any tax due. (See exception below under “May 10.”)
May 10
- Report income tax withholding and FICA taxes for first quarter 2018 (Form 941), if you deposited on time and in full all of the associated taxes due.
June 15
- If a calendar-year C corporation, pay the second installment of 2018 estimated income taxes.
Home-related tax breaks are valuable on 2017 returns, will be less so for 2018

Home ownership is a key element of the American dream for many, and the U.S. tax code includes many tax breaks that help support this dream. If you own a home, you may be eligible for several valuable breaks when you file your 2017 return. But under the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act, your home-related breaks may not be as valuable when you file your 2018 return next year.
2017 vs. 2018
Here’s a look at various home-related tax breaks for 2017 vs. 2018:
Property tax deduction. For 2017, property tax is generally fully deductible — unless you’re subject to the alternative minimum tax (AMT). For 2018, your total deduction for all state and local taxes, including both property taxes and either income taxes or sales taxes, is capped at $10,000.
Mortgage interest deduction. For 2017, you generally can deduct interest on up to a combined total of $1 million of mortgage debt incurred to purchase, build or improve your principal residence and a second residence. However, for 2018, if the mortgage debt was incurred on or after December 15, 2017, the debt limit generally is $750,000.
Home equity debt interest deduction. For 2017, interest on home equity debt used for any purpose (debt limit of $100,000) may be deductible. (If home equity debt isn’t used for home improvements, the interest isn’t deductible for AMT purposes). For 2018, the TCJA suspends the home equity interest deduction. But the IRS has clarified that such interest generally still will be deductible if used for home improvements.
Mortgage insurance premium deduction. This break expired December 31, 2017, but Congress might extend it.
Home office deduction. For 2017, if your home office use meets certain tests, you may be able to deduct associated expenses or use a simplified method for claiming the deduction. Employees claim this as a miscellaneous itemized deduction, which means there will be tax savings only to the extent that the home office deduction plus other miscellaneous itemized deductions exceeds 2% of adjusted gross income. The self-employed can deduct home office expenses from self-employment income. For 2018, miscellaneous itemized deductions subject to the 2% floor are suspended, so only the self-employed can deduct home office expenses.
Home sale gain exclusion. When you sell your principal residence, you can exclude up to $250,000 ($500,000 for married couples filing jointly) of gain if you meet certain tests. Changes to this break had been proposed, but they weren’t included in the final TCJA that was signed into law.
Debt forgiveness exclusion. This break for homeowners who received debt forgiveness in a foreclosure, short sale or mortgage workout for a principal residence expired December 31, 2017, but Congress might extend it.
Additional rules and limits apply to these breaks. To learn more, contact us. We can help you determine which home-related breaks you’re eligible to claim on your 2017 return and how your 2018 tax situation may be affected by the TCJA.
Defer tax with a Section 1031 exchange, but new limits apply this year

Normally when appreciated business assets such as real estate are sold, tax is owed on the appreciation. But there’s a way to defer this tax: a Section 1031 “like kind” exchange. However, the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA) reduces the types of property eligible for this favorable tax treatment.
What is a like-kind exchange?
Section 1031 of the Internal Revenue Code allows you to defer gains on real or personal property used in a business or held for investment if, instead of selling it, you exchange it solely for property of a “like kind.” Thus, the tax benefit of an exchange is that you defer tax and, thereby, have use of the tax savings until you sell the replacement property.
This technique is especially flexible for real estate, because virtually any type of real estate will be considered to be of a like kind, as long as it’s business or investment property. For example, you can exchange a warehouse for an office building, or an apartment complex for a strip mall.
Deferred and reverse exchanges
Although a like-kind exchange may sound quick and easy, it’s relatively rare for two owners to simply swap properties. You’ll likely have to execute a “deferred” exchange, in which you engage a qualified intermediary (QI) for assistance.
When you sell your property (the relinquished property), the net proceeds go directly to the QI, who then uses them to buy replacement property. To qualify for tax-deferred exchange treatment, you generally must identify replacement property within 45 days after you transfer the relinquished property and complete the purchase within 180 days after the initial transfer.
An alternate approach is a “reverse” exchange. Here, an exchange accommodation titleholder (EAT) acquires title to the replacement property before you sell the relinquished property. You can defer capital gains by identifying one or more properties to exchange within 45 days after the EAT receives the replacement property and, typically, completing the transaction within 180 days.
Changes under the TCJA
There had been some concern that tax reform would include the elimination of like-kind exchanges. The good news is that the TCJA still generally allows tax-deferred like-kind exchanges of business and investment real estate.
But there’s also some bad news: For 2018 and beyond, the TCJA eliminates tax-deferred like-kind exchange treatment for exchanges of personal property. However, prior-law rules that allow like-kind exchanges of personal property still apply if one leg of an exchange was completed by December 31, 2017, but one leg remained open on that date. Keep in mind that exchanged personal property must be of the same asset or product class.
Complex rules
The rules for like-kind exchanges are complex, so these arrangements present some risks. If, say, you exchange the wrong kind of property or acquire cash or other non-like-kind property in a deal, you may still end up incurring a sizable tax hit. If you’re exploring a like-kind exchange, contact us. We can help you ensure you’re in compliance with the rules.
Casualty losses can provide a 2017 deduction, but rules tighten for 2018

If you suffered damage to your home or personal property last year, you may be able to deduct these “casualty” losses on your 2017 federal income tax return. For 2018 through 2025, however, the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act suspends this deduction except for losses due to an event officially declared a disaster by the President.
What is a casualty? It’s a sudden, unexpected or unusual event, such as a natural disaster (hurricane, tornado, flood, earthquake, etc.), fire, accident, theft or vandalism. A casualty loss doesn’t include losses from normal wear and tear or progressive deterioration from age or termite damage.
Here are some things you should know about deducting casualty losses on your 2017 return:
When to deduct. Generally, you must deduct a casualty loss on your return for the year it occurred. However, if you have a loss from a federally declared disaster area, you may have the option to deduct the loss on an amended return for the immediately preceding tax year.
Amount of loss. Your loss is generally the lesser of 1) your adjusted basis in the property before the casualty (typically, the amount you paid for it), or 2) the decrease in fair market value of the property as a result of the casualty. This amount must be reduced by any insurance or other reimbursement you received or expect to receive. (If the property was insured, you must have filed a timely claim for reimbursement of your loss.)
$100 rule. After you’ve figured your casualty loss on personal-use property, you must reduce that loss by $100. This reduction applies to each casualty loss event during the year. It doesn’t matter how many pieces of property are involved in an event.
10% rule. You must reduce the total of all your casualty losses on personal-use property for the year by 10% of your adjusted gross income (AGI). In other words, you can deduct these losses only to the extent they exceed 10% of your AGI.
Note that special relief has been provided to certain victims of Hurricanes Harvey, Irma and Maria and California wildfires that affects some of these rules. For details on this relief or other questions about casualty losses, please contact us.
Make sure repairs to tangible property were actually repairs before you deduct the cost

Repairs to tangible property, such as buildings, machinery, equipment or vehicles, can provide businesses a valuable current tax deduction — as long as the so-called repairs weren’t actually “improvements.” The costs of incidental repairs and maintenance can be immediately expensed and deducted on the current year’s income tax return. But costs incurred to improve tangible property must be depreciated over a period of years.
So the size of your 2017 deduction depends on whether the expense was a repair or an improvement.
Betterment, restoration or adaptation
In general, a cost that results in an improvement to a building structure or any of its building systems (for example, the plumbing or electrical system) or to other tangible property must be depreciated. An improvement occurs if there was a betterment, restoration or adaptation of the unit of property.
Under the “betterment test,” you generally must depreciate amounts paid for work that is reasonably expected to materially increase the productivity, efficiency, strength, quality or output of a unit of property or that is a material addition to a unit of property.
Under the “restoration test,” you generally must depreciate amounts paid to replace a part (or combination of parts) that is a major component or a significant portion of the physical structure of a unit of property.
Under the “adaptation test,” you generally must depreciate amounts paid to adapt a unit of property to a new or different use — one that isn’t consistent with your ordinary use of the unit of property at the time you originally placed it in service.
Seeking safety
Distinguishing between repairs and improvements can be difficult, but a couple of IRS safe harbors can help:
1. Routine maintenance safe harbor. Recurring activities dedicated to keeping property in efficient operating condition can be expensed. These are activities that your business reasonably expects to perform more than once during the property’s “class life,” as defined by the IRS.
Amounts incurred for activities outside the safe harbor don’t necessarily have to be depreciated, though. These amounts are subject to analysis under the general rules for improvements.
2. Small business safe harbor. For buildings that initially cost $1 million or less, qualified small businesses may elect to deduct the lesser of $10,000 or 2% of the unadjusted basis of the property for repairs, maintenance, improvements and similar activities each year. A qualified small business is generally one with gross receipts of $10 million or less.
There is also a de minimis safe harbor as well as an exemption for materials and supplies up to a certain threshold. To learn more about these safe harbors and exemptions and other ways to maximize your tangible property deductions, contact us.
Size of charitable deductions depends on many factors

Whether you’re claiming charitable deductions on your 2017 return or planning your donations for 2018, be sure you know how much you’re allowed to deduct. Your deduction depends on more than just the actual amount you donate.
Type of gift
One of the biggest factors affecting your deduction is what you give:
Cash. You may deduct 100% gifts made by check, credit card or payroll deduction.
Ordinary-income property. For stocks and bonds held one year or less, inventory, and property subject to depreciation recapture, you generally may deduct only the lesser of fair market value or your tax basis.
Long-term capital gains property. You may deduct the current fair market value of appreciated stocks and bonds held for more than one year.
Tangible personal property. Your deduction depends on the situation:
- If the property isn’t related to the charity’s tax-exempt function (such as a painting donated for a charity auction), your deduction is limited to your basis.
- If the property is related to the charity’s tax-exempt function (such as a painting donated to a museum for its collection), you can deduct the fair market value.
Vehicle. Unless the vehicle is being used by the charity, you generally may deduct only the amount the charity receives when it sells the vehicle.
Use of property. Examples include use of a vacation home and a loan of artwork. Generally, you receive no deduction because it isn’t considered a completed gift.
Services. You may deduct only your out-of-pocket expenses, not the fair market value of your services. You can deduct 14 cents per charitable mile driven.
Other factors
First, you’ll benefit from the charitable deduction only if you itemize deductions rather than claim the standard deduction. Also, your annual charitable donation deductions may be reduced if they exceed certain income-based limits.
In addition, your deduction generally must be reduced by the value of any benefit received from the charity. Finally, various substantiation requirements apply, and the charity must be eligible to receive tax-deductible contributions.
2018 planning
While December’s Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA) preserves the charitable deduction, it temporarily makes itemizing less attractive for many taxpayers, reducing the tax benefits of charitable giving for them.
Itemizing saves tax only if itemized deductions exceed the standard deduction. For 2018 through 2025, the TCJA nearly doubles the standard deduction — plus, it limits or eliminates some common itemized deductions. As a result, you may no longer have enough itemized deductions to exceed the standard deduction, in which case your charitable donations won’t save you tax.
You might be able to preserve your charitable deduction by “bunching” donations into alternating years, so that you’ll exceed the standard deduction and can claim a charitable deduction (and other itemized deductions) every other year.
Let us know if you have questions about how much you can deduct on your 2017 return or what your charitable giving strategy should be going forward, in light of the TCJA.
Don’t forget: 2017 tax filing deadline for pass-through entities is March 15

When it comes to income tax returns, April 15 (actually April 17 this year, because of a weekend and a Washington, D.C., holiday) isn’t the only deadline taxpayers need to think about. The federal income tax filing deadline for calendar-year partnerships, S corporations and limited liability companies (LLCs) treated as partnerships or S corporations for tax purposes is March 15. While this has been the S corporation deadline for a long time, it’s only the second year the partnership deadline has been in March rather than in April.
Why the deadline change?
One of the primary reasons for moving up the partnership filing deadline was to make it easier for owners to file their personal returns by the April filing deadline. After all, partnership (and S corporation) income passes through to the owners. The earlier date allows owners to use the information contained in the pass-through entity forms to file their personal returns.
What about fiscal-year entities?
For partnerships with fiscal year ends, tax returns are now due the 15th day of the third month after the close of the tax year. The same deadline applies to fiscal-year S corporations. Under prior law, returns for fiscal-year partnerships were due the 15th day of the fourth month after the close of the fiscal tax year.
What about extensions?
If you haven’t filed your calendar-year partnership or S corporation return yet, you may be thinking about an extension. Under the current law, the maximum extension for calendar-year partnerships is six months (until September 17, 2018, for 2017 returns). This is up from five months under prior law. So the extension deadline is the same — only the length of the extension has changed. The extension deadline for calendar-year S corporations also is September 17, 2018, for 2017 returns.
Whether you’ll be filing a partnership or an S corporation return, you must file for the extension by March 15 if it’s a calendar-year entity.
When does an extension make sense?
Filing for an extension can be tax-smart if you’re missing critical documents or you face unexpected life events that prevent you from devoting sufficient time to your return right now.
But keep in mind that, to avoid potential interest and penalties, you still must (with a few exceptions) pay any tax due by the unextended deadline. There may not be any tax liability from the partnership or S corporation return. If, however, filing for an extension for the entity return causes you to also have to file an extension for your personal return, you need to keep this in mind related to the individual tax return April 17 deadline.
Have more questions about the filing deadlines that apply to you or avoiding interest and penalties? Contact us.
What’s your mileage deduction?

Individuals can deduct some vehicle-related expenses in certain circumstances. Rather than keeping track of the actual costs, you can use a standard mileage rate to compute your deductions. For 2017, you might be able to deduct miles driven for business, medical, moving and charitable purposes. For 2018, there are significant changes to some of these deductions under the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA).
Mileage rates vary
The rates vary depending on the purpose and the year:
Business: 53.5 cents (2017), 54.5 cents (2018)
Medical: 17 cents (2017), 18 cents (2018)
Moving: 17 cents (2017), 18 cents (2018)
Charitable: 14 cents (2017 and 2018)
The business standard mileage rate is considerably higher than the medical, moving and charitable rates because the business rate contains a depreciation component. No depreciation is allowed for the medical, moving or charitable use of a vehicle. The charitable rate is lower than the medical and moving rate because it isn’t adjusted for inflation.
In addition to deductions based on the standard mileage rate, you may deduct related parking fees and tolls.
2017 and 2018 limits
The rules surrounding the various mileage deductions are complex. Some are subject to floors and some require you to meet specific tests in order to qualify.
For example, if you’re an employee, only business mileage not reimbursed by your employer is deductible. It’s a miscellaneous itemized deduction subject to a 2% of adjusted gross income (AGI) floor. For 2017, this means mileage is deductible only to the extent that your total miscellaneous itemized deductions for the year exceed 2% of your AGI. For 2018, it means that you can’t deduct the mileage, because the TCJA suspends miscellaneous itemized deductions subject to the 2% floor for 2018 through 2025.
If you’re self-employed, business mileage can be deducted against self-employment income. Therefore, it’s not subject to the 2% floor and is still deductible for 2018 through 2025, as long as it otherwise qualifies.
Miles driven for health-care-related purposes are deductible as part of the medical expense deduction. And an AGI floor applies. Under the TCJA, for 2017 and 2018, medical expenses are deductible to the extent they exceed 7.5% of your adjusted gross income. For 2019, the floor will return to 10%, unless Congress extends the 7.5% floor.
And while miles driven related to moving can be deductible on your 2017 return, the move must be work-related and meet other tests. For 2018 through 2025, under the TCJA, moving expenses are deductible only for certain military families.
Substantiation and more
There are also substantiation requirements, which include tracking miles driven. And, in some cases, you might be better off deducting actual expenses rather than using the mileage rates.
We can help ensure you deduct all the mileage you’re entitled to on your 2017 tax return but don’t risk back taxes and penalties later for deducting more than allowed. Contact us for assistance and to learn how your mileage deduction for 2018 might be affected by the TCJA.
Sec. 179 expensing provides small businesses tax savings on 2017 returns — and more savings in the future

If you purchased qualifying property by December 31, 2017, you may be able to take advantage of Section 179 expensing on your 2017 tax return. You’ll also want to keep this tax break in mind in your property purchase planning, because the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA), signed into law this past December, significantly enhances it beginning in 2018.
2017 Sec. 179 benefits
Sec. 179 expensing allows eligible taxpayers to deduct the entire cost of qualifying new or used depreciable property and most software in Year 1, subject to various limitations. For tax years that began in 2017, the maximum Sec. 179 deduction is $510,000. The maximum deduction is phased out dollar for dollar to the extent the cost of eligible property placed in service during the tax year exceeds the phaseout threshold of $2.03 million.
Qualified real property improvement costs are also eligible for Sec. 179 expensing. This real estate break applies to:
- Certain improvements to interiors of leased nonresidential buildings,
- Certain restaurant buildings or improvements to such buildings, and
- Certain improvements to the interiors of retail buildings.
Deductions claimed for qualified real property costs count against the overall maximum for Sec. 179 expensing.
Permanent enhancements
The TCJA permanently enhances Sec. 179 expensing. Under the new law, for qualifying property placed in service in tax years beginning in 2018, the maximum Sec. 179 deduction is increased to $1 million, and the phaseout threshold is increased to $2.5 million. For later tax years, these amounts will be indexed for inflation. For purposes of determining eligibility for these higher limits, property is treated as acquired on the date on which a written binding contract for the acquisition is signed.
The new law also expands the definition of eligible property to include certain depreciable tangible personal property used predominantly to furnish lodging. The definition of qualified real property eligible for Sec. 179 expensing is also expanded to include the following improvements to nonresidential real property: roofs, HVAC equipment, fire protection and alarm systems, and security systems.
Save now and save later
Many rules apply, so please contact us to learn if you qualify for this break on your 2017 return. We’d also be happy to discuss your future purchasing plans so you can reap the maximum benefits from enhanced Sec. 179 expensing and other tax law changes under the TCJA.
Tax credit for hiring from certain “target groups” can provide substantial tax savings

Many businesses hired in 2017, and more are planning to hire in 2018. If you’re among them and your hires include members of a “target group,” you may be eligible for the Work Opportunity tax credit (WOTC). If you made qualifying hires in 2017 and obtained proper certification, you can claim the WOTC on your 2017 tax return.
Whether or not you’re eligible for 2017, keep the WOTC in mind in your 2018 hiring plans. Despite its proposed elimination under the House’s version of the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act, the credit survived the final version that was signed into law in December, so it’s also available for 2018.
“Target groups,” defined
Target groups include:
- Qualified individuals who have been unemployed for 27 weeks or more,
- Designated community residents who live in Empowerment Zones or rural renewal counties,
- Long-term family assistance recipients,
- Qualified ex-felons,
- Qualified recipients of Temporary Assistance for Needy Families (TANF),
- Qualified veterans,
- Summer youth employees,
- Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP) recipients,
- Supplemental Security Income benefits recipients, and
- Vocational rehabilitation referrals for individuals who suffer from an employment handicap resulting from a physical or mental handicap.
Before you can claim the WOTC, you must obtain certification from a “designated local agency” (DLA) that the hired individual is indeed a target group member. You must submit IRS Form 8850, “Pre-Screening Notice and Certification Request for the Work Opportunity Credit,” to the DLA no later than the 28th day after the individual begins work for you. Unfortunately, this means that, if you hired someone from a target group in 2017 but didn’t obtain the certification, you can’t claim the WOTC on your 2017 return.
A potentially valuable credit
Qualifying employers can claim the WOTC as a general business credit against their income tax. The amount of the credit depends on the:
- Target group of the individual hired,
- Wages paid to that individual, and
- Number of hours that individual worked during the first year of employment.
The maximum credit that can be earned for each member of a target group is generally $2,400 per employee. The credit can be as high as $9,600 for certain veterans.
Employers aren’t subject to a limit on the number of eligible individuals they can hire. In other words, if you hired 10 individuals from target groups that qualify for the $2,400 credit, your total credit would be $24,000.
Remember, credits reduce your tax bill dollar-for-dollar; they don’t just reduce the amount of income subject to tax like deductions do. So that’s $24,000 of actual tax savings.
Offset hiring costs
The WOTC can provide substantial tax savings when you hire qualified new employees, offsetting some of the cost. Contact us for more information.
Tax deduction for moving costs: 2017 vs. 2018

If you moved for work-related reasons in 2017, you might be able to deduct some of the costs on your 2017 return — even if you don’t itemize deductions. (Or, if your employer reimbursed you for moving expenses, that reimbursement might be excludable from your income.) The bad news is that, if you move in 2018, the costs likely won’t be deductible, and any employer reimbursements will probably be included in your taxable income.
Suspension for 2018–2025
The Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA), signed into law this past December, suspends the moving expense deduction for the same period as when lower individual income tax rates generally apply: 2018 through 2025. For this period it also suspends the exclusion from income of qualified employer reimbursements of moving expenses.
The TCJA does provide an exception to both suspensions for active-duty members of the Armed Forces (and their spouses and dependents) who move because of a military order that calls for a permanent change of station.
Tests for 2017
If you moved in 2017 and would like to claim a deduction on your 2017 return, the first requirement is that the move be work-related. You don’t have to be an employee; the self-employed can also be eligible for the moving expense deduction.
The second is a distance test. The new main job location must be at least 50 miles farther from your former home than your former main job location was from that home. So a work-related move from city to suburb or from town to neighboring town probably won’t qualify, even if not moving would have increased your commute significantly.
Finally, there’s a time test. You must work full time at the new job location for at least 39 weeks during the first year. If you’re self-employed, you must meet that test plus work full time for at least 78 weeks during the first 24 months at the new job location. (Certain limited exceptions apply.)
Deductible expenses
The moving expense deduction is an “above-the-line” deduction, which means it’s subtracted from your gross income to determine your adjusted gross income. It’s not an itemized deduction, so you don’t have to itemize to benefit.
Generally, you can deduct:
- Transportation and lodging expenses for yourself and household members while moving,
- The cost of packing and transporting your household goods and other personal property,
- The expense of storing and insuring these items while in transit, and
- Costs related to connecting or disconnecting utilities.
But don’t expect to deduct everything. Meal costs during move-related travel aren’t deductible • nor is any part of the purchase price of a new home or expenses incurred selling your old one. And, if your employer later reimburses you for any of the moving costs you’ve deducted, you may have to include the reimbursement as income on your tax return.
Please contact us if you have questions about whether you can deduct moving expenses on your 2017 return or about what other tax breaks won’t be available for 2018 under the TCJA.
Families with college students may save tax on their 2017 returns with one of these breaks

Whether you had a child in college (or graduate school) last year or were a student yourself, you may be eligible for some valuable tax breaks on your 2017 return. One such break that had expired December 31, 2016, was just extended under the recently passed Bipartisan Budget Act of 2018: the tuition and fees deduction.
But a couple of tax credits are also available. Tax credits can be especially valuable because they reduce taxes dollar-for-dollar; deductions reduce only the amount of income that’s taxed.
Higher education breaks 101
While multiple higher-education breaks are available, a taxpayer isn’t allowed to claim all of them. In most cases you can take only one break per student, and, for some breaks, only one per tax return. So first you need to see which breaks you’re eligible for. Then you need to determine which one will provide the greatest benefit.
Also keep in mind that you generally can’t claim deductions or credits for expenses that were paid for with distributions from tax-advantaged accounts, such as 529 plans or Coverdell Education Savings Accounts.
Credits
Two credits are available for higher education expenses:
- The American Opportunity credit — up to $2,500 per year per student for qualifying expenses for the first four years of postsecondary education.
- The Lifetime Learning credit — up to $2,000 per tax return for postsecondary education expenses, even beyond the first four years.
But income-based phaseouts apply to these credits.
If you’re eligible for the American Opportunity credit, it will likely provide the most tax savings. If you’re not, consider claiming the Lifetime Learning credit. But first determine if the tuition and fees deduction might provide more tax savings.
Deductions
Despite the dollar-for-dollar tax savings credits offer, you might be better off deducting up to $4,000 of qualified higher education tuition and fees. Because it’s an above-the-line deduction, it reduces your adjusted gross income, which could provide additional tax benefits. But income-based limits also apply to the tuition and fees deduction.
Be aware that the tuition and fees deduction was extended only through December 31, 2017. So it won’t be available on your 2018 return unless Congress extends it again or makes it permanent.
Maximizing your savings
If you don’t qualify for breaks for your child’s higher education expenses because your income is too high, your child might. Many additional rules and limits apply to the credits and deduction, however. To learn which breaks your family might be eligible for on your 2017 tax returns — and which will provide the greatest tax savings — please contact us.
Small business owners: A SEP may give you one last 2017 tax and retirement saving opportunity

Are you a high-income small-business owner who doesn’t currently have a tax-advantaged retirement plan set up for yourself? A Simplified Employee Pension (SEP) may be just what you need, and now may be a great time to establish one. A SEP has high contribution limits and is simple to set up. Best of all, there’s still time to establish a SEP for 2017 and make contributions to it that you can deduct on your 2017 income tax return.
2018 deadlines for 2017
A SEP can be set up as late as the due date (including extensions) of your income tax return for the tax year for which the SEP is to first apply. That means you can establish a SEP for 2017 in 2018 as long as you do it before your 2017 return filing deadline. You have until the same deadline to make 2017 contributions and still claim a potentially hefty deduction on your 2017 return.
Generally, other types of retirement plans would have to have been established by December 31, 2017, in order for 2017 contributions to be made (though many of these plans do allow 2017 contributions to be made in 2018).
High contribution limits
Contributions to SEPs are discretionary. You can decide how much to contribute each year. But be aware that, if your business has employees other than yourself: 1) Contributions must be made for all eligible employees using the same percentage of compensation as for yourself, and 2) employee accounts are immediately 100% vested. The contributions go into SEP-IRAs established for each eligible employee.
For 2017, the maximum contribution that can be made to a SEP-IRA is 25% of compensation (or 20% of self-employed income net of the self-employment tax deduction) of up to $270,000, subject to a contribution cap of $54,000. (The 2018 limits are $275,000 and $55,000, respectively.)
Simple to set up
A SEP is established by completing and signing the very simple Form 5305-SEP (“Simplified Employee Pension — Individual Retirement Accounts Contribution Agreement”). Form 5305-SEP is not filed with the IRS, but it should be maintained as part of the business’s permanent tax records. A copy of Form 5305-SEP must be given to each employee covered by the SEP, along with a disclosure statement.
Additional rules and limits do apply to SEPs, but they’re generally much less onerous than those for other retirement plans. Contact us to learn more about SEPs and how they might reduce your tax bill for 2017 and beyond.
TCJA temporarily lowers medical expense deduction threshold

With rising health care costs, claiming whatever tax breaks related to health care that you can is more important than ever. But there’s a threshold for deducting medical expenses that may be hard to meet. Fortunately, the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA) has temporarily reduced the threshold.
What expenses are eligible?
Medical expenses may be deductible if they’re “qualified.” Qualified medical expenses involve the costs of diagnosis, cure, mitigation, treatment or prevention of disease, and the costs for treatments affecting any part or function of the body. Examples include payments to physicians, dentists and other medical practitioners, as well as equipment, supplies, diagnostic devices and prescription drugs.
Mileage driven for health-care-related purposes is also deductible at a rate of 17 cents per mile for 2017 and 18 cents per mile for 2018. Health insurance and long-term care insurance premiums can also qualify, with certain limits.
Expenses reimbursed by insurance or paid with funds from a tax-advantaged account such as a Health Savings Account or Flexible Spending Account can’t be deducted. Likewise, health insurance premiums aren’t deductible if they’re taken out of your paycheck pretax.
The AGI threshold
Before 2013, you could claim an itemized deduction for qualified unreimbursed medical expenses paid for you, your spouse and your dependents, to the extent those expenses exceeded 7.5% of your adjusted gross income (AGI). AGI includes all of your taxable income items reduced by certain “above-the-line” deductions, such as those for deductible IRA contributions and student loan interest.
As part of the Affordable Care Act, a higher deduction threshold of 10% of AGI went into effect in 2014 for most taxpayers and was scheduled to go into effect in 2017 for taxpayers age 65 or older. But under the TCJA, the 7.5%-of-AGI deduction threshold now applies to all taxpayers for 2017 and 2018.
However, this lower threshold is temporary. Beginning January 1, 2019, the 10% threshold will apply to all taxpayers, including those over age 65, unless Congress takes additional action.
Consider “bunching” expenses into 2018
Because the threshold is scheduled to increase to 10% in 2019, you might benefit from accelerating deductible medical expenses into 2018, to the extent they’re within your control.
However, keep in mind that you have to itemize deductions to deduct medical expenses. Itemizing saves tax only if your total itemized deductions exceed your standard deduction. And with the TCJA’s near doubling of the standard deduction for 2018, many taxpayers who’ve typically itemized may no longer benefit from itemizing.
Contact us if you have questions about what expenses are eligible and whether you can qualify for a deduction on your 2017 tax return. We can also help you determine whether bunching medical expenses into 2018 will likely save you tax.
Claiming bonus depreciation on your 2017 tax return may be particularly beneficial

With bonus depreciation, a business can recover the costs of depreciable property more quickly by claiming additional first-year depreciation for qualified assets. The Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA), signed into law in December, enhances bonus depreciation.
Typically, taking this break is beneficial. But in certain situations, your business might save more tax long-term by skipping it. That said, claiming bonus depreciation on your 2017 tax return may be particularly beneficial.
Pre- and post-TCJA
Before TCJA, bonus depreciation was 50% and qualified property included new tangible property with a recovery period of 20 years or less (such as office furniture and equipment), off-the-shelf computer software, water utility property and qualified improvement property.
The TCJA significantly expands bonus depreciation: For qualified property placed in service between September 28, 2017, and December 31, 2022 (or by December 31, 2023, for certain property with longer production periods), the first-year bonus depreciation percentage increases to 100%. In addition, the 100% deduction is allowed for not just new but also used qualifying property.
But be aware that, under the TCJA, beginning in 2018 certain types of businesses may no longer be eligible for bonus depreciation. Examples include real estate businesses and auto dealerships, depending on the specific circumstances.
A good tax strategy • or not?
Generally, if you’re eligible for bonus depreciation and you expect to be in the same or a lower tax bracket in future years, taking bonus depreciation is likely a good tax strategy (though you should also factor in available Section 179 expensing). It will defer tax, which generally is beneficial.
On the other hand, if your business is growing and you expect to be in a higher tax bracket in the near future, you may be better off forgoing bonus depreciation. Why? Even though you’ll pay more tax this year, you’ll preserve larger depreciation deductions on the property for future years, when they may be more powerful — deductions save more tax when you’re paying a higher tax rate.
What to do on your 2017 return
The greater tax-saving power of deductions when rates are higher is why 2017 may be a particularly good year to take bonus depreciation. As you’re probably aware, the TCJA permanently replaces the graduated corporate tax rates of 15% to 35% with a flat corporate rate of 21% beginning with the 2018 tax year. It also reduces most individual rates, which benefits owners of pass-through entities such as S corporations, partnerships and, typically, limited liability companies, for tax years beginning in 2018 through 2025.
If your rate will be lower in 2018, there’s a greater likelihood that taking bonus depreciation for 2017 would save you more tax than taking all of your deduction under normal depreciation schedules over a period of years, especially if the asset meets the deadlines for 100% bonus depreciation.
If you’re unsure whether you should take bonus depreciation on your 2017 return — or you have questions about other depreciation-related breaks, such as Sec. 179 expensing — contact us.
State and local sales tax deduction remains, but subject to a new limit
Individual taxpayers who itemize their deductions can deduct either state and local income taxes or state and local sales taxes. The ability to deduct state and local taxes — including income or sales taxes, as well as property taxes — had been on the tax reform chopping block, but it ultimately survived. However, for 2018 through 2025, the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act imposes a new limit on the state and local tax deduction. Will you benefit from the sales tax deduction on your 2017 or 2018 tax return?
Your 2017 return
The sales tax deduction can be valuable if you reside in a state with no or low income tax or purchased a major item in 2017, such as a car or boat. How do you determine whether you can save more by deducting sales tax on your 2017 return? Compare your potential deduction for state and local income tax to your potential deduction for state and local sales tax.
This isn’t as difficult as you might think: You don’t have to have receipts documenting all of the sales tax you actually paid during the year to take full advantage of the deduction. Your deduction can be determined by using an IRS sales tax calculator that will base the deduction on your income and the sales tax rates in your locale plus the tax you actually paid on certain major purchases (for which you will need substantiation).
Your 2018 return
Under the TCJA, for 2018 through 2025, your total deduction for all state and local taxes combined — including property tax — is limited to $10,000. You still must choose between deducting income and sales tax; you can’t deduct both, even if your total state and local tax deduction wouldn’t exceed $10,000.
Also keep in mind that the TCJA nearly doubles the standard deduction. So even if itemizing has typically benefited you in the past, you could end up being better off taking the standard deduction when you file your 2018 return.
So if you’re considering making a large purchase in 2018, you shouldn’t necessarily count on the sales tax deduction providing you significant tax savings. You need to look at what your total state and local tax liability likely will be, as well as whether your total itemized deductions are likely to exceed the standard deduction.
Questions?
Let us know if you have questions about whether you can benefit from the sales tax deduction on your 2017 return or about the impact of the TCJA on your 2018 tax planning. We’d be pleased to help.
2 tax credits just for small businesses may reduce your 2017 and 2018 tax bills

Tax credits reduce tax liability dollar-for-dollar, potentially making them more valuable than deductions, which reduce only the amount of income subject to tax. Maximizing available credits is especially important now that the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act has reduced or eliminated some tax breaks for businesses. Two still-available tax credits are especially for small businesses that provide certain employee benefits.
1. Credit for paying health care coverage premiums
The Affordable Care Act (ACA) offers a credit to certain small employers that provide employees with health coverage. Despite various congressional attempts to repeal the ACA in 2017, nearly all of its provisions remain intact, including this potentially valuable tax credit.
The maximum credit is 50% of group health coverage premiums paid by the employer, if it contributes at least 50% of the total premium or of a benchmark premium. For 2017, the full credit is available for employers with 10 or fewer full-time equivalent employees (FTEs) and average annual wages of $26,200 or less per employee. Partial credits are available on a sliding scale to businesses with fewer than 25 FTEs and average annual wages of less than $52,400.
The credit can be claimed for only two years, and they must be consecutive. (Credits claimed before 2014 don’t count, however.) If you meet the eligibility requirements but have been waiting to claim the credit until a future year when you think it might provide more savings, claiming the credit for 2017 may be a good idea. Why? It’s possible the credit will go away in the future if lawmakers in Washington continue to try to repeal or replace the ACA.
At this point, most likely any ACA repeal or replacement wouldn’t go into effect until 2019 (or possibly later). So if you claim the credit for 2017, you may also be able to claim it on your 2018 return next year (provided you again meet the eligibility requirements). That way, you could take full advantage of the credit while it’s available.
2. Credit for starting a retirement plan
Small employers (generally those with 100 or fewer employees) that create a retirement plan may be eligible for a $500 credit per year for three years. The credit is limited to 50% of qualified start-up costs.
Of course, you generally can deduct contributions you make to your employees’ accounts under the plan. And your employees enjoy the benefit of tax-advantaged retirement saving.
If you didn’t create a retirement plan in 2017, you might still have time to do so. Simplified Employee Pensions (SEPs) can be set up as late as the due date of your tax return, including extensions. If you’d like to set up a different type of plan, consider doing so for 2018 so you can potentially take advantage of the retirement plan credit (and other tax benefits) when you file your 2018 return next year.
Determining eligibility
Providing employee benefits can help businesses attract and retain the best workers. But the cost can be out of reach for some small businesses. Two tax credits can help make benefits more affordable for eligible small employers: 1) a credit equal to as much as 50% of health coverage premiums paid, and 2) a credit of up to $500 for creating a retirement plan. Contact us to learn if you can take these or other credits on your 2017 tax return and to plan for credits you might be able to claim on your 2018 return if you take appropriate actions this year.
Can you deduct home office expenses?

Working from home has become commonplace. But just because you have a home office space doesn’t mean you can deduct expenses associated with it. And for 2018, even fewer taxpayers will be eligible for a home office deduction.
Changes under the TCJA
For employees, home office expenses are a miscellaneous itemized deduction. For 2017, this means you’ll enjoy a tax benefit only if these expenses plus your other miscellaneous itemized expenses (such as unreimbursed work-related travel, certain professional fees and investment expenses) exceed 2% of your adjusted gross income.
For 2018 through 2025, this means that, if you’re an employee, you won’t be able to deduct any home office expenses. Why? The Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA) suspends miscellaneous itemized deductions subject to the 2% floor for this period.
If, however, you’re self-employed, you can deduct eligible home office expenses against your self-employment income. Therefore, the deduction will still be available to you for 2018 through 2025.
Other eligibility requirements
If you’re an employee, your use of your home office must be for your employer’s convenience, not just your own. If you’re self-employed, generally your home office must be your principal place of business, though there are exceptions.
Whether you’re an employee or self-employed, the space must be used regularly (not just occasionally) and exclusively for business purposes. If, for example, your home office is also a guest bedroom or your children do their homework there, you can’t deduct the expenses associated with that space.
2 deduction options
If you’re eligible, the home office deduction can be a valuable tax break. You have two options for the deduction:
1. Deduct a portion of your mortgage interest, property taxes, insurance, utilities and certain other expenses, as well as the depreciation allocable to the office space. This requires calculating, allocating and substantiating actual expenses.
2. Take the “safe harbor” deduction. Only one simple calculation is necessary: $5 × the number of square feet of the office space. The safe harbor deduction is capped at $1,500 per year, based on a maximum of 300 square feet.
More rules and limits
Be aware that we’ve covered only a few of the rules and limits here. If you think you may be eligible for the home office deduction on your 2017 return or would like to know if there’s anything additional you need to do to be eligible on your 2018 return, contact us.
Meals, entertainment and transportation may cost businesses more under the TCJA

Along with tax rate reductions and a new deduction for pass-through qualified business income, the new tax law brings the reduction or elimination of tax deductions for certain business expenses. Two expense areas where the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA) changes the rules — and not to businesses’ benefit — are meals/entertainment and transportation. In effect, the reduced tax benefits will mean these expenses are more costly to a business’s bottom line.
Meals and entertainment
Prior to the TCJA, taxpayers generally could deduct 50% of expenses for business-related meals and entertainment. Meals provided to an employee for the convenience of the employer on the employer’s business premises were 100% deductible by the employer and tax-free to the recipient employee.
Under the new law, for amounts paid or incurred after December 31, 2017, deductions for business-related entertainment expenses are disallowed.
Meal expenses incurred while traveling on business are still 50% deductible, but the 50% limit now also applies to meals provided via an on-premises cafeteria or otherwise on the employer’s premises for the convenience of the employer. After 2025, the cost of meals provided through an on-premises cafeteria or otherwise on the employer’s premises will no longer be deductible.
Transportation
The TCJA disallows employer deductions for the cost of providing commuting transportation to an employee (such as hiring a car service), unless the transportation is necessary for the employee’s safety.
The new law also eliminates employer deductions for the cost of providing qualified employee transportation fringe benefits. Examples include parking allowances, mass transit passes and van pooling. These benefits are, however, still tax-free to recipient employees.
Transportation expenses for employee work-related travel away from home are still deductible (and tax-free to the employee), as long as they otherwise qualify for such tax treatment. (Note that, for 2018 through 2025, employees can’t deduct unreimbursed employee business expenses, such as travel expenses, as a miscellaneous itemized deduction.)
Assessing the impact
The TCJA’s changes to deductions for meals, entertainment and transportation expenses may affect your business’s budget. Depending on how much you typically spend on such expenses, you may want to consider changing some of your policies and/or benefits offerings in these areas. We’d be pleased to help you assess the impact on your business.
Personal exemptions and standard deductions and tax credits, oh my!

Under the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA), individual income tax rates generally go down for 2018 through 2025. But that doesn’t necessarily mean your income tax liability will go down. The TCJA also makes a lot of changes to tax breaks for individuals, reducing or eliminating some while expanding others. The total impact of all of these changes is what will ultimately determine whether you see reduced taxes. One interrelated group of changes affecting many taxpayers are those to personal exemptions, standard deductions and the child credit.
Personal exemptions
For 2017, taxpayers can claim a personal exemption of $4,050 each for themselves, their spouses and any dependents. For families with children and/or other dependents, such as elderly parents, these exemptions can really add up.
For 2018 through 2025, the TCJA suspends personal exemptions. This will substantially increase taxable income for large families. However, enhancements to the standard deduction and child credit, combined with lower tax rates, might mitigate this increase.
Standard deduction
Taxpayers can choose to itemize certain deductions on Schedule A or take the standard deduction based on their filing status instead. Itemizing deductions when the total will be larger than the standard deduction saves tax, but it makes filing more complicated.
For 2017, the standard deductions are $6,350 for singles and separate filers, $9,350 for head of household filers, and $12,700 for married couples filing jointly.
The TCJA nearly doubles the standard deductions for 2018 to $12,000 for singles and separate filers, $18,000 for heads of households, and $24,000 for joint filers. (These amounts will be adjusted for inflation for 2019 through 2025.)
For some taxpayers, the increased standard deduction could compensate for the elimination of the exemptions, and perhaps even provide some additional tax savings. But for those with many dependents or who itemize deductions, these changes might result in a higher tax bill — depending in part on the extent to which they can benefit from enhancements to the child credit.
Child credit
Credits can be more powerful than exemptions and deductions because they reduce taxes dollar-for-dollar, rather than just reducing the amount of income subject to tax. For 2018 through 2025, the TCJA doubles the child credit to $2,000 per child under age 17.
The new law also makes the child credit available to more families than in the past. For 2018 through 2025, the credit doesn’t begin to phase out until adjusted gross income exceeds $400,000 for joint filers or $200,000 for all other filers, compared with the 2017 phaseout thresholds of $110,000 and $75,000, respectively.
The TCJA also includes, for 2018 through 2025, a $500 credit for qualifying dependents other than qualifying children.
Tip of the iceberg
Many factors will influence the impact of the TCJA on your tax liability for 2018 and beyond. And what’s discussed here is just the tip of the iceberg. For example, the TCJA also makes many changes to itemized deductions. For help assessing the impact on your tax situation, please contact us.
Your 2017 tax return may be your last chance to take the “manufacturers’ deduction”

While many provisions of the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA) will save businesses tax, the new law also reduces or eliminates some tax breaks for businesses. One break it eliminates is the Section 199 deduction, commonly referred to as the “manufacturers’ deduction.” When it’s available, this potentially valuable tax break can be claimed by many types of businesses beyond just manufacturing companies. Under the TCJA, 2017 is the last tax year noncorporate taxpayers can take the deduction (2018 for C corporation taxpayers).
The basics
The Sec. 199 deduction, also called the “domestic production activities deduction,” is 9% of the lesser of qualified production activities income or taxable income. The deduction is also limited to 50% of W-2 wages paid by the taxpayer that are allocable to domestic production gross receipts (DPGR).
Yes, the deduction is available to traditional manufacturers. But businesses engaged in activities such as construction, engineering, architecture, computer software production and agricultural processing also may be eligible.
The deduction isn’t allowed in determining net self-employment earnings and generally can’t reduce net income below zero. But it can be used against the alternative minimum tax.
Calculating DPGR
To determine a company’s Sec. 199 deduction, its qualified production activities income must be calculated. This is the amount of DPGR exceeding the cost of goods sold and other expenses allocable to that DPGR. Most companies will need to allocate receipts between those that qualify as DPGR and those that don’t • unless less than 5% of receipts aren’t attributable to DPGR.
DPGR can come from a number of activities, including the construction of real property in the United States, as well as engineering or architectural services performed stateside to construct real property. It also can result from the lease, rental, licensing or sale of qualifying production property, such as tangible personal property (for example, machinery and office equipment), computer software, and master copies of sound recordings.
The property must have been manufactured, produced, grown or extracted in whole or “significantly” within the United States. While each situation is assessed on its merits, the IRS has said that, if the labor and overhead incurred in the United States accounted for at least 20% of the total cost of goods sold, the activity typically qualifies.
Learn more
Contact us to learn whether this potentially powerful deduction could reduce your business’s tax liability when you file your 2017 return. We can also help address any questions you may have about other business tax breaks that have been reduced or eliminated by the TCJA.
Full article: Don’t be a victim of tax identity theft: File your 2017 return early

The IRS has just announced that it will begin accepting 2017 income tax returns on January 29. You may be more concerned about the April 17 filing deadline, or even the extended deadline of October 15 (if you file for an extension by April 17). After all, why go through the hassle of filing your return earlier than you have to?
But it can be a good idea to file as close to January 29 as possible: Doing so helps protect you from tax identity theft.
All-too-common scam
Here’s why early filing helps: In an all-too-common scam, thieves use victims’ personal information to file fraudulent tax returns electronically and claim bogus refunds. This is usually done early in the tax filing season. When the real taxpayers file, they’re notified that they’re attempting to file duplicate returns.
A victim typically discovers the fraud after he or she files a tax return and is informed by the IRS that the return has been rejected because one with the same Social Security number has already been filed for the same tax year. The IRS then must determine who the legitimate taxpayer is.
Tax identity theft can cause major headaches to straighten out and significantly delay legitimate refunds. But if you file first, it will be the tax return filed by a potential thief that will be rejected — not yours.
The IRS is working with the tax industry and states to improve safeguards to protect taxpayers from tax identity theft. But filing early may be your best defense.
W-2s and 1099s
Of course, in order to file your tax return, you’ll need to have your W-2s and 1099s. So another key date to be aware of is January 31 — the deadline for employers to issue 2017 Form W-2 to employees and, generally, for businesses to issue Form 1099 to recipients of any 2017 interest, dividend or reportable miscellaneous income payments.
If you don’t receive a W-2 or 1099, first contact the entity that should have issued it. If by mid-February you still haven’t received it, you can contact the IRS for help.
Earlier refunds
Of course, if you’ll be getting a refund, another good thing about filing early is that you’ll get your refund sooner. The IRS expects over 90% of refunds to be issued within 21 days. E-filing and requesting a direct deposit refund generally will result in a quicker refund and also can be more secure. If you have questions about tax identity theft or would like help filing your 2017 return early, please contact us.
New tax law gives pass-through businesses a valuable deduction

Although the drop of the corporate tax rate from a top rate of 35% to a flat rate of 21% may be one of the most talked about provisions of the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA), C corporations aren’t the only type of entity significantly benefiting from the new law. Owners of noncorporate “pass-through” entities may see some major — albeit temporary — relief in the form of a new deduction for a portion of qualified business income (QBI).
A 20% deduction
For tax years beginning after December 31, 2017, and before January 1, 2026, the new deduction is available to individuals, estates and trusts that own interests in pass-through business entities. Such entities include sole proprietorships, partnerships, S corporations and, typically, limited liability companies (LLCs). The deduction generally equals 20% of QBI, subject to restrictions that can apply if taxable income exceeds the applicable threshold — $157,500 or, if married filing jointly, $315,000.
QBI is generally defined as the net amount of qualified items of income, gain, deduction and loss from any qualified business of the noncorporate owner. For this purpose, qualified items are income, gain, deduction and loss that are effectively connected with the conduct of a U.S. business. QBI doesn’t include certain investment items, reasonable compensation paid to an owner for services rendered to the business or any guaranteed payments to a partner or LLC member treated as a partner for services rendered to the partnership or LLC.
The QBI deduction isn’t allowed in calculating the owner’s adjusted gross income (AGI), but it reduces taxable income. In effect, it’s treated the same as an allowable itemized deduction.
The limitations
For pass-through entities other than sole proprietorships, the QBI deduction generally can’t exceed the greater of the owner’s share of:
- 50% of the amount of W-2 wages paid to employees by the qualified business during the tax year, or
- The sum of 25% of W-2 wages plus 2.5% of the cost of qualified property.
Qualified property is the depreciable tangible property (including real estate) owned by a qualified business as of year end and used by the business at any point during the tax year for the production of qualified business income.
Another restriction is that the QBI deduction generally isn’t available for income from specified service businesses. Examples include businesses that involve investment-type services and most professional practices (other than engineering and architecture).
The W-2 wage limitation and the service business limitation don’t apply as long as your taxable income is under the applicable threshold. In that case, you should qualify for the full 20% QBI deduction.
Careful planning required
Additional rules and limits apply to the QBI deduction, and careful planning will be necessary to gain maximum benefit. Please contact us for more details.
The TCJA temporarily expands bonus depreciation

The Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA) enhances some tax breaks for businesses while reducing or eliminating others. One break it enhances — temporarily — is bonus depreciation. While most TCJA provisions go into effect for the 2018 tax year, you might be able to benefit from the bonus depreciation enhancements when you file your 2017 tax return.
Pre-TCJA bonus depreciation
Under pre-TCJA law, for qualified new assets that your business placed in service in 2017, you can claim a 50% first-year bonus depreciation deduction. Used assets don’t qualify. This tax break is available for the cost of new computer systems, purchased software, vehicles, machinery, equipment, office furniture, etc.
In addition, 50% bonus depreciation can be claimed for qualified improvement property, which means any qualified improvement to the interior portion of a nonresidential building if the improvement is placed in service after the date the building is placed in service. But qualified improvement costs don’t include expenditures for the enlargement of a building, an elevator or escalator, or the internal structural framework of a building.
TCJA expansion
The TCJA significantly expands bonus depreciation: For qualified property placed in service between September 28, 2017, and December 31, 2022 (or by December 31, 2023, for certain property with longer production periods), the first-year bonus depreciation percentage increases to 100%. In addition, the 100% deduction is allowed for not just new but also used qualifying property.
The new law also allows 100% bonus depreciation for qualified film, television and live theatrical productions placed in service on or after September 28, 2017. Productions are considered placed in service at the time of the initial release, broadcast or live commercial performance.
Beginning in 2023, bonus depreciation is scheduled to be reduced 20 percentage points each year. So, for example, it would be 80% for property placed in service in 2023, 60% in 2024, etc., until it would be fully eliminated in 2027.
For certain property with longer production periods, the reductions are delayed by one year. For example, 80% bonus depreciation would apply to long-production-period property placed in service in 2024.
Bonus depreciation is only one of the business tax breaks that have changed under the TCJA. Contact us for more information on this and other changes that will impact your business.
Most individual tax rates go down under the TCJA

The Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA) generally reduces individual tax rates for 2018 through 2025. It maintains seven individual income tax brackets but reduces the rates for all brackets except 10% and 35%, which remain the same.
It also makes some adjustments to the income ranges each bracket covers. For example, the 2017 top rate of 39.6% kicks in at $418,401 of taxable income for single filers and $470,701 for joint filers, but the reduced 2018 top rate of 37% takes effect at $500,001 and $600,001, respectively.
Below is a look at the 2018 brackets under the TCJA. Keep in mind that the elimination of the personal exemption, changes to the standard and many itemized deductions, and other changes under the new law could affect the amount of your income that’s subject to tax. Contact us for help assessing what your tax rate likely will be for 2018.
Single individuals
| Taxable income | Tax |
| Not over $9,525 | 10% of the taxable income |
| Over $9,525 but not over $38,700 | $952.50 plus 12% of the excess over $9,525 |
| Over $38,700 but not over $82,500 | $4,453.50 plus 22% of the excess over $38,700 |
| Over $82,500 but not over $157,500 | $14,089.50 plus 24% of the excess over $82,500 |
| Over $157,500 but not over $200,000 | $32,089.50 plus 32% of the excess over $157,500 |
| Over $200,000 but not over $500,000 | $45,689.50 plus 35% of the excess over $200,000 |
| Over $500,000 | $150,689.50 plus 37% of the excess over $500,000 |
Heads of households
| Taxable income | Tax |
| Not over $13,600 | 10% of the taxable income |
| Over $13,600 but not over $51,800 | $1,360 plus 12% of the excess over $13,600 |
| Over $51,800 but not over $82,500 | $5,944 plus 22% of the excess over $51,800 |
| Over $82,500 but not over $157,500 | $12,698 plus 24% of the excess over $82,500 |
| Over $157,500 but not over $200,000 | $30,698 plus 32% of the excess over $157,500 |
| Over $200,000 but not over $500,000 | $44,298 plus 35% of the excess over $200,000 |
| Over $500,000 | $149,298 plus 37% of the excess over $500,000 |
Married individuals filing joint returns and surviving spouses
| Taxable income | Tax |
| Not over $19,050 | 10% of the taxable income |
| Over $19,050 but not over $77,400 | $1,905 plus 12% of the excess over $19,050 |
| Over $77,400 but not over $165,000 | $8,907 plus 22% of the excess over $77,400 |
| Over $165,000 but not over $315,000 | $28,179 plus 24% of the excess over $165,000 |
| Over $315,000 but not over $400,000 | $64,179 plus 32% of the excess over $315,000 |
| Over $400,000 but not over $600,000 | $91,379 plus 35% of the excess over $400,000 |
| Over $600,000 | $161,379 plus 37% of the excess over $600,000 |
Married individuals filing separate returns
| Taxable income | Tax |
| Not over $9,525 | 10% of the taxable income |
| Over $9,525 but not over $38,700 | $952.50 plus 12% of the excess over $9,525 |
| Over $38,700 but not over $82,500 | $4,453.50 plus 22% of the excess over $38,700 |
| Over $82,500 but not over $157,500 | $14,089.50 plus 24% of the excess over $82,500 |
| Over $157,500 but not over $200,000 | $32,089.50 plus 32% of the excess over $157,500 |
| Over $200,000 but not over $300,000 | $45,689.50 plus 35% of the excess over $200,000 |
| Over $300,000 | $80,689.50 plus 37% of the excess over $300,000 |
Tax Cuts and Jobs Act: Key provisions affecting businesses

The recently passed tax reform bill, commonly referred to as the “Tax Cuts and Jobs Act” (TCJA), is the most expansive federal tax legislation since 1986. It includes a multitude of provisions that will have a major impact on businesses.
Here’s a look at some of the most significant changes. They generally apply to tax years beginning after December 31, 2017, except where noted.
- Replacement of graduated corporate tax rates ranging from 15% to 35% with a flat corporate rate of 21%
- Repeal of the 20% corporate alternative minimum tax (AMT)
- New 20% qualified business income deduction for owners of flow-through entities (such as partnerships, limited liability companies and S corporations) and sole proprietorships — through 2025
- Doubling of bonus depreciation to 100% and expansion of qualified assets to include used assets — effective for assets acquired and placed in service after September 27, 2017, and before January 1, 2023
- Doubling of the Section 179 expensing limit to $1 million and an increase of the expensing phaseout threshold to $2.5 million
- Other enhancements to depreciation-related deductions
- New disallowance of deductions for net interest expense in excess of 30% of the business’s adjusted taxable income (exceptions apply)
- New limits on net operating loss (NOL) deductions
- Elimination of the Section 199 deduction, also commonly referred to as the domestic production activities deduction or manufacturers’ deduction — effective for tax years beginning after December 31, 2017, for noncorporate taxpayers and for tax years beginning after December 31, 2018, for C corporation taxpayers
- New rule limiting like-kind exchanges to real property that is not held primarily for sale
- New tax credit for employer-paid family and medical leave — through 2019
- New limitations on excessive employee compensation
- New limitations on deductions for employee fringe benefits, such as entertainment and, in certain circumstances, meals and transportation
Keep in mind that additional rules and limits apply to what we’ve covered here, and there are other TCJA provisions that may affect your business. Contact us for more details and to discuss what your business needs to do in light of these changes.
Tax Cuts and Jobs Act: Key provisions affecting individuals

On December 20, Congress completed passage of the largest federal tax reform law in more than 30 years. Commonly called the “Tax Cuts and Jobs Act” (TCJA), the new law means substantial changes for individual taxpayers.
The following is a brief overview of some of the most significant provisions. Except where noted, these changes are effective for tax years beginning after December 31, 2017, and before January 1, 2026.
- Drops of individual income tax rates ranging from 0 to 4 percentage points (depending on the bracket) to 10%, 12%, 22%, 24%, 32%, 35% and 37%
- Near doubling of the standard deduction to $24,000 (married couples filing jointly), $18,000 (heads of households), and $12,000 (singles and married couples filing separately)
- Elimination of personal exemptions
- Doubling of the child tax credit to $2,000 and other modifications intended to help more taxpayers benefit from the credit
- Elimination of the individual mandate under the Affordable Care Act requiring taxpayers not covered by a qualifying health plan to pay a penalty — effective for months beginning after December 31, 2018, and permanent
- Reduction of the adjusted gross income (AGI) threshold for the medical expense deduction to 7.5% for regular and AMT purposes — for 2017 and 2018
- New $10,000 limit on the deduction for state and local taxes (on a combined basis for property and income taxes; $5,000 for separate filers)
- Reduction of the mortgage debt limit for the home mortgage interest deduction to $750,000 ($375,000 for separate filers), with certain exceptions
- Elimination of the deduction for interest on home equity debt
- Elimination of the personal casualty and theft loss deduction (with an exception for federally declared disasters)
- Elimination of miscellaneous itemized deductions subject to the 2% floor (such as certain investment expenses, professional fees and unreimbursed employee business expenses)
- Elimination of the AGI-based reduction of certain itemized deductions
- Elimination of the moving expense deduction (with an exception for members of the military in certain circumstances)
- Expansion of tax-free Section 529 plan distributions to include those used to pay qualifying elementary and secondary school expenses, up to $10,000 per student per tax year — permanent
- AMT exemption increase, to $109,400 for joint filers, $70,300 for singles and heads of households, and $54,700 for separate filers
- Doubling of the gift and estate tax exemptions, to $10 million (expected to be $11.2 million for 2018 with inflation indexing)
Be aware that additional rules and limits apply. Also, there are many more changes in the TCJA that will impact individuals. If you have questions or would like to discuss how you might be affected, please contact us.
401(k) retirement plan contribution limit increases for 2018; most other limits are stagnant

Retirement plan contribution limits are indexed for inflation, but with inflation remaining low, most of the limits remain unchanged for 2018. But one piece of good news for taxpayers who’re already maxing out their contributions is that the 401(k) limit has gone up by $500. The only other limit that has increased from the 2017 level is for contributions to defined contribution plans, which has gone up by $1,000.
| Type of limit | 2018 limit |
| Elective deferrals to 401(k), 403(b), 457(b)(2) and 457(c)(1) plans |
$18,500 |
| Contributions to defined contribution plans | $55,000 |
| Contributions to SIMPLEs | $12,500 |
| Contributions to IRAs | $5,500 |
| Catch-up contributions to 401(k), 403(b), 457(b)(2) and 457(c)(1) plans |
$6,000 |
| Catch-up contributions to SIMPLEs | $3,000 |
| Catch-up contributions to IRAs | $1,000 |
If you’re not already maxing out your contributions to other plans, you still have an opportunity to save more in 2018. And if you turn age 50 in 2018, you can begin to take advantage of catch-up contributions.
Higher-income taxpayers should also be pleased that some limits on their retirement plan contributions that had been discussed as part of tax reform didn’t make it into the final legislation.
However, keep in mind that there are still additional factors that may affect how much you’re allowed to contribute (or how much your employer can contribute on your behalf). For example, income-based limits may reduce or eliminate your ability to make Roth IRA contributions or to make deductible traditional IRA contributions.
If you have questions about how much you can contribute to tax-advantaged retirement plans in 2018, check with us.
This year’s company holiday party is probably tax deductible, but next year’s may not be

Many businesses are hosting holiday parties for employees this time of year. It’s a great way to reward your staff for their hard work and have a little fun. And you can probably deduct 100% of your 2017 party’s cost as a meal and entertainment (M&E) expense. Next year may be a different story.
The 100% deduction
- For recreational or social activities for employees, such as holiday parties and summer picnics,
- For food and beverages furnished at the workplace primarily for employees, and
- That are excludable from employees’ income as de minimis fringe benefits.
There is one caveat for a 100% deduction: The entire staff must be invited. Otherwise, expenses are deductible under the regular business entertainment rules.
Additional requirements
Whether you deduct 50% or 100% of allowable expenses, there are a number of requirements, including certain records you must keep to prove your expenses.
If your company has substantial meal and entertainment expenses, you can reduce your 2017 tax bill by separately accounting for and documenting expenses that are 100% deductible. If doing so would create an administrative burden, you may be able to use statistical sampling methods to estimate the portion of meal and entertainment expenses that are fully deductible.
Possible changes for 2018
It appears the M&E deduction for employee parties — along with deductions for many other M&E expenses — will be eliminated beginning in 2018 under the reconciled version of the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act. For more information about deducting business meals and entertainment, including how to take advantage of the 100% deduction when you file your 2017 return, please contact us.
What you need to know about year-end charitable giving in 2017

Charitable giving can be a powerful tax-saving strategy: Donations to qualified charities are generally fully deductible, and you have complete control over when and how much you give. Here are some important considerations to keep in mind this year to ensure you receive the tax benefits you desire.
Delivery date
To be deductible on your 2017 return, a charitable donation must be made by Dec. 31, 2017. According to the IRS, a donation generally is “made” at the time of its “unconditional delivery.” But what does this mean? Is it the date you, for example, write a check or make an online gift via your credit card? Or is it the date the charity actually receives the funds — or perhaps the date of the charity’s acknowledgment of your gift?
The delivery date depends in part on what you donate and how you donate it. Here are a few examples for common donations:
Check. The date you mail it.
Credit card. The date you make the charge.
Pay-by-phone account. The date the financial institution pays the amount.
Stock certificate. The date you mail the properly endorsed stock certificate to the charity.
Qualified charity status
To be deductible, a donation also must be made to a “qualified charity” — one that’s eligible to receive tax-deductible contributions.
The IRS’s online search tool, Exempt Organizations (EO) Select Check, can help you more easily find out whether an organization is eligible to receive tax-deductible charitable contributions. You can access EO Select Check at http://apps.irs.gov/app/eos. Information about organizations eligible to receive deductible contributions is updated monthly.
Potential impact of tax reform
The charitable donation deduction isn’t among the deductions that have been proposed for elimination or reduction under tax reform. In fact, income-based limits on how much can be deducted in a particular year might be expanded, which will benefit higher-income taxpayers who make substantial charitable gifts.
However, for many taxpayers, accelerating into this year donations that they might normally give next year may make sense for a couple of tax-reform-related reasons:
- If your tax rate goes down for 2018, then 2017 donations will save you more tax because deductions are more powerful when rates are higher.
- If the standard deduction is raised significantly and many itemized deductions are eliminated or reduced, then it may not make sense for you to itemize deductions in 2018, in which case you wouldn’t benefit from charitable donation deduction next year.
Many additional rules apply to the charitable donation deduction, so please contact us if you have questions about the deductibility of a gift you’ve made or are considering making — or the potential impact of tax reform on your charitable giving plans.
Should you buy a business vehicle before year end?

One way to reduce your 2017 tax bill is to buy a business vehicle before year end. But don’t make a purchase without first looking at what your 2017 deduction would be and whether tax reform legislation could affect the tax benefit of a 2017 vs. 2018 purchase.
Your 2017 deduction
Business-related purchases of new or used vehicles may be eligible for Section 179 expensing, which allows you to immediately deduct, rather than depreciate over a period of years, some or all of the vehicle’s cost. But the size of your 2017 deduction will depend on several factors. One is the gross vehicle weight rating.
The normal Sec. 179 expensing limit generally applies to vehicles with a gross vehicle weight rating of more than 14,000 pounds. The limit for 2017 is $510,000, and the break begins to phase out dollar-for-dollar when total asset acquisitions for the tax year exceed $2.03 million.
But a $25,000 limit applies to SUVs rated at more than 6,000 pounds but no more than 14,000 pounds. Vehicles rated at 6,000 pounds or less are subject to the passenger automobile limits. For 2017, under current law, the depreciation limit is $3,160. And the amount that may be deducted under the combination of Modified Accelerated Cost Recovery System (MACRS) depreciation and Sec. 179 for the first year is limited under the luxury auto rules to $11,160.
In addition, if a vehicle is used for business and personal purposes, the associated expenses, including depreciation, must be allocated between deductible business use and nondeductible personal use. The depreciation limit is reduced if the business use is less than 100%. If the business use is 50% or less, you can’t use Sec. 179 expensing or the accelerated regular MACRS; you must use the straight-line method.
Factoring in tax reform
If tax reform legislation is signed into law and it will cause your marginal rate to go down in 2018, then purchasing a vehicle by December 31, 2017, could save you more tax than waiting until 2018. Why? Tax deductions are more powerful when rates are higher. But if your 2017 Sec. 179 expense deduction would be reduced or eliminated because of the asset acquisition phaseout, then you might be better off waiting until 2018 to buy.
Also be aware that tax reform legislation could affect the depreciation limits for passenger vehicles, even if purchased in 2017.
These are just a few factors to look at. Many additional rules and limits apply to these breaks. So if you’re considering a business vehicle purchase, contact us to discuss whether it would make more tax sense to buy this year or next.
7 last-minute tax-saving tips

The year is quickly drawing to a close, but there’s still time to take steps to reduce your 2017 tax liability — you just must act by December 31:
January 31
- Pay your 2017 property tax bill that’s due in early 2018. Make your January 1 mortgage payment.
- Incur deductible medical expenses (if your deductible medical expenses for the year already exceed the 10% of adjusted gross income floor).
- Pay tuition for academic periods that will begin in January, February or March of 2018 (if it will make you eligible for a tax credit on your 2017 return).
- Donate to your favorite charities.
- Sell investments at a loss to offset capital gains you’ve recognized this year.
- Ask your employer if your bonus can be deferred until January.
Many of these strategies could be particularly beneficial if tax reform is signed into law this year that, beginning in 2018, reduces tax rates and limits or eliminates certain deductions (such as property tax, mortgage interest and medical expense deductions — though the Senate bill would actually reduce the medical expense deduction AGI floor to 7.5% for 2017 and 2018, potentially allowing more taxpayers to qualify for the deduction in these years and to enjoy a larger deduction).
Keep in mind, however, that in certain situations these strategies might not make sense. For example, if you’ll be subject to the alternative minimum tax this year or be in a higher tax bracket next year, taking some of these steps could have undesirable results. (Even with tax reform legislation, some taxpayers might find themselves in higher brackets next year.)
If you’re unsure whether these steps are right for you, consult us before taking action.
2018 Q1 tax calendar: Key deadlines for businesses and other employers

Here are some of the key tax-related deadlines affecting businesses and other employers during the first quarter of 2018. Keep in mind that this list isn’t all-inclusive, so there may be additional deadlines that apply to you. Contact us to ensure you’re meeting all applicable deadlines and to learn more about the filing requirements.
January 31
* File 2017 Forms W-2, “Wage and Tax Statement,” with the Social Security Administration and provide copies to your employees.
* Provide copies of 2017 Forms 1099-MISC, “Miscellaneous Income,” to recipients of income from your business where required.
* File 2017 Forms 1099-MISC reporting nonemployee compensation payments in Box 7 with the IRS.
* File Form 940, “Employer’s Annual Federal Unemployment (FUTA) Tax Return,” for 2017. If your undeposited tax is $500 or less, you can either pay it with your return or deposit it. If it’s more than $500, you must deposit it. However, if you deposited the tax for the year in full and on time, you have until February 12 to file the return.
* File Form 941, “Employer’s Quarterly Federal Tax Return,” to report Medicare, Social Security and income taxes withheld in the fourth quarter of 2017. If your tax liability is less than $2,500, you can pay it in full with a timely filed return. If you deposited the tax for the quarter in full and on time, you have until February 12 to file the return. (Employers that have an estimated annual employment tax liability of $1,000 or less may be eligible to file Form 944,“Employer’s Annual Federal Tax Return.”)
* File Form 945, “Annual Return of Withheld Federal Income Tax,” for 2017 to report income tax withheld on all nonpayroll items, including backup withholding and withholding on accounts such as pensions, annuities and IRAs. If your tax liability is less than $2,500, you can pay it in full with a timely filed return. If you deposited the tax for the year in full and on time, you have until February 12 to file the return.
February 28
* File 2017 Forms 1099-MISC with the IRS if 1) they’re not required to be filed earlier and 2) you’re filing paper copies. (Otherwise, the filing deadline is April 2.)
March 15
* If a calendar-year partnership or S corporation, file or extend your 2017 tax return and pay any tax due. If the return isn’t extended, this is also the last day to make 2017 contributions to pension and profit-sharing plans.
Even if your income is high, your family may be able to benefit from the 0% long-term capital gains rate

We’re entering the giving season, and if making financial gifts to your loved ones is part of your plans — or if you’d simply like to reduce your capital gains tax — consider giving appreciated stock instead of cash this year. Doing so might allow you to eliminate all federal tax liability on the appreciation, or at least significantly reduce it.
Leveraging lower rates
Investors generally are subject to a 15% tax rate on their long-term capital gains (20% if they’re in the top ordinary income tax bracket of 39.6%). But the long-term capital gains rate is 0% for gain that would be taxed at 10% or 15% based on the taxpayer’s ordinary-income rate.
In addition, taxpayers with modified adjusted gross income (MAGI) over $200,000 per year ($250,000 for joint filers and $125,000 for married filing separately) may owe the net investment income tax (NIIT). The NIIT equals 3.8% of the lesser of your net investment income or the amount by which your MAGI exceeds the applicable threshold.
If you have loved ones in the 0% bracket, you may be able to take advantage of it by transferring appreciated assets to them. The recipients can then sell the assets at no or a low federal tax cost.
The strategy in action
Faced with a long-term capital gains tax rate of 23.8% (20% for the top tax bracket, plus the 3.8% NIIT), Rick and Sara decide to transfer some appreciated stock to their adult daughter, Maia. Just out of college and making only enough from her entry-level job to leave her with $25,000 in taxable income, Maia falls into the 15% income tax bracket. Therefore, she qualifies for the 0% long-term capital gains rate.
However, the 0% rate applies only to the extent that capital gains “fill up” the gap between Maia’s taxable income and the top end of the 15% bracket. In 2017, the 15% bracket for singles tops out at $37,950.
When Maia sells the stock her parents transferred to her, her capital gains are $20,000. Of that amount $12,950 qualifies for the 0% rate and the remaining $7,050 is taxed at 15%. Maia pays only $1,057.50 of federal tax on the sale vs. the $4,760 her parents would have owed had they sold the stock themselves.
Additional considerations
Before acting, make sure the recipients won’t be subject to the “kiddie tax.” Also consider any gift and generation-skipping transfer (GST) tax consequences.
For more information on transfer taxes, the kiddie tax or capital gains planning, please contact us. We can help you find the strategies that will best achieve your goals.
Accrual-basis taxpayers: These year-end tips could save you tax

With the possibility that tax law changes could go into effect next year that would significantly reduce income tax rates for many businesses, 2017 may be an especially good year to accelerate deductible expenses. Why? Deductions save more tax when rates are higher.
Timing income and expenses can be a little more challenging for accrual-basis taxpayers than for cash-basis ones. But being an accrual-basis taxpayer also offers valuable year-end tax planning opportunities when it comes to deductions.
Tracking incurred expenses
The key to saving tax as an accrual-basis taxpayer is to properly record and recognize expenses that were incurred this year but won’t be paid until 2018. This will enable you to deduct those expenses on your 2017 federal tax return. Common examples of such expenses include:
- Commissions, salaries and wages,
- Payroll taxes,
- Advertising,
- Interest,
- Utilities,
- Insurance, and
- Property taxes.
You can also accelerate deductions into 2017 without actually paying for the expenses in 2017 by charging them on a credit card. (This works for cash-basis taxpayers, too.)
As noted, accelerating deductible expenses into 2017 may be especially beneficial if tax rates go down for 2018.
Prepaid expenses
Also review all prepaid expense accounts. Then write off any items that have been used up before the end of the year.
If you prepay insurance for a period of time beginning in 2017, you can expense the entire amount this year rather than spreading it between 2017 and 2018, as long as a proper method election is made. This is treated as a tax expense and thus won’t affect your internal financials.
And there’s more …
Here are a few more year-end tax tips to consider:
- Review your outstanding receivables and write off any receivables you can establish as uncollectible.
- Pay interest on all shareholder loans to or from the company.
- Update your corporate record book to record decisions and be better prepared for an audit.
To learn more about how these and other year-end tax strategies may help your business reduce its 2017 tax bill, contact us.
You may need to add RMDs to your year-end to-do list

As the end of the year approaches, most of us have a lot of things on our to-do lists, from gift shopping to donating to our favorite charities to making New Year’s Eve plans. For taxpayers “of a certain age” with a tax-advantaged retirement account, as well as younger taxpayers who’ve inherited such an account, there may be one more thing that’s critical to check off the to-do list before year end: Take required minimum distributions (RMDs).
A huge penalty
After you reach age 70½, you generally must take annual RMDs from your:
- IRAs (except Roth IRAs), and
- Defined contribution plans, such as 401(k) plans (unless you’re still an employee and not a 5%-or-greater shareholder of the employer sponsoring the plan)
An RMD deferral is available in the initial year, but then you’ll have to take two RMDs the next year. The RMD rule can be avoided for Roth 401(k) accounts by rolling the balance into a Roth IRA.
For taxpayers who inherit a retirement plan, the RMD rules generally apply to defined-contribution plans and both traditional and Roth IRAs. (Special rules apply when the account is inherited from a spouse.)
RMDs usually must be taken by December 31. If you don’t comply, you can owe a penalty equal to 50% of the amount you should have withdrawn but didn’t.
Should you withdraw more than the RMD?
Taking only RMDs generally is advantageous because of tax-deferred compounding. But a larger distribution in a year your tax bracket is low may save tax.
Be sure, however, to consider the lost future tax-deferred growth and, if applicable, whether the distribution could: 1) cause Social Security payments to become taxable, 2) increase income-based Medicare premiums and prescription drug charges, or 3) affect other tax breaks with income-based limits.
Also keep in mind that, while retirement plan distributions aren’t subject to the additional 0.9% Medicare tax or 3.8% net investment income tax (NIIT), they are included in your modified adjusted gross income (MAGI). That means they could trigger or increase the NIIT, because the thresholds for that tax are based on MAGI.
For more information on RMDs or tax-savings strategies for your retirement plan distributions, please contact us.
Getting around the $25 deduction limit for business gifts

At this time of year, it’s common for businesses to make thank-you gifts to customers, clients, employees and other business entities and associates. Unfortunately, the tax rules limit the deduction for business gifts to $25 per person per year, a limitation that has remained the same since it was added into law back in 1962. Fifty-five years later, the $25 limit is unrealistically small in many business gift-giving situations. Fortunately, there are a few exceptions.
The exceptions
Here’s a quick rundown of the major exceptions to the $25 limit:
Gifts to a business entity. The $25 limit applies only to gifts directly or indirectly given to an individual. Gifts given to a company for use in the business aren’t subject to the limit. For example, a gift of a $200 reference manual to a company for its employees to use while doing their jobs would be fully deductible because it’s used in the company’s business.
Gifts to a married couple. If you have a business connection with both spouses and the gift is for both of them, the $25 limit doubles to $50.
Incidental costs of making a gift. Such costs aren’t subject to the limit. For example, the costs of custom engraving on jewelry or of packing, insuring and mailing a gift are deductible over and above the $25 limit for the gift itself.
Gifts to employees. Although employee gifts have their own limitations and may be treated as taxable compensation, an employer is generally allowed to deduct the full cost of gifts made to employees.
Gifts vs. entertainment expenses
In some situations related to gifts of tickets to sporting or other events, a taxpayer may choose whether to claim the deduction as a gift or as entertainment. Under current law, entertainment expenses are normally 50% deductible, so the gift deduction is a better deal for lower-priced tickets. But once the combined price of the gifted tickets exceeds $50, claiming them as an entertainment expense is more beneficial.
Be aware, however, that the elimination of the entertainment expense deduction has been included in proposed tax reform legislation. If legislation with such a provision is signed into law, it likely won’t go into effect until 2018.
Track and document
To the extent your business qualifies for any of these exceptions, be sure to track the qualifying expenses separately (typically by charging them to a separate account in your accounting records) so that a full deduction can be claimed.
In addition, you must retain documentation of the following:
- A description of the gift,
- The gift’s cost,
- The date the gift was made,
- The business purpose of the gift, and
- The business relationship to the taxpayer of the person receiving the gift.
If you have any questions regarding the types of gifts or gift-giving situations that may qualify for a full deduction or how to properly isolate and account for them in your records, please contact us.






















































